Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BIOL 1150/1151 Exam 4. Study Guide and Exam Prep. Contains 40 Questions and Answers... (All)
BIOL 1150/1151 Exam 4. Study Guide and Exam Prep. Contains 40 Questions and Answers...
Document Content and Description Below
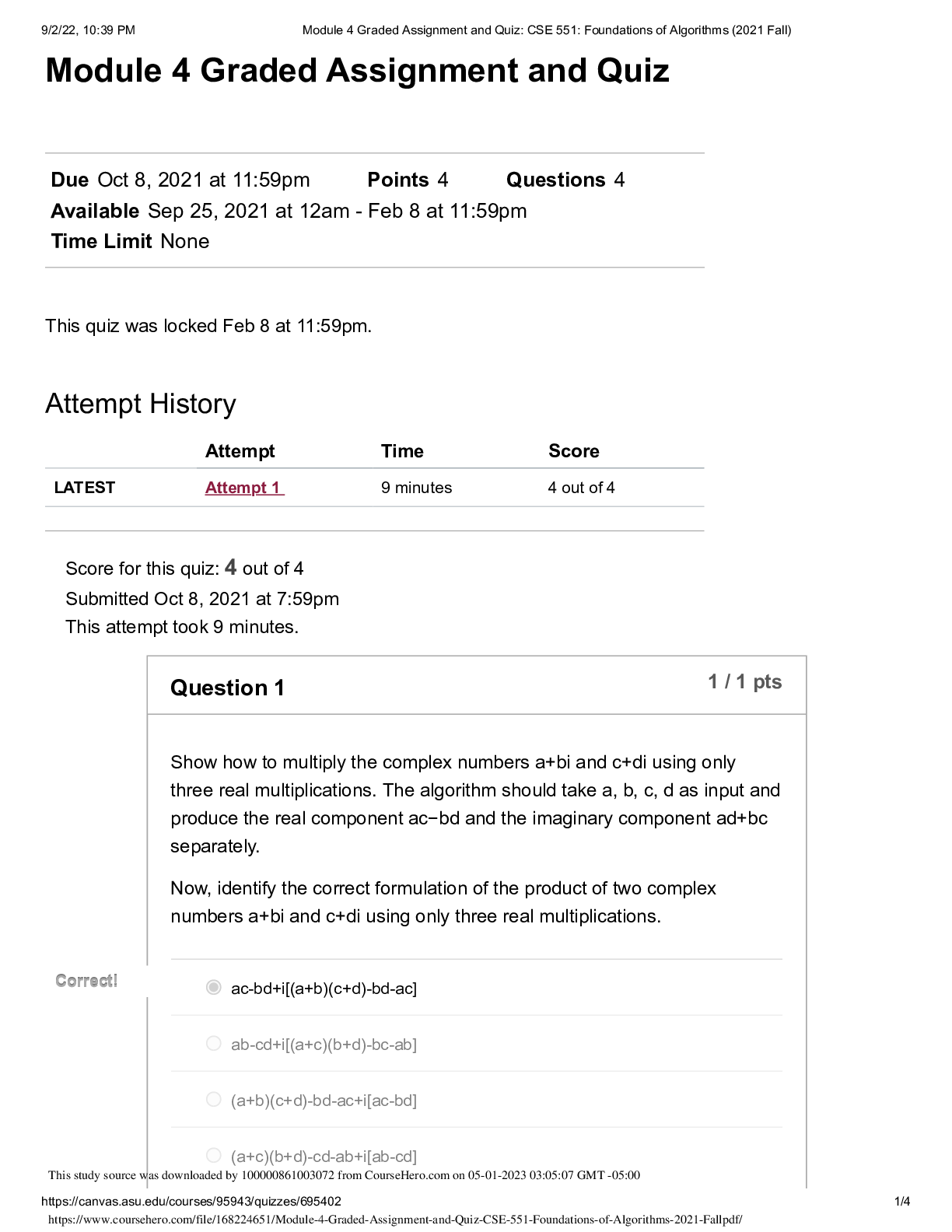
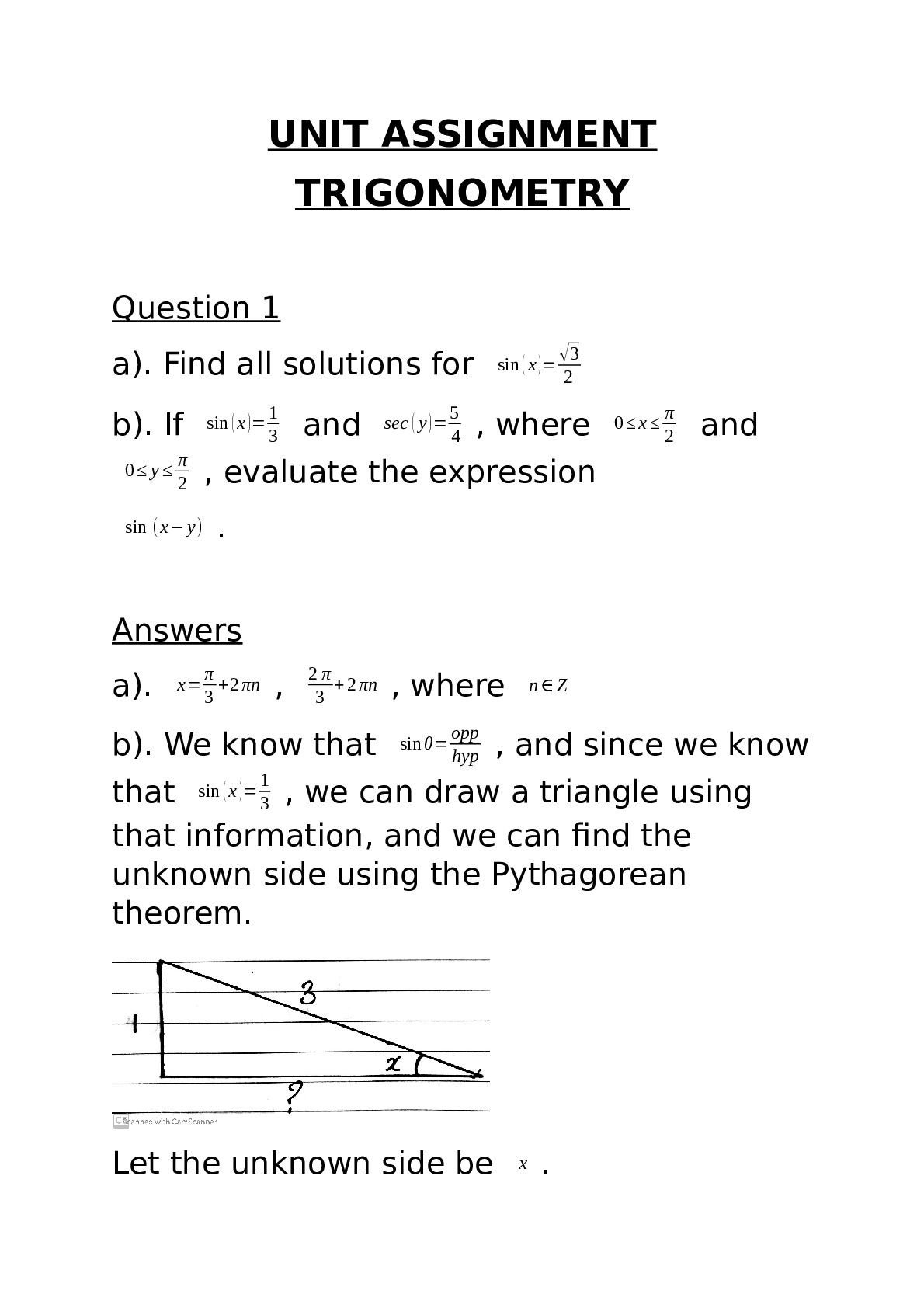
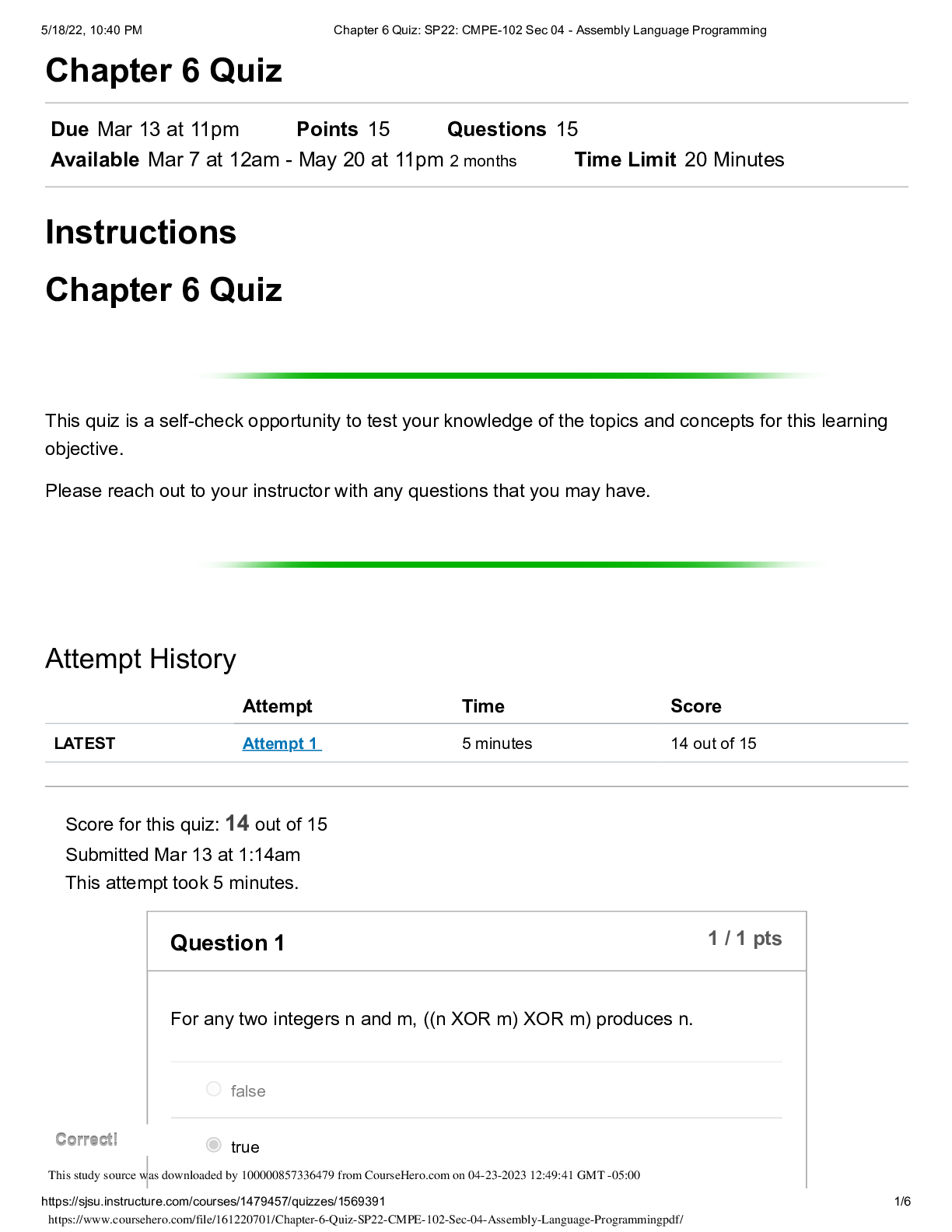
Dr. Anderson NAME____________________________________ BIOL 1150/1151 Exam #4 Multiple Choice Questions: Please select the best answer from the choices provided. [35 questions at 1 point each] 1. W... hat is the final result of mitosis? a. two genetically identical haploid cells b. Two genetically identical diploid cells c. Four genetically identical haploid cells d. Four genetically identical diploid cells 2. Metaphase occurs prior to the splitting of centromeres. It is characterized by _____. a. separation of sister chromatids b. cytokinesis c. aligning of chromosomes on the equator d. splitting of the centromeres 3. Mitosis is the process of chromosome separation. Cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells in a process known as _____. a. interphase b. prophase c. telophase d. cytokinesis 4. If the gametes of a fruit fly have six chromosomes. How many chromosomes would you find in a somatic cell from a fruit fly? a. six b. twelve c. nine d. a diploid number 5. If meiosis produces haploid cells, how is the diploid number restored for those organisms that spend most of their life cycle in the diploid state? a. Reverse transcription b. DNA replication c. Fertilization d. Magic 6. A man who carries an allele of an X-linked gene will pass it on to _____. a. All of his daughters b. All of his sons c. Half of his daughters d. Half of his sons e. All of his children This study source was downloaded by 100000810073548 from CourseHero.com on 04-12-2022 10:47:07 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/32610889/BIOL-1150-Exam-4-keyed-F16doc/7. Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy is a human disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. Only boys are affected, and they are always born to phenotypically normal parents. Due to the severity of the disease, the boys die in their teens. Is this disorder likely to be caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Is its inheritance sex-linked or autosomal? a. recessive, autosomal b. dominant, sex-linked c. incomplete dominant, sex linked d. recessive, sex-linked 8. A diploid individual with two different alleles for a particular gene is said to be: a. homozygous for that gene b. homozygous for every gene c. heterozygous for every gene d. heterozygous for that gene 9. If a baby has “his father's nose,” it's because________. a. the baby has been cobbled together from a bunch of used parts b. the baby has not inherited the “suppress father's nose allele” from his mother. c. the baby has inherited many alleles from his father that work together to shape the baby's nose d. the baby has inherited the “father's nose” allele from his father. e. the baby has inherited the “father's nose” allele from his mother. 10. Trisomy 21 is a consequence of _______________________, the unequal distribution of chromosomes during meiosis. a. recombination b. cytokinesis c. nondisjunction d. crossing over 11. Most genes come in alternative forms called: a. Chromosomes b. Gametes c. Alleles d. Recessive 12. Albinism (lack of skin and hair pigmentation) is caused by a recessive autosomal allele. A woman and man, both normally pigmented, have an albino child together. For this trait, what is the genotype of the albino child? a. It depends on the sex of the child. b. homozygous dominant c. It is unknown because not enough information is provided d. homozygous recessive e. heterozygous 13. A cross between homozygous red-eyed flies and homozygous white-eyed flies results in progeny that all have white eyes. This result demonstrates: a. That white is dominant to red b. That red is dominant to white c. That red and white are co-dominant d. That red shows incomplete dominance 14. The phenotype of an organism is _____________. a. the chronological expression of its genes b. its genetic make-up c. the