*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > South University- NSG 5003 Week 5 Midterm Exam 1- Advanced Pathophysiology Question And Answers/Rate (All)
South University- NSG 5003 Week 5 Midterm Exam 1- Advanced Pathophysiology Question And Answers/Rated A
Document Content and Description Below
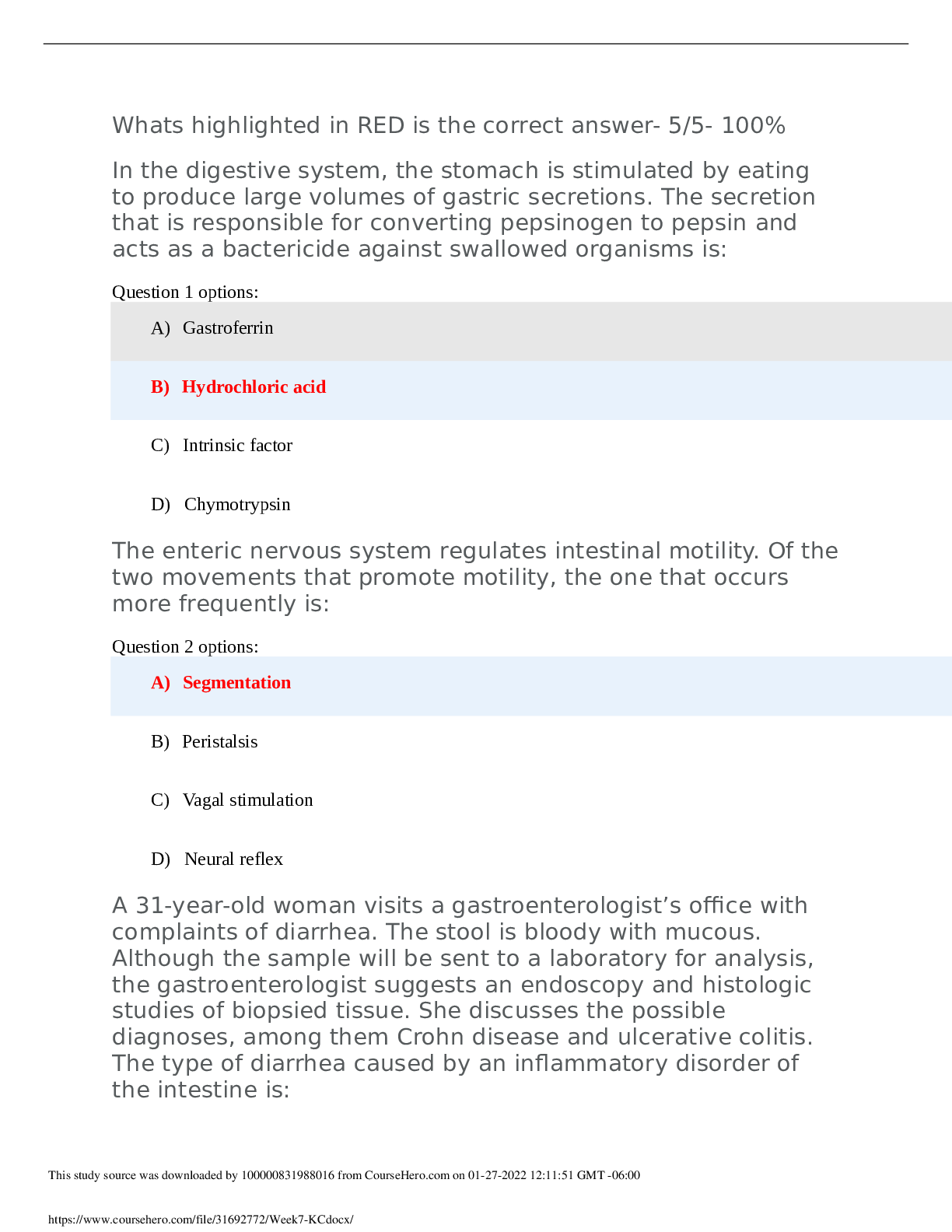
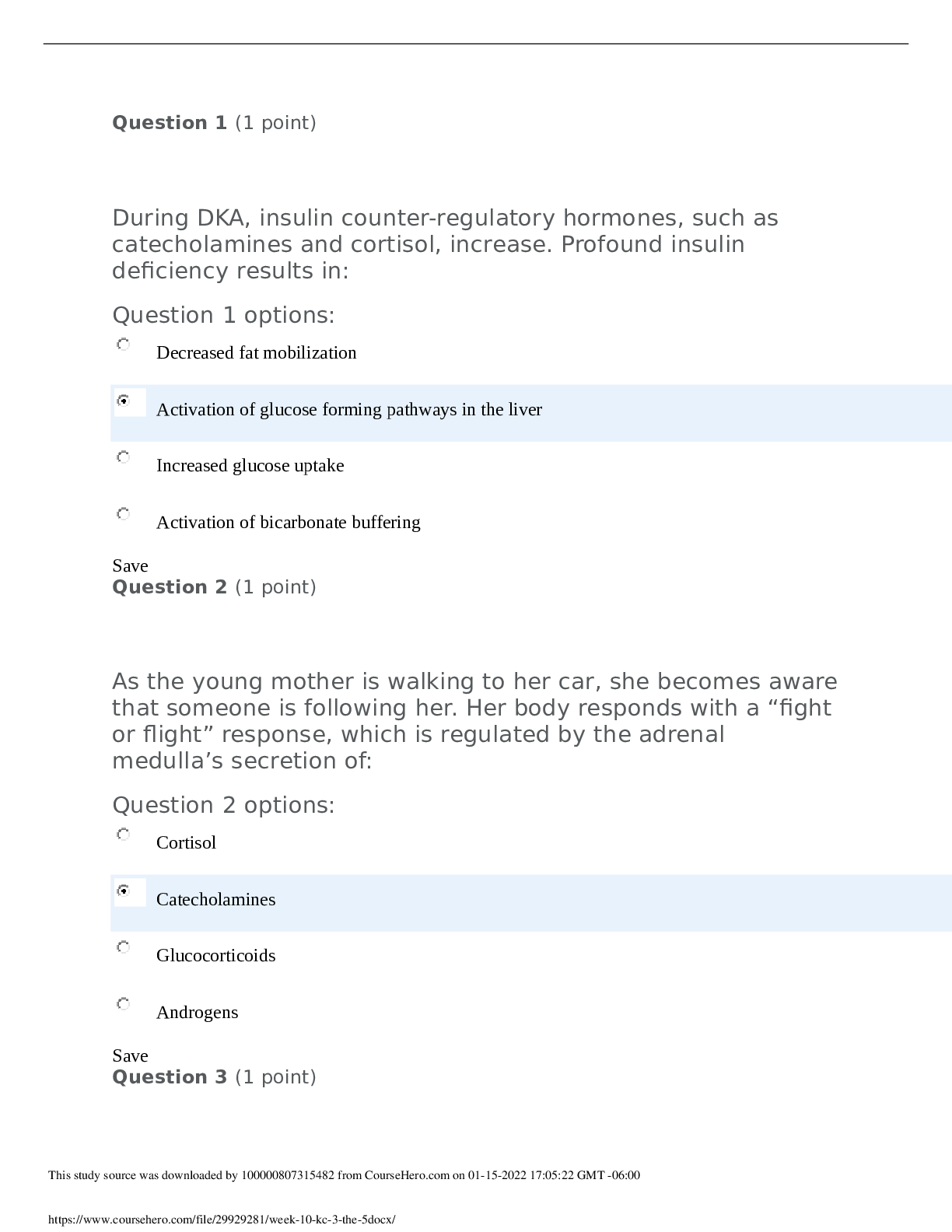
What causes the rapid change in the resting membrane potential to initiate an action potential? Question 1 options: Potassium gates open and potassium rushes into the cell, changing the membrane po... tential from negative to positive Sodium gates open and sodium rushes into the cell, changing the membrane potential from negative to positive. Sodium gates close, allowing potassium into the cell to change the membrane potential from positive to negative. Potassium gates close, allowing sodium into the cell to change the membrane potential from positive to negative. Save Question 2 (5 points) What is a consequence of leakage of lysosomal enzymes during chemical injury? Question 2 options: Enzymatic digestion of the nucleus and nucleolus occurs, halting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis. Influx of potassium ions into the mitochondria occurs, halting the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. Edema of the Golgi body occurs, preventing the transport of proteins out of the cell. Shift of calcium out of the plasma membrane occurs, destroying the cytoskeleton. Save Question 3 (5 points) In hypoxic injury, sodium enters the cell and causes swelling because: Question 3 options: The cell membrane permeability increases for sodium during periods of hypoxia. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is insufficient to maintain the pump that keeps sodium out of the cell. The lactic acid produced by the hypoxia binds with sodium in the cell. Sodium cannot be transported to the cell membrane during hypoxia. Save Question 4 (5 points) What mechanisms occur in the liver cells as a result of lipid accumulation? Question 4 options: Obstruction of the common bile duct, preventing the flow of bile from the liver to the gallbladder Increased synthesis of triglycerides from fatty acids and decreased synthesis of apoproteins Increased binding of lipids with apoproteins to form lipoproteins Increased conversion of fatty acids to phospholipids Save Question 5 (5 points) Which solution is best to use when cleaning a wound that is healing by 101. During an Immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated hypersensitivity reaction, the degranulation of mast cells is a result of which receptor action? Question 5 options: Histamine bound to H2 Chemotactic factor binding to the receptor Epinephrine bound to mast cells Acetylcholine bound to mast cells Save Question 6 (5 points) What is the mechanism that results in type II hypersensitivity reactions? Question 6 options: Antibodies coat mast cells by binding to receptors that signal its degranulation, followed by a discharge of preformed mediators. Antibodies bind to soluble antigens that were released into body fluids, and the immune complexes are then deposited in the tissues. Cytotoxic T (Tc) lymphocytes or lymphokine-producing helper T 1 (Th1) cells directly attack and destroy cellular targets. Antibodies bind to the antigens on the cell surface. Save Question 7 (5 points) Type III hypersensitivity reactions are a result of which of the following? Question 7 options: Antibodies coating mast cells by binding to receptors that signal its degranulation, followed by the discharge of preformed mediators Antibodies binding to soluble antigens that were released into body fluids and the immune complexes being deposited in the tissues Cytotoxic T (Tc) cells or lymphokine-producing helper T 1 (Th1) cells directly attacking and destroying cellular targets Antibodies binding to the antigen