*NURSING > EXAM > Canadian Fundamentals of Nursing, 6th Edition/Chapter 30: Vital Signs/Rated A+ (All)
Canadian Fundamentals of Nursing, 6th Edition/Chapter 30: Vital Signs/Rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
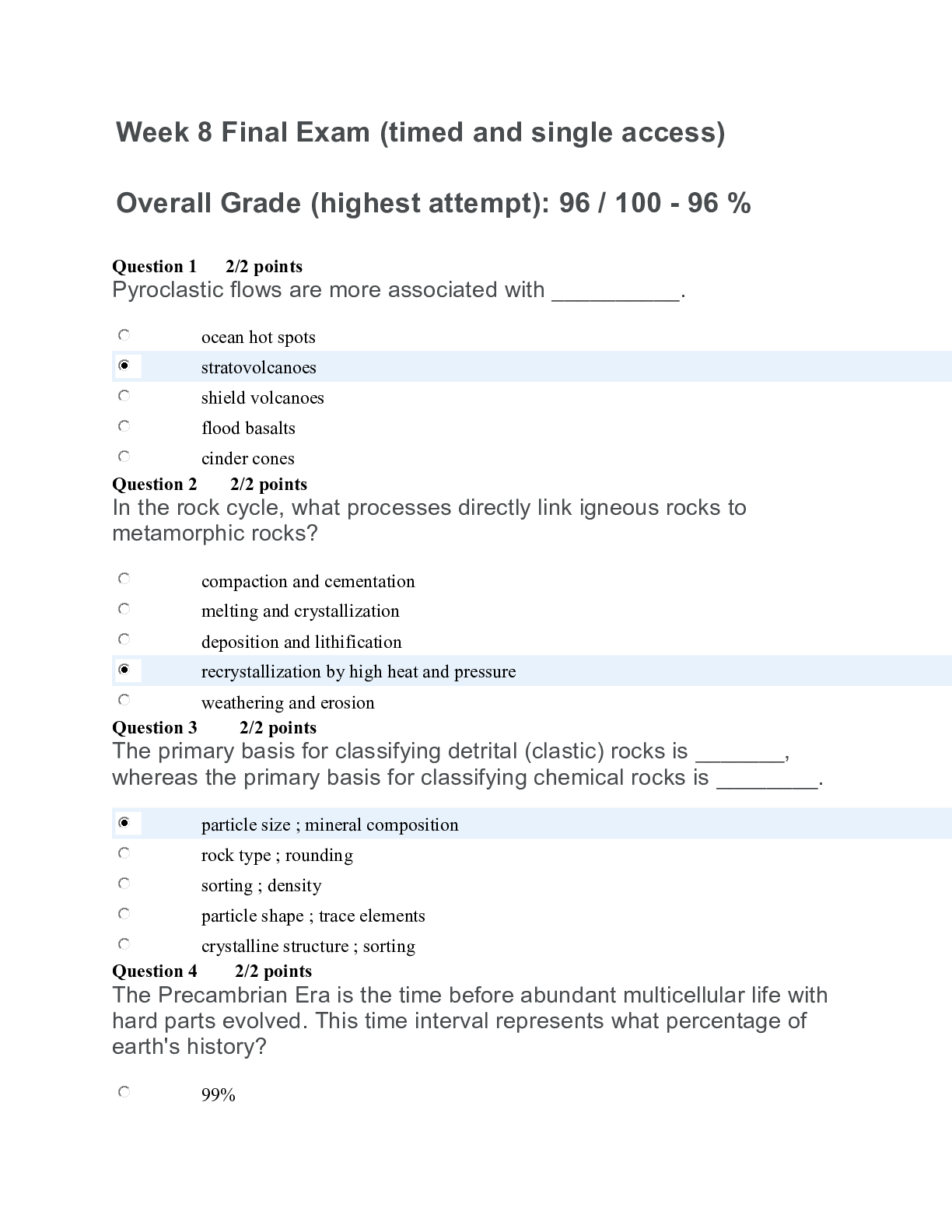
Chapter 30: Vital Signs Potter et al: Canadian Fundamentals of Nursing, 6th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the posterior hypothalamus help control temperature? 2. Of the following me chanisms of ... heat loss by the body, identify the mechanism that transfers heat away by using air movement? 3. The patient has a temperature of 40.7°C (105.2°F). The nurse is attempting to lower his temperature by providing tepid sponge baths and placing cool compresses in strategic body locations. The nurse is attempting to lower the patient’s temperature through the use of which of the following? 4. When focusing on temperature regulation of newborns and infants, what should the nurse know? .COM 5. The nurse working the night shift on a surgical unit is making rounds at 0400 hours. She notices that the patient’s temperature is 36°C (96.8°F), whereas at 1600 hours the preceding day, it was 37°C (98.6°F). What should the nurse do? 6. The nurse is caring for a patient who has a temperature reading of 38°C (100.4°F). His last two temperature readings were 37°C (98.6°F) and 36°C (96.8°F). The nurse should 7. When heat loss mechanisms of the body are unable to keep pace with excess heat production, the result is known as 8. The nurse is caring for a patient who has an elevated temperature. What should the nurse know? respirations, and blood pressure. TOP: Assessment MSC: NCLEX: Physiological Integrity 9. The patient is restless and has a temperature of 39°C (102.2°F). What is one of the first things the nurse should do? a. Place the patient on oxygen. b. Restrict fluid intake. c. Increase patient activity. d. Increase patient’s metabolic rate. ANS: A During a fever, cellular metabolism increases, and oxygen consumption rises. Myocardial hypoxia produces angina. Cerebral hypoxia produces confusion. Interventions during a fever include oxygen therapy. Dehydration is a serious problem through increased respiration and diaphoresis, and a dehydrated patient is at risk for fluid volume deficit. Fluids should not be restricted. Increasing