form it achieves as an adult d. a hypothesis of its evolutionary origins e. its physical characteristics 15. In humans, cleft chins are dominant to smooth chins. If a heterozygous female reproduces with a homozygous cleft-chinned male, what is the probability that the offspring will be smooth chinned? a. 0% b. 100% c. 25% d. 75% 16. The liver cells of a horse contain 64 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in the horse's egg cells: a. 32 b. 16 c. 128 d. 64 e. 8 17. Red is dominant to white. If a heterozygous (Rr) flower is crossed with a heterozygous (Rr) flower what will the phenotype of the offspring be? a. a 1:1 ratio – red to white b. All red flowers c. a 3:1 ratio - red to white d. 100% Rr e. a 1:2:1 ratio RR:Rr:rr 18. Somatic cells can include: a. Kidney cells b. Blood cells c. Muscle cells d. All of the above e. None of the above 19. What are the two major methods of cellular division in eukaryotic cells? a. Meiosis and fission b. Meiosis and cloning c. Fission and cloning d. Mitosis and fission e. Meiosis and mitosis 20. Cytokinesis: a. refers to the division of a cell's cytoplasm b. occurs during prophase c. results in greater diversity among daughter cells d. occurs during mitosis but not meiosis e. all of the above are true 21. If a true-breeding (homozygous), blue-flowered plant was crossed with a true-breeding white-flowered plant, what phenotypic ratio would we observe in the progeny resulting from this cross? Assume the white-flowered trait is completely dominant. a. 75% blue, 25% white b. 100% blue c. 100% light blue d. 100% white e. There is not enough information 22. One of the four nucleotide bases in DNA is replaced by a different base in RNA. Which base is it, and what is it replaced by? a. guanine, replaced by cytosine b. thymine, replaced by uracil c. thymine, replaced by guanine d. adenine, replaced by uracil e. cytosine, replaced by guanine 23. Are mutations harmful or helpful? a. All mutations are harmful. b. All mutations are helpful. c. Most mutations yield valuable new genetic variety, but a few are harmful. d. Most mutations are harmful, but occasionally a mutation results in a new, useful trait. e. Mutations have no effect on an organism one way or the other. 