Health Care > CASE STUDY > CS Heart Failure case study latest 100% (All)
CS Heart Failure case study latest 100%
Document Content and Description Below
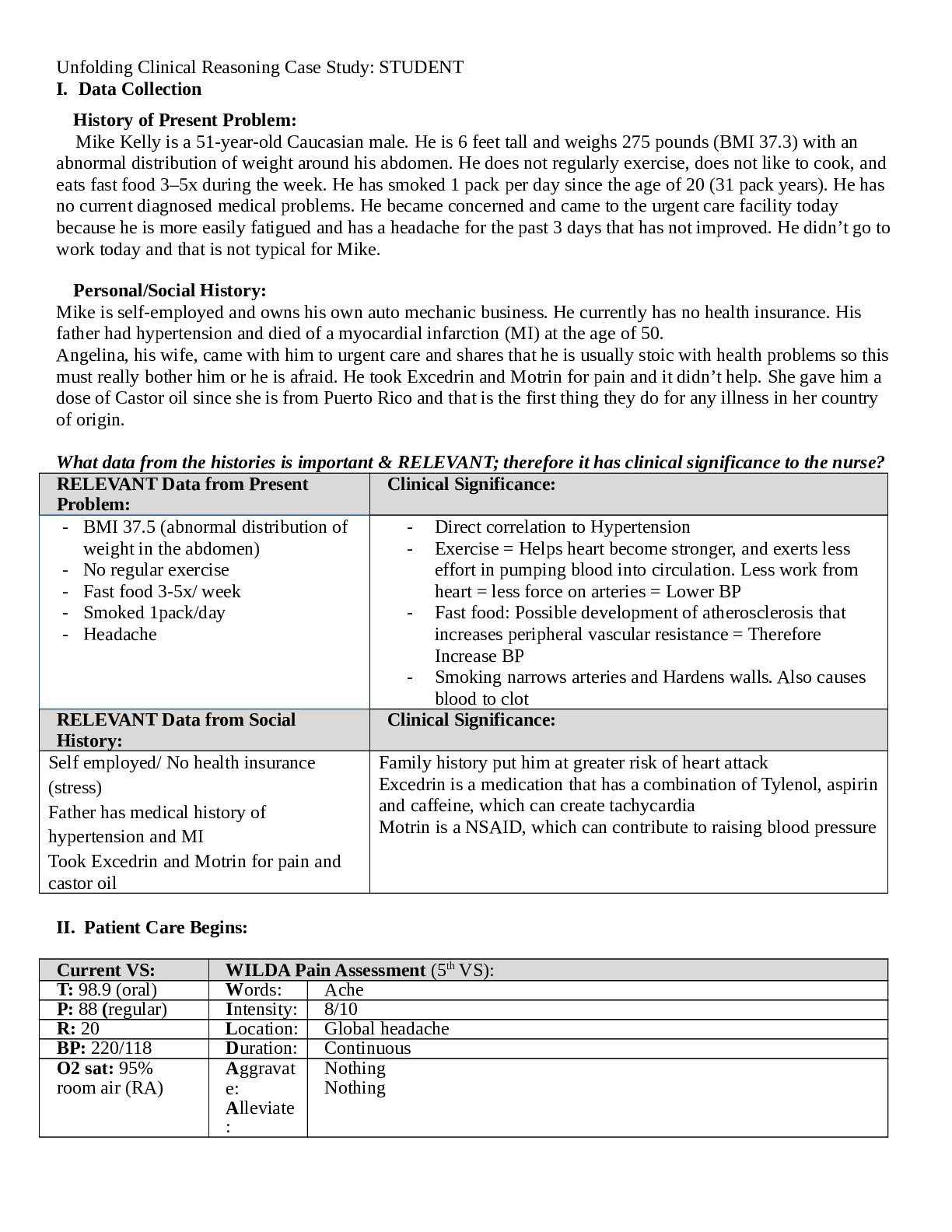
JoAnn Smith, 72 years old Primary Concept Perfusion Interrelated Concepts (In order of emphasis) 1. Gas Exchange 2. Fluid and Electrolyte Balance 3. Clinical Judgment 4. Patient Education 5. C... ommunication 6. Collaboration UNFOLDING Reasoning Case Study: STUDENT History of Present Problem: Heart Failure JoAnn Smith is a 72-year-old woman who has a history of myocardial infarction (MI) four years ago and systolic heart failure secondary to ischemic cardiomyopathy with a current ejection fraction (EF) of only 15%. She presents to the emergency department (ED) for shortness of breath (SOB) the past three days. Her shortness of breath has progressed from SOB with activity to becoming SOB at rest. The last two nights she had to sleep in her recliner chair to rest comfortably upright. She is able to speak only in partial sentences and then has to take a breath when talking to the nurse. She has noted increased swelling in her lower legs and has gained six pounds in the last three days. She is being transferred from the ED to the cardiac step-down where you are the nurse assigned to care for her. Personal/Social History: JoAnn is a retired math teacher who is unable to maintain the level of activity she has been accustomed to because of the progression of her heart failure the past two years. She has struggled with depression the past two years and has been more withdrawn since her husband of 52 years died unexpectedly three months ago from a myocardial infarction. What data from the histories is RELEVANT and has clinical significance to the nurse? RELEVANT Data from Present Problem: Clinical Significance: MI four years ago, increase shortness of breath at rest; can only speak in partial sentences, ischemic cardiomyopathy with EF of 15% last two nights slept in recliner increased swelling in lower legs gained 6 pounds in last 3 days MI is significant because it decreases heart function due to death of myocardial muscle EF of 15% shows that the heart is having a hard time pumping blood out to rest of the body therefore starving it of oxygenated blood. Weight gain and increased swelling signifies she is fluid overloaded and it can be reason why she is having a hard time talking, breathing, being active and why she has to sleep in a recliner the past 2 nights RELEVANT Data from Social History: Clinical Significance: Retired math teacher, recent widow, history of depression, decreasing activity level Depression might affect her enthusiasm to recover, to stick to a therapy regimen What is the RELATIONSHIP of your patient’s past medical history (PMH) and current meds? (Which medication treats which condition? Draw lines to connect) PMH: Home Meds: Pharm. Classification: Expected Outcome: Diabetes mellitus type II Hypertension Atrial fibrillation Hyperlipidemia Chronic renal insufficiency (baseline creatinine 2.0) Cerebral vascular accident (CVA) with no residual deficits Heart failure (systolic) secondary to ischemic cardiomyopathy MI with stent x2 to LAD 4 years ago 1. ASA 81 mg PO daily 2. Carvedilol 3.25 mg PO daily 3. Lisinopril 5 mg PO daily 4. Ezetimide 10 mg PO daily 5. Hydralazine 25 mg PO 4x daily 6. Torsemide 20 mg PO bid 7. KCL 20 meq PO daily 