SOPHIA BUS 3062 Milestone 2,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
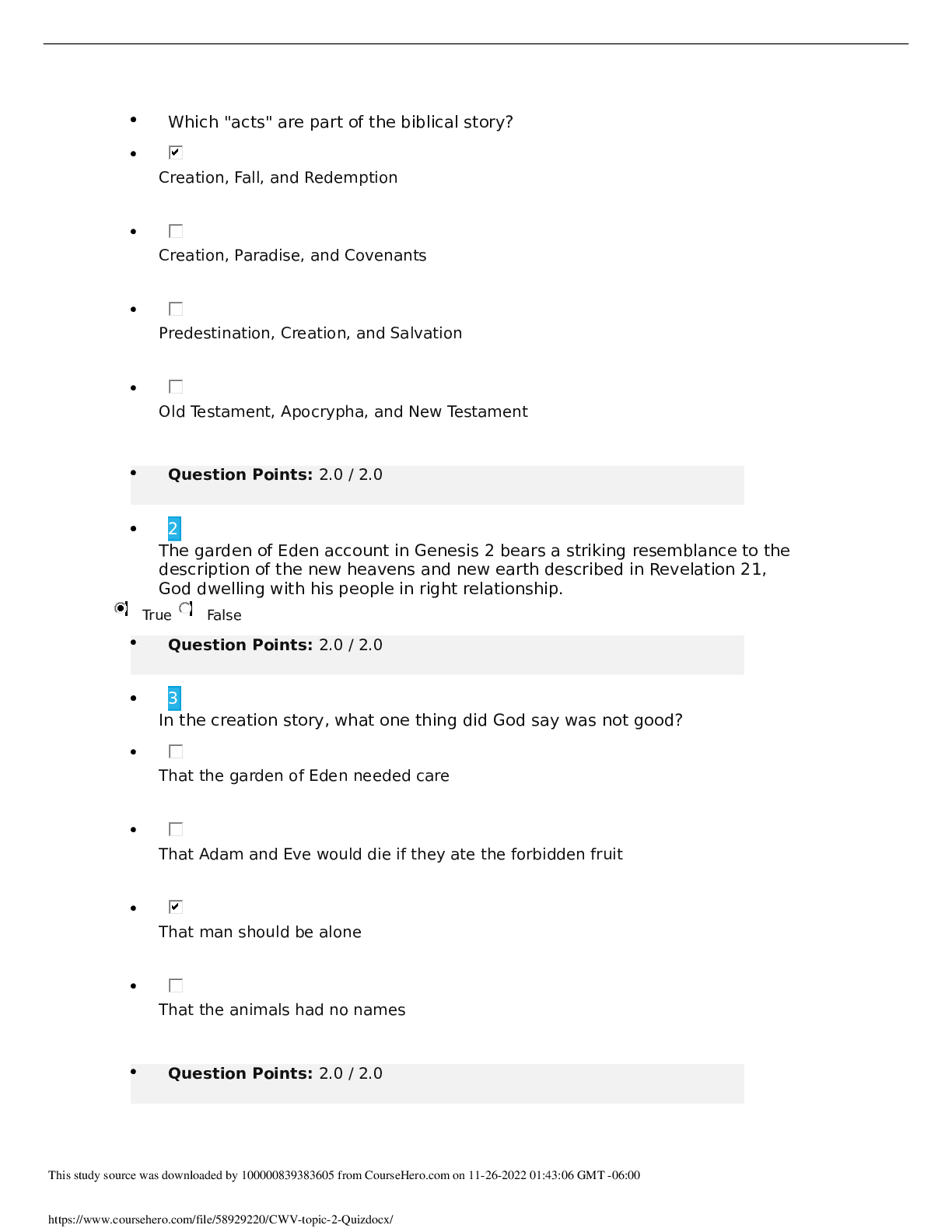
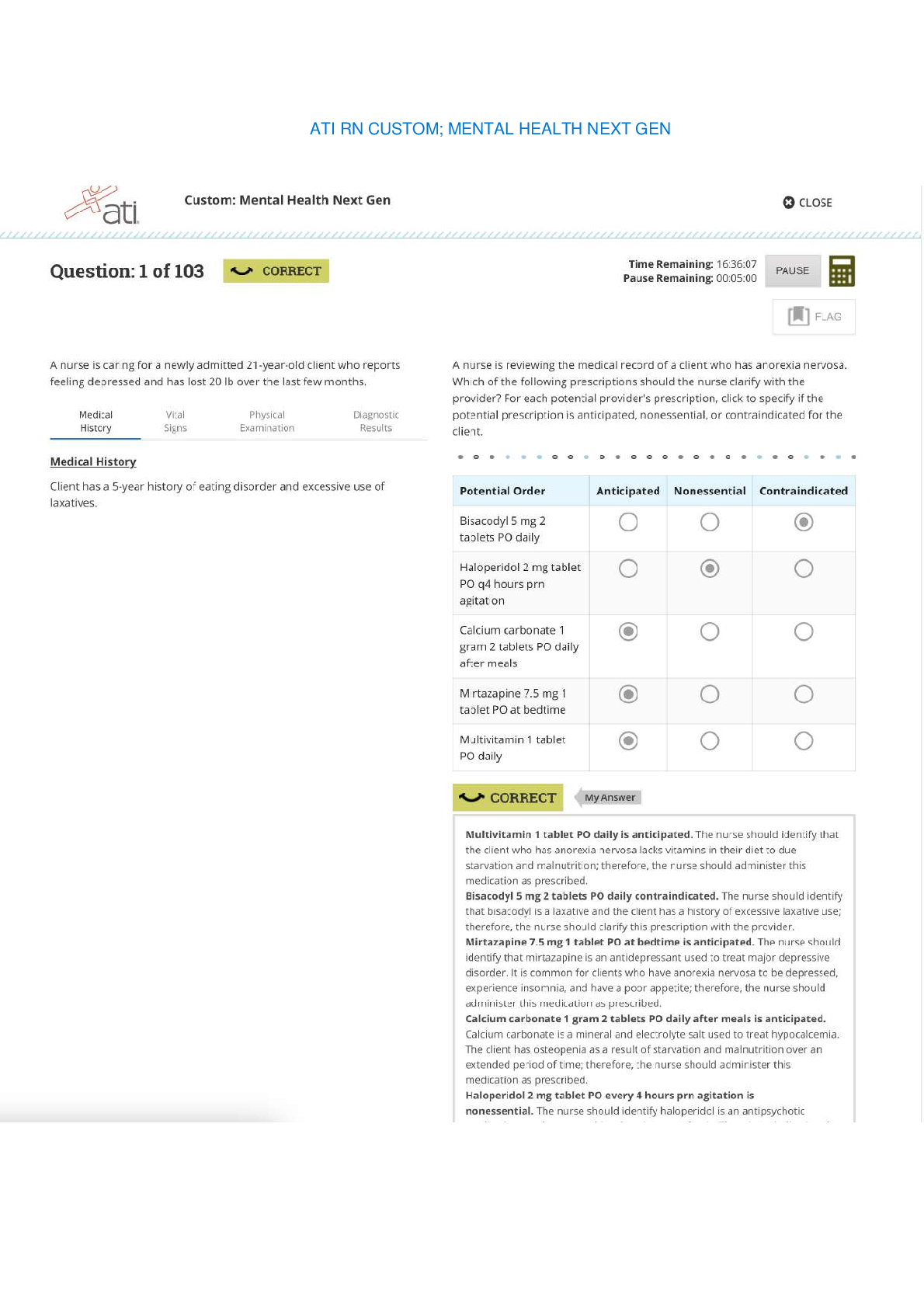
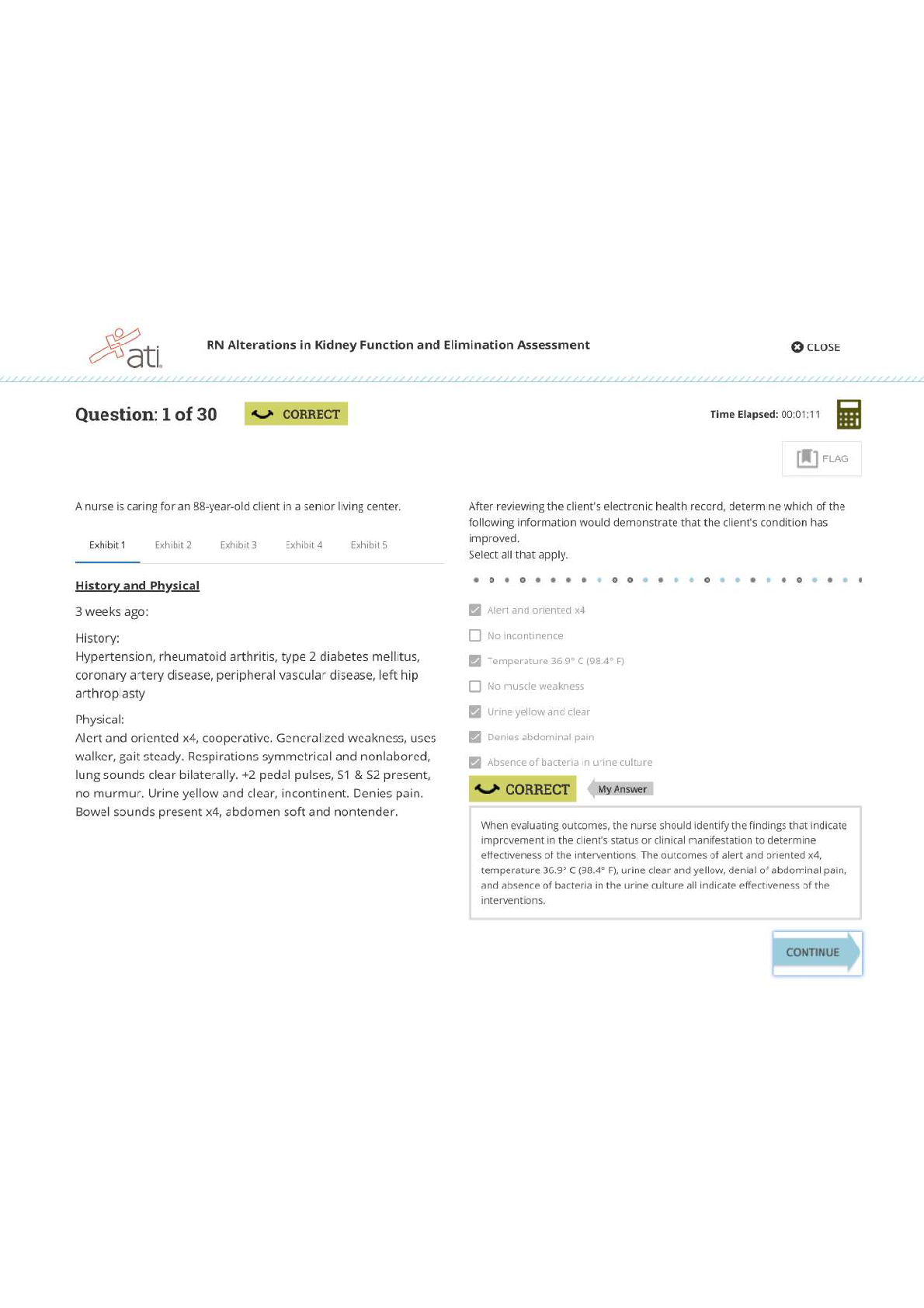
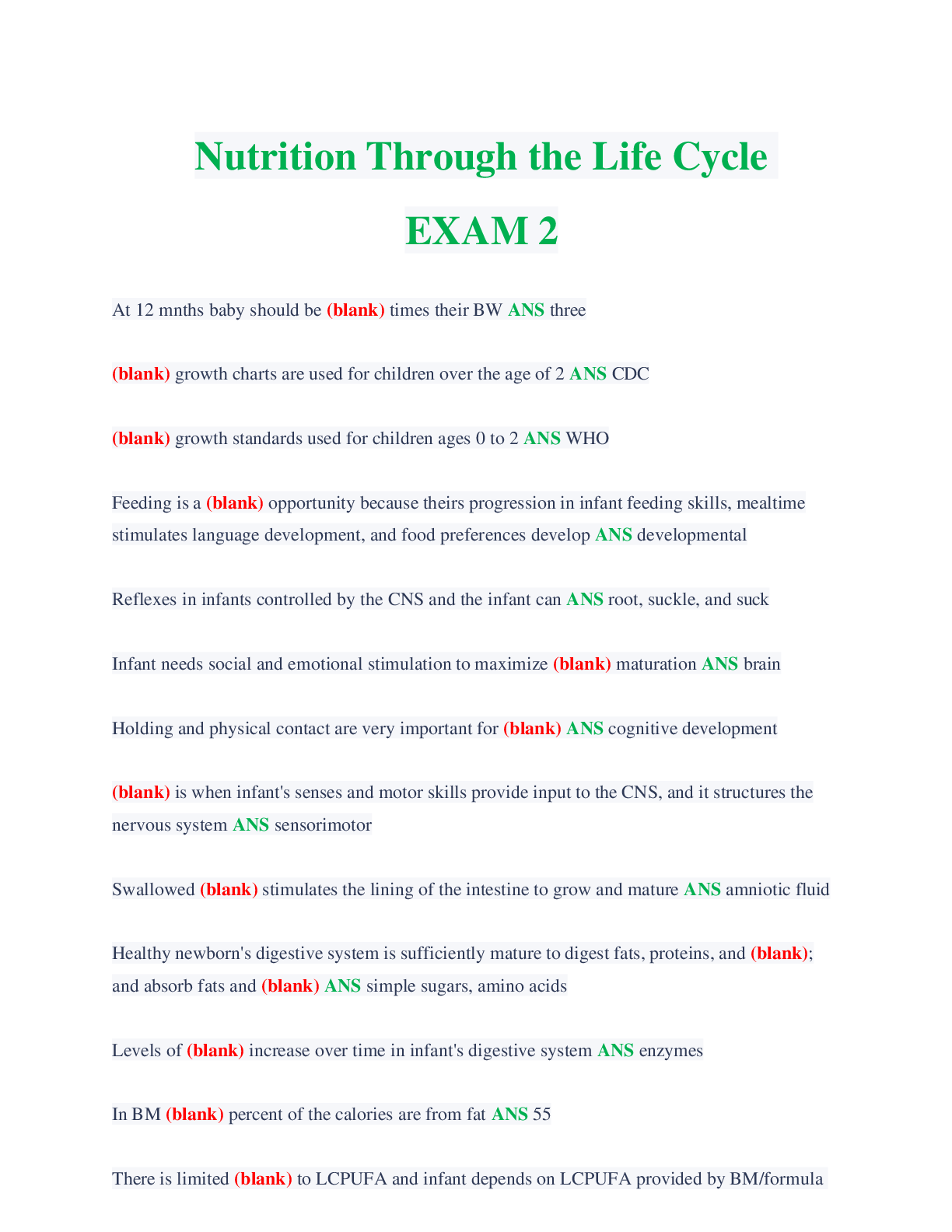
You loan $30,000 of your life savings to a friend for five years at 2% simple interest annually. What is the value of your $30,000 in five years? • $27,000 • $33,000 • $26,878 �... � $33,122 2 Select the best definition of an annuity-due. • An annuity whose payments are made at the beginning of the period • An annuity whose payments are made at the end of the period • An annuity whose payments can be made at any point during the period • An annuity that has matured 3 What effect would a CCC credit rating likely have on a bond? • The bond would have a higher interest rate to compensate for increased risk. • The bond would have a typical interest rate because the bond is considered investment grade. • The bond would have a lower interest rate because the credit rating is poor. • The bond's interest rate would be unaffected because credit rating agencies are not considered impartial. 4 An investment fund that uses more complex investment strategies to generate returns for their wealthy or institutional investors is a(n) __________. • hedge fund • mutual fund • exchange-traded fund • index fund 5 When an