Financial Accounting > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Test Bank for Fundamentals of Advanced Accounting 5th Edition Hoyle, Schaefer, Doupnik (All)
Test Bank for Fundamentals of Advanced Accounting 5th Edition Hoyle, Schaefer, Doupnik
Document Content and Description Below
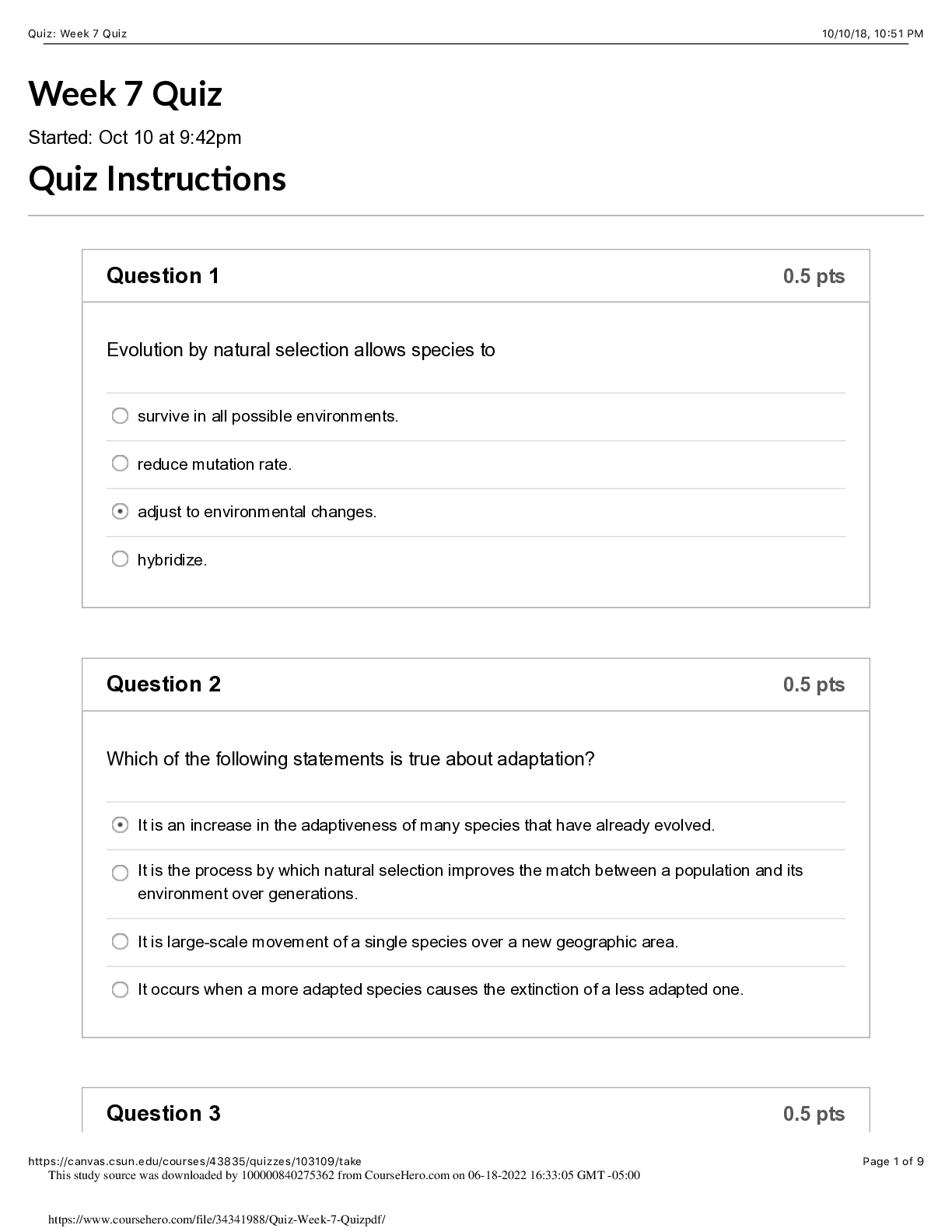
At the date of an acquisition which is not a bargain purchase, the acquisition method A. consolidates the subsidiary's assets at fair value and the liabilities at book value. B. consolidates all s... ubsidiary assets and liabilities at book value. C. consolidates all subsidiary assets and liabilities at fair value. D. consolidates current assets and liabilities at book value, long-term assets and liabilities at fair value. E. consolidates the subsidiary's assets at book value and the liabilities at fair value. Full file at http://testbankscafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-Fundamentals-of-Advanced-Accounting-5th-Edition-Hoyle,-Schaefer,- Doupnik 2. In an acquisition where control is achieved, how would the land accounts of the parent and the land accounts of the subsidiary be combined? A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D E. Option E 3. Lisa Co. paid cash for all of the voting common stock of Victoria Corp. Victoria will continue to exist as a separate corporation. Entries for the consolidation of Lisa and Victoria would be recorded in A. a worksheet. B. Lisa's general journal. C. Victoria's general journal. D. Victoria's secret consolidation journal. E. the general journals of both companies. Full file at http://testbankscafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-Fundamentals-of-Advanced-Accounting-5th-Edition-Hoyle,-Schaefer,- Doupnik 4. Using the acquisition method for a business combination, goodwill is generally defined as: A. Cost of the investment less the subsidiary's book value at the beginning of the year. B. Cost of the investment less the subsidiary's book value at the acquisition date. C. Cost of the investment less the subsidiary's fair value at the beginning of the year. D. Cost of the investment less the subsidiary's fair value at acquisition date. E. is no longer allowed under federal law. 5. Direct combination costs and stock issuance costs are often incurred in the process of making a controlling investment in another company. How should those costs be accounted for in a pre-2009 purchase transaction? A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D E. Option E Full file at http://testbankscafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-Fundamentals-of-Advanced-Accounting-5th-Edition-Hoyle,-Schaefer,- Doupnik 