8. Warfarin 5 mg PO daily 9. Glyburide 5 mg PO daily Antiplatelets Beta blocker ACE inhibitor Cholesterol medication Vasodilator Diuretic Electrolyte replacement Anticoagulant Antidiabetic Decrease chance of clot formation Decrease blood pressure Decrease blood pressure, helps with heart failure, decrease chance of death from heart attack Decrease cholesterol Decrease blood pressure Decrease swelling, decrease fluid overload Increase serum potassium Thins the blood, decrease chance of clot forming Treat type 2 diabetes, helps control blood sugar levels What medications treat which conditions? One disease process often influences the development of other illnesses. Based on your knowledge of pathophysiology, (if applicable), which disease likely developed FIRST that created a “domino effect” in her life? Circle what PMH problem likely started FIRST Diabetes Type 2 Underline what PMH problem(s) FOLLOWED as domino(s) DMT2>hyperlipidemia>hypertension>afib>CVA>MI>CKI>HF Patient Care Begins: Current VS: P-Q-R-S-T Pain Assessment (5th VS): T: 98.6 F/37.0 C (oral) Provoking/Palliative: P: 92 (irregular) Quality: Denies Pain R: 26 (regular) Region/Radiation: BP: 162/54 MAP: 90 Severity: O2 sat: 90% (6 liters n/c) Timing: What VS data is RELEVANT and must be recognized as clinically significant by the nurse? RELEVANT VS Data: Clinical Significance: P:92 bpm, irregular R: 26, regular O2 sat: 90%, 6L n/c BP: 162/54 c MAP:90 Pulse is irregular due to atrial fibrillation, increases oxygen demand needs therefore breaths faster and need greater amount of O2 supplied by external oxygen device (nasal canula), Heart has to pump faster to get oxygenated blood out to systemic circulation MAP of 90 suggests that heart has low cardiac output therefore needs higher pressure to get blood to vital organs Current Assessment: GENERAL APPEARANCE: Appears anxious, restless RESP: Breath sounds have coarse crackles scattered throughout both lung fields ant/post, labored respiratory effort, patient sitting upright CARDIAC: Rhythm: atrial fibrillation, pale, cool to the touch, pulses palpable throughout, 3+ pitting edema lower extremities from knees down bilaterally, S3 gallop, irregular, no jugular venous distention (JVD) noted NEURO: Alert and oriented to person, place, time, and situation (x4) GI: Abdomen soft/nontender, bowel sounds audible per auscultation in all four quadrants GU: Voiding without difficulty, urine clear/yellow SKIN: Skin integrity intact, skin turgor elastic, no tenting present What assessment data is RELEVANT and must be recognized as clinically significant by the nurse? RELEVANT Assessment Data: Clinical Significance: Gen: appears anxious, restless Resp: coarse crackles through out both lung fields, labored respiratory effort though pt is sitting upright Cardiac: A.Fib, 3+pitting edema LE,s3 gallop, irregular General appearance suggests she is in some distress Lung sounds suggest trouble breathing, fluid overload A.Fib is a dysrhythmia that can impede proper perfusion of blood to body decrease it’s ability to pump oxygenated blood Pitting edema is another sign that pt is fluid overloaded S3 gallop murmur suggest possible mitral stenosis [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 04, 2022
Number of pages
19
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 04, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
27

 (1).png)