activity would increase the metabolic rate further, which would not be advisable. DIF: Apply REF: 531 OBJ: Describe factors that cause variations in body temperature, pulse, oxygen saturation, respirations, and blood pressure. TOP: Implementation MSC: NCLEX: Physiological Integrity 10. The patient needs temperatures measured every two hours. Which of the following cannot be delegated to an unregulated care provider? a. Selecting appropriate route and device. b. Obtaining temperature measurement at ordered frequency. c. Being aware of the usualNvaUluReSs IfoNr tGheTpBa.tieCnOt. M d. Assessing changes in body temperature. ANS: D The nurse is responsible for assessing changes in body temperature. The nurse instructs an unregulated care provider to select the appropriate route and device to measure temperature, to obtain temperature measurement at ordered frequency, and to be aware of the usual values for the patient. DIF: Apply REF: 532 OBJ: Appropriately delegate vital sign measurement to unregulated care providers. TOP: Implementation MSC: NCLEX: Safe and Effective Care Environment 11. The patient requires routine temperature assessment but is confused and easily agitated and has a history of seizures. The nurse’s best option would be to take his temperature a. Orally. b. Tympanically. c. Rectally. d. By the axillary method. ANS: B The tympanic route is easily accessible, necessitates minimal patient repositioning, and often can be used without disturbing the patient. Its measurement time is also very rapid. Oral temperature measurements require patient cooperation and are not recommended for patients with a history of epilepsy. Rectal temperature measurements require positioning and may increase patient agitation. Axillary temperature measurements take a long time and continuous positioning by the nurse. The patient’s agitation state may not allow for long periods of attention. DIF: Apply REF: 537 (Box 30-4) OBJ: Explain variations in technique used to assess an infant’s, a child’s, and an adult’s vital signs. TOP: Implementation MSC: NCLEX: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages
Instant download

Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2022
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
49

 (1).png)
 (1).png)
.png)

 (1).png)


 (1).png)









.png)