6. How are direct and indirect costs accounted for when applying the acquisition method for a business combination? A. Option A B. Option B C. Option C D. Option D E. Option E 7. What is the primary accounting difference between accounting for when the subsidiary is dissolved and when the subsidiary retains its incorporation? A. If the subsidiary is dissolved, it will not be operated as a separate division. B. If the subsidiary is dissolved, assets and liabilities are consolidated at their book values. C. If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, there will be no goodwill associated with the acquisition. D. If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, assets and liabilities are consolidated at their book values. E. If the subsidiary retains its incorporation, the consolidation is not formally recorded in the accounting records of the acquiring company. Full file at http://testbankscafe.eu/Test-Bank-for-Fundamentals-of-Advanced-Accounting-5th-Edition-Hoyle,-Schaefer,- Doupnik 8. According to GAAP, the pooling of interest method for business combinations A. Is preferred to the purchase method. B. Is allowed for all new acquisitions. C. Is no longer allowed for business combinations after June 30, 2001. D. Is no longer allowed for business combinations after December 31, 2001. E. Is only allowed for large corporate mergers like Exxon and Mobil. 9. An example of a difference in types of business combination is: A. A statutory merger can only be effected by an asset acquisition while a statutory consolidation can only be effected by a capital stock acquisition. B. A statutory merger can only be effected by a capital stock acquisition while a statutory consolidation can only be effected by an asset acquisition. C. A statutory merger requires dissolution of the acquired company while a statutory consolidation does not require dissolution. D. A statutory consolidation requires dissolution of the acquired company while a statutory merger does not require dissolution. E. Both a statutory merger and a statutory consolidation can only be effected by an asset acquisition but only a statutory consolidation requires dissolution of the acquired company. Full file at http://testbankscafe.eu/Te [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 376 pages
.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 07, 2022
Number of pages
376
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
36






.png)










 (1).png)
2.png)



Test Bank for Fundamentals of Nursing 2nd Edition by Yoost.png)








.png)

.png)