on the cell surface Save Question 8 (5 points) Tissue damage caused by the deposition of circulating immune complexes containing an antibody against the host deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the cause of which disease? Question 8 options: Hemolytic anemia Pernicious anemia Systemic lupus erythematosus Myasthenia gravis Save Question 9 (5 points) Why does tissue damage occur in acute rejection after organ transplantation? Question 9 options: Th1 cells release cytokines that activate infiltrating macrophages, and cytotoxic T (Tc) cells directly attack the endothelial cells of the transplanted tissue. Circulating immune complexes are deposited in the endothelial cells of transplanted tissue, where the complement cascade lyses tissue. Receptors on natural killer (NK) cells recognize antigens on the cell surface of the transplanted tissue, which releases lysosomal enzymes that destroy tissue. Antibodies coat the surface of the transplanted tissue to which mast cells bind and liberate preformed chemical mediators that destroy tissue. Save Question 10 (5 points) Oncogenes are genes that are capable of: Question 10 options: Undergoing mutation that directs the synthesis of proteins to accelerate the rate of tissue proliferation Directing synthesis of proteins to regulate growth and to provide necessary replacement of tissue Encoding proteins that negatively regulate the synthesis of proteins to slow or halt the replacement of tissue Undergoing mutation that directs malignant tissue toward blood vessels and lymph nodes for metastasis Save Question 11 (5 points) After the baroreceptor reflex is stimulated, the resulting impulse is transmitted f [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 18, 2022
Number of pages
18
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 18, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
106

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)

.png)
.png)