NURS 6550N MIDTERM EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS;TOP SCORE
Document Content and Description Below
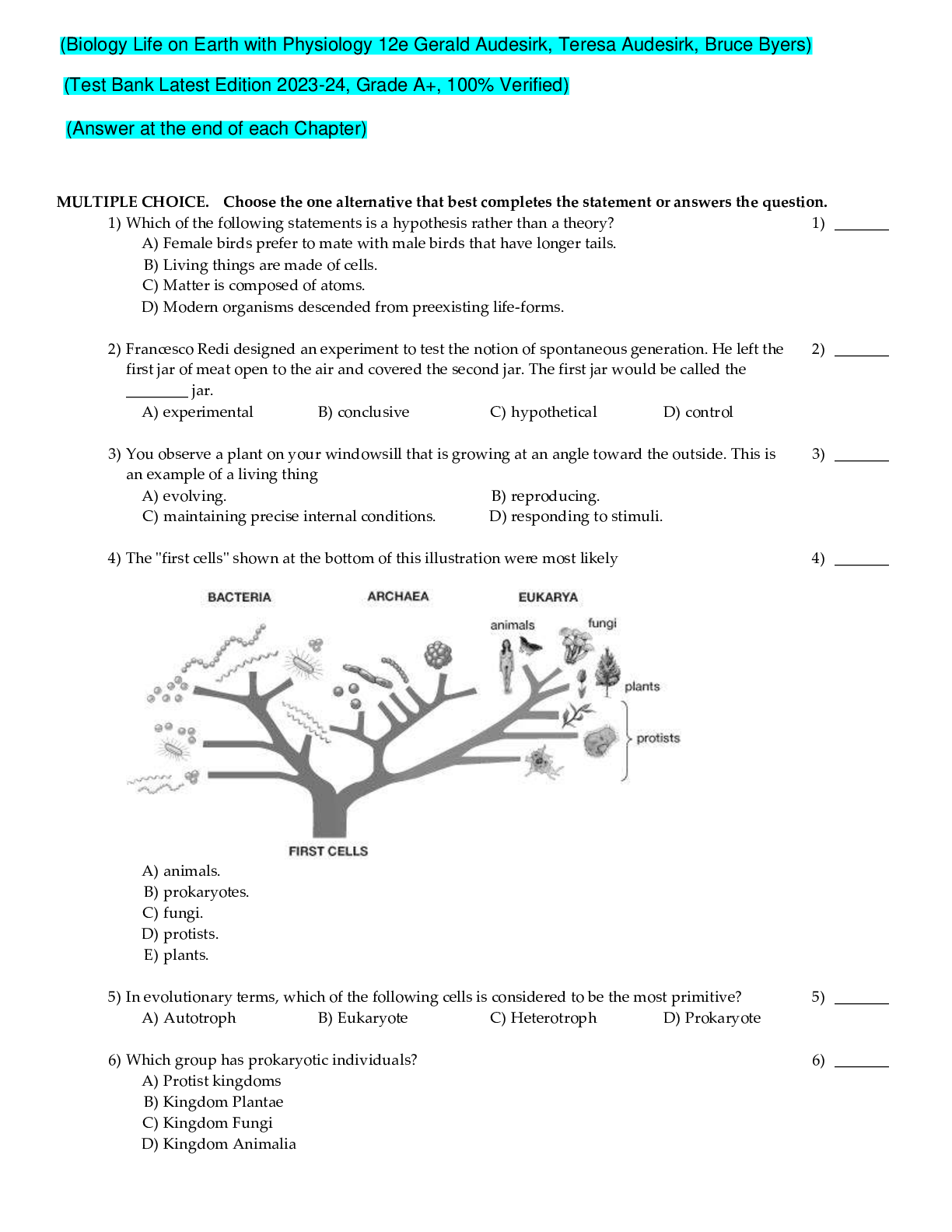
The AGACNP is caring for a patient who is quite ill and has developed, among other things, a large right sided pleural effusion. Thoracentesis is sent for pleural fluid analysis. While evaluating the ... fluid analysis, the AGACNP knows that a fluid identified as a(n) __________ is the least worrisome type. Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. A transudate is essentially just water and can occur as a consequence of increased hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary vessels. It typically implies that the some condition has produced an imbalance in colloid-hydrostatic pressures, such as CHF or hypoalbuminemia. While it can represent a serious problem, it may also represent a transient imbalance. Conversely, “B” is not correct as an exudate has more protein in it and implies a condition characterized by protein leaking from vessels, such as a malignancy or some serious systemic stressor. “C” is not correct—a chyliform effusion is characterized by fat and indicates a pathology causing massive triglyceride degradation. “D” is not correct as a hemorrhagic effusion is blood and typically means traumatic injury. Question 2 0 out of 1 points Mrs. Miller is transported to the emergency department by paramedics. She is having profound, unremitting chest pain, is diaphoretic and pale. She has jugular venous distention and a widened pulse pressure. Suspecting ascending aortic aneurysm, the AGACNP order which test to confirm the diagnosis? Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. It is the most widely used diagnostic tool as it rapidly and precisely can outline the thoracic and abdominal aorta. “A” is not the correct answer—there are radiographic findings that suggest thoracic aneurysm, but they need confirmation by CT. “B” is not the correct answer as ultrasound is not nearly as precise as a CT scan. “C” is not correct—MRI is only indicated when the patient cannot have a contrast CT. Question 3 1 out of 1 points Certain subgroups of the elderly population are at an increased risk for rapid deterioration and long-term care placement. Which of the following is not considered a high risk factor for long term care placement? Response Feedback: “A” is the correct answer; men are at higher risk for long-term care placement than women. In addition to male gender, other risk factors include age over 80, living alone, bowel or bladder incontinence, history of falls, dysfunctional coping, and intellectual impairment. Question 4 0 out of 1 points A patient with anterior epistaxis has been treated with 20 minutes of direct pressure to the cartilaginous portion of the nose. Following pressure the patient is instructed to gently blow the nose. Expected findings in the patient who has been successfully treated include all of the following except a: Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. If bleeding is successfully stopped with 20 minutes of directed pressure, there will be residual blood and clot formation. This is evacuated either by gentle suction or having the patient gently blow. Residual blood and formed clot may present as a sudden gush of dark blood or discharge with or without a clot—these are all typical expected findings. However, if bleeding is not stopped, it will continue as a bright red steady trickle. When this occurs, more invasive measures are indicated. Question 5 0 out of 1 points Kevin is a 14-year-old male who presents for evaluation of a fever of 102.5° F and significant right ear pain. He appears quite ill and says he feels nauseous. Otoscopic evaluation reveals pain to palpation, a very erythematous and bulging tympanic membrane with bullous myringitis. The AGACNP knows that antibiotic therapy must be selected to cover: Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacteria that infects the head and neck in immunocompetent persons, and is the primary treatment target when treating otitis media, bacterial sinusitis, and bacterial pharyngitis. “A” is not correct—while likely on broken skin and soft tissue, it is not common in the ear, nose, or throat unless specific risk factors exist. “B” is not correct—this is much more likely in an immunocompromised patient or a patient on mechanical ventilation. “C” is not correct—it is the second most common organism, but strep is the primary treatment target. Question 6 1 out of 1 points P.M. is a 71-year-old gay male patient who presents as an outpatient for evaluation of increasing shortness of breath. The diagnostic evaluation ultimately supports a diagnosis of community acquired pneumonia. The AGACNP appreciates right middle lobe consolidation on chest radiography. Pending sputum cultures, empiric antibiotic therapy must be initiated to cover which organism? Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. This patient presents from the outpatient population where the most common cause of pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae, and is the primary treatment target for any patient being treated empirically. “A” is not correct—while the patient’s sexual orientation is offered in the provided history, there is no indication that he has HIV/AIDS or any other condition characterized by immunosuppression that would increase his risk for this organism. “B” is not correct, as this organism is not typically seen in the outpatient population without specific risk, e.g. immunosuppression or chronic ventilator therapy. “C” is not the correct answer as this organism is not likely absent specific risk such as instrumentation or known colonization. Question 7 0 out of 1 points Which of the following is the greatest risk factor for vascular dementia? Response Feedback : “B” is the correct answer. Vascular dementia is a consequence of vascular disease, and is more likely to occur in patients with risk factors for target organ damage, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes. “A” is not a distinct risk factor for vascular dementia; it is a risk for Alzheimer’s dementia. “C” likewise increases risk for Parkinson’s dementia, but does not present a risk for vascular dementia. “D” is not a risk factor for vascular dementia. Although there may be some familial risk for certain vascular diseases that may lead to vascular dementia, there is no clear familial tendency for this type of dementia. Question 8 1 out of 1 points J.R. is a 55-year-old male who presents for a commercial driver’s license physical examination with a blood pressure of 170/102 mm Hg. He has no medical history and is without complaint. Which of the following findings constitutes hypertensive urgency? Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. According to the Joint National Committee (JNC) report, hypertensive urgency is described as hypertension in the setting of progressive target organ damage, such as renal involvement with protein leaking, left ventricular hypertrophy, or retinal changes. “A” is not correct— the headache may or may not be relevant, but because there are many non-hypertension causes, a headache alone does not constitute target organ damage. “C” is not correct—it may indicate carotid plaque, but this is not a consequence of hypertension. “D” is not correct as a 1+ palpable pulse may be a normal finding--it must be taken in the context of the rest of the examination. Question 9 0 out of 1 points Because of the commonly recognized adverse effects of atypical antipsychotics, annual laboratory assessment for patients taking these medications should include a: Response “C” is the correct answer. The atypical antipsychotics such as olanzapine Feedback : (Zyprexa), clozapine (Clozaril), and quetiapine (Seroquel) are classically associated with dyslipidemia and annual lipid panels should be performed in patients of all ages who take these medications. “A” is incorrect—this is the appropriate annual screening tool for patients on lithium due to lithium-related iodine suppression of the thyroid gland. There are no specific indications for “B” and “D” unique to patients taking atypical antipsychotics. Those laboratory assessments should only be ordered as indicated by any other significant patient history. Question 10 1 out of 1 points K.R. presents for an evaluation of eye discomfort. He works in a fabricating shop for a custom automobile restoration company and while working he felt like something flew into his eye. He was wearing eye protection at the time but still has the sensation that something is there. Physical examination is significant for some tearing and he reports a persistent sense of something in his eye. Which of the following is