investor purchases stock, he or she becomes a(n) __________ of the issuing company. • employee • director • creditor • owner 6 You would like to have $10,000 in an account after eight years’ time. If the account earns 2.5% compounded interest yearly, how much would you have to deposit today? • $8,207 • $9,765 • $8,333 • $9,464 7 Which of the following is a disadvantage of bonds for a potential investor? • They are more likely than stocks to end up valueless if a company goes bankrupt. • Some bonds can be redeemed early by the issuer. • Bondholders risk a significant price drop if a large number of bonds are sold at once. • They have less legal protection than stocks. 8 Which of the following is true for calculating the future value of multiple cash flows? • If the cash flows aren't uniform, you must find the FV of each cash flow and then add them together. • It is more complex to find the FV of annuities than the FV of irregular cash flows. • To find the FV of multiple annuities, multiply the sum of all the present values by the interest rate plus time period. • You can only find the FV of multiple cash flows if they all have the same interest rate. 9 Select the statement that correctly explains the relationship between interest rates and present or future value. • Assuming other variables stay the same, if the interest rate decreases, the present value of an investment decreases. • Assuming other variables stay the same, if the interest rate increases, the future value of an investment increases. • The interest rate and the future value of an investment are inversely related. • Assuming other variables stay the same, if the interest rate decreases, the future value of an investment increases. 10 Which of the following accurately describes a flat yield curve? • A curve with a minimal spread between short-term and long-term maturities and that indicates concern or doubt about the strength of the economy. • A curve that slopes downward as maturities lengthen and that indicates confidence that economic activity will grow in the future. • A curve that rises sharply and then levels off as maturities lengthen and that indicates a transition between a period of economic stagnation to one of growth. • A curve that slopes upward as maturities lengthen and that indicates fear that the economy is about to enter a recession. 11 In calculating the yield of an investment, what is the relationship between APR and APY? • APR is always slightly higher than APY if an investment is earning compounding interest. • APR is always slightly lower than APY if an investment is earning compounding interest. • APR can be higher or lower than the APY of a compounding investment, depending on how high the interest rate is. • APR and APY are two ways of expressing the same measurement of yield. 