24. Which of the following nucleotide bases are present in equal amounts in DNA? a. adenine and thymine b. adenine and guanine c. guanine and cytosine d. thymine and guanine e. Both a) and c) are correct 25. The process of using the information encoded in mRNA molecules to assemble polypeptides from amino acids is called_______. a. Translation b. Transcription c. Replication. d. The one gene – one enzyme hypothesis e. Transduction 26. DNA is now often used as evidence in criminal trials. It is particularly useful because it can be found in: a. hair b. saliva c. blood d. dead skin cells e. all of the above 27. A given section of template DNA with the sequence AATGGCTAT is transcribed. What is the corresponding sequence on the mRNA transcription? a. UUGAACGUA b. CCGTTAGCT c. GGTAACTGT d. TTACCGATA e. UUACCGAUA 28. Using the table provided above, determine the amino acid sequence of the following mRNA: AUG UCU ACC CGA UAA? a. Methionine, Arginine, Proline, Isoleucine, Tyrosine b. Arginine, Serine, Proline, Valine, Stop c. Methionine, Serine, Threonine, Arginine, Stop d. Valine, Glycine, Aspartic Acid, Alanine, Serine e. Serine, Valine, Threonine, Glutamine, Stop 29. For the karyotype above, does this DNA come from a gamete or a somatic cell? a. A somatic cell b. A gamete c. You cannot tell from the information provided 30. Is the individual in this karyotype a male or female? a. male b. female c. neither 31. During which phase of mitosis do spindle fibers pull the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell? a. anaphase b. metaphase c. prophase d. telophase 32. What is a specific segment of DNA that contains the information to make a protein? a. chromatid b. chromosome c. gene d. locus 33. Someone who is homozygous __________. a. has only dominant alleles for a gene b. has only recessive alleles for a gene c. has two different alleles for a gene d. has two copies of the same allele for a gene 34. The AB blood type is an example of ____________. a. blending b. codominance c. incomplete dominance d. complete dominance 35. Genetic engineering provides a way to produce large quantities of a particular gene product such as human growth hormone. a. True b. False Short Answer Questions: Please choose three of the following to answer as thoroughly as possible. [3 questions at 5 points each] 1. Color blindness is a sex-linked trait. Construct a Punnet square for the following scenario: a normal male reproduces with a female who is a carrier for color blindness. What are the odds of having a child who is color-blind? Would that individual be male or female? What are the odds of having a child who is a carrier for color-blindness? Will that child be male or female? 2. Draw and briefly describe what is happening in the 5 steps of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis). 3. For the coding strand DNA sequence, ATGGAAAATCTGTACTTTCAGTAA, answer the following questions: What is the sequence of the template strand? What is the mRNA sequence? What is the amino acid sequence of the translated polypeptide? (use the table from question 27) 4. The karyotype shown represents a genetic disorder where there is an error in chromosome sorting. What is the term used to describe this type of disorder? Which chromosome has an abnormal number? What is the name of the resulting syndrome? Why do chromosomal sorting disorders typically result in a syndrome rather than a single phenotypic alteration? 5. Explain how you might use a test cross to determine whether a particular trait is dominant or recessive. Assume the parents are both homozygous (one for one trait, one for the other). What would be the phenotypic ratios of their offspring? What would be the phenotypic ratio, if two of those offspring bred? 6. Explain the following terms and how they relate to each other: homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, recessive, genotype and phenotype [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 12, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 12, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
179