not indicated in the diagnostic evaluation? Response Feedback : “B” is the correct answer. The patient’s history is consistent with a metal injury and so an MRI should be avoided. “A” may or not be indicated as the history progresses, but there is no contraindication to it should the examiner determine the need to rule out an abrasion. “C” and “D” are both mechanisms to visualize behind the cornea which may be necessary if a penetration injury (which may occur with a high-velocity injury) is suspected. Question 11 0 out of 1 points D.E. is a 41-year-old female who had lumbar surgery two days ago to repair a ruptured nucleus pulposus. She has been doing well postoperatively but today is complaining of resting fatigue and some shortness of breath at rest. In ruling out a pulmonary embolus the AGACNP first orders a: Response Feedback : “B” is the correct answer. The D-dimer is a highly sensitive serology and is the least invasive mechanism by which a pulmonary embolus may be ruled out; a negative D-dimer virtually eliminates pulmonary embolus from the differential diagnosis. “A” is not correct—while it can be used to make the diagnosis it is more invasive and less specific than other options. “D” is not correct—there is no indication that the patient is on warfarin, and in any event it would not be used to rule in or out pulmonary embolus “C” is not accurate when after surgery, as it will be positive after surgery. Question 12 0 out of 1 points Mr. Nixon is being treated with unfractionated heparin infusion for acute pulmonary embolus. In order to avoid a potentially fatal complication of heparin infusion, the AGACNP monitors: Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. An uncommon but potentially serious consequence of heparin infusion is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Some patients make autoantibodies in response to exogenous heparin that activate their own platelets. When this occurs, heparin must be immediately discontinued and thrombin inhibitors started. “A” is not correct —this is not affected by heparin, but is monitored in those on Coumadin. “B” is not correct—this is also unaffected by heparin, but monitored on Coumadin. “C” is not correct—this is monitored to assess therapeutic efficacy, but not for complications. Question 13 1 out of 1 points Differentiating vertigo from near-syncope and ataxia is one of the goals of history-taking when a patient presents as “dizzy.” The AGACP knows that vertigo is the problem when the patient reports the primary symptom as: Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. Dizzy is a layperson’s term and can mean many different things to patients and health care providers. When the patient identifies the primary symptom as a sense of spinning this supports vertigo, which is usually an inner ear problem. This versus ataxia which is neurologic or near-syncope which may be cardiac, neurological, or neurocardiogenic. “B” is not correct—this may occur with vertigo, but when it is the primary symptom it is most likely ataxia and neurological causes should be considered. “C” is not correct as coincident nausea is not specific and can occur with any of these complaints. “D” is not correct as it is also not specific; while ataxia cannot occur when supine near-syncope can. Question 14 1 out of 1 points Mr. Banks has been admitted for surgical resection of a metastatic tumor, during surgery it is discovered that he has widespread, diffuse metastasis throughout the abdomen. Surgery is no longer an option, and his oncologist says that chemotherapy is unlikely to produce any meaningful benefit. Mr. Banks is concerned that his sons will not support a transfer to comfort care. The AGACNP advises that he: Response Feedback : “B” is the correct answer. If there is any concern about disagreement among family members, or any concern at all that a patient’s wishes will not be carried out, the best action is to ensure that there is a clearly defined legally executed document. “A” is not correct. Living wills are not legally enforceable documents and when dissention arises among family members they may not be carried out. “C” is not correct - while the patient should arrange for his care as long as he is capable of doing so, if questions arise at such a time that he is not capable of answering his next of kin will need to do so. “D” is not correct -- identifying the proxy is not enough without assigning legal rights and responsibilities. While “A,” “C,” and “D” should all be done and will support his care, the only way to ensure that one’s wishes are carried out is to ensure that a legally enforceable direction is in place. Question 15 1 out of 1 points Mr. Wilkerson is a 77-year-old male who is being evaluated and treated for his cardiogenic pain. His vital signs are as follows: Temperature of 99.1° F, pulse of 100 bpm, respirations of 22 bpm, and blood pressure of 168/100 mm Hg. A 12-lead ECG reveals deep ST segment depression in leads V3-V6. The AGACNP recognizes which of the following as a contraindication to rTPA therapy? Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. rTPA is not indicated in patients with ST segment depression; this is not a ST elevation MI. “A” is not correct as age > 80 is a relative contraindication. “B” is not correct as a temperature of 99.1° F is an expected response to myocardial necrosis, and “C” is not correct—the blood pressure is not prohibitive until > 180/110 mm hg. Question 16 1 out of 1 points A 71-year-old patient is recovering from a particularly severe exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He has been in the hospital for almost two weeks and was on mechanical ventilation for 7 days. While discussing his discharge plan he tells you that he is really going to quit smoking this time. He acknowledges that he has been "sneaking" cigarettes in the hospital for two days, but he has established a timeline to decrease the number of cigarettes daily. According to his plan his last cigarette will be the last day of the month. This patient’s behavior is consistent with which stage of the Transtheoretical Model of Change? Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. The Transtheoretical model of change is characterized by 5 stages. “A” is when the patient has no intention to make a change. “B” is when the patient is intending to make a change in the next 6 months. “C” is when the patient is ready to take action or has already taken some action, as this patient has in establishing his plan to quit by the end of the month. “D” is the overt action that attains a criterion sufficient to reduce disease risk—in this patient the action stage would be characterized by actual smoking cessation. The final phase, not presented in the answer choices here, is maintenance. Question 17 1 out of 1 points While assessing a patient with a known psychiatric history, the AGACNP knows that the primary difference between a psychotic and neurotic disorders is: Response Feedback : “B” is the correct answer. Patients with psychotic disorders are characterized by a distinct alteration in their perception of reality which may be manifest by visual or auditory hallucinations or impaired thought processes. Neurotic disorders, while many times very serious, are seen in patients who remain aware and interactive with the reality. “A” is incorrect as neurotic disorders may be characterized by a tendency or actual act of harm, such as the self-mutilating actions classic of a borderline personality, suicide by a depressed patient, or even murder or torture committed by an antisocial personality. While dangerous, none of those disorders include a dis-connect from reality as part of the presentation. “C” is incorrect as antipsychotic medications are used to manage a variety of neurotic disorders such as depression or oppositional defiant disorder. “D” is incorrect as lack of conscience and remorse is typical of antisocial personalities. Question 18 0 out of 1 points L.T. is an 85-year-old male who is admitted for evaluation of profound diarrhea that has produced significant dehydration. He also complains of being very tired lately, and feeling like he is going to vomit all of the time. His vital signs are significant for a pulse of 41 b.p.m. and a blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg. A gastrointestinal evaluation including stool for blood, white blood cells, and ova and parasites is negative. He insists that he has not started any new medications or made any diet changes; the only thing new is that he got new eye drops for his glaucoma. The AGACNP correctly assumes that his new eye drops are: Response Feedback : “B” is the correct answer. The accelerated GI motility and bradycardia are cholinergic adverse effects