12 Select the statement that is true of preferred stock. • Preferred stock can be converted into common stock. • Preferred stock does not change in value. • Preferred stock has less protection than common stock if a company goes bankrupt. • Preferred stockholders have a degree of control over corporate policy. 13 Which descriptor relates to the asset-based approach for valuing corporations? • Analyzes what the company owns • Involves an analysis of risk • Considers the weighted average cost of capital • Multiplies the share price by number of shares outstanding 14 Rochelle wants to buy a bond, but she wants to avoid interest rate risk. She also prefers to receive a payment every three months instead of the traditional six months. What type of bond should she buy? • Zero-coupon • Government • Floating-rate • Fixed-rate 15 Janice purchased a $1,000 10-year Treasury note that promised to pay her 1.125% interest every 6 months for the life of the loan. Which of those numbers is the par value of the note? • 1,000 • 6 • 1.125 • 10 16 Consider what you have learned about valuing bonds. • A: Coupon rate = 3.5%, YTM = 4% • B: Coupon rate = 3.2%, YTM = 3.2% • C: Coupon rate = 2.8%, YTM = 3.5% • D: Coupon rate = 4%, YTM = 3.7% Which of the bonds is selling at a premium? • B • D • A • C 17 Hunter is going to receive $3,000 in one year and he wants to know its equivalent value today. The process of determining the answer is called ______. • rating • discounting • compounding • pricing 18 Select the pairing that is correctly matched. • Preferred stock: stockholder receives interest from the issuer • Preferred stock: cannot be converted for common stock shares • Common stock: the value of the stock is dependant upon the overall value of the company • Common stock: the issuer must honor any missed dividend payments 19 Determine the value of a stock with the following variables using the constant growth model: • Current annual dividend: $2.75 per share • Required return rate: 8.5% • Constant growth rate: 6% • $116.60 • $114.70 • $119.35 • $110.00 20 Select the true statement about default risk. • Default risk relates to a bond's periodic coupon payments, but not to its maturity payment. • Bondholders are guaranteed to be repaid in full if a company enters bankruptcy. • It is the risk that the bond's price will fall below its par value. • Bondholders have a degree of legal protection against default risk, but it is not comprehensive. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 24, 2020
Number of pages
5
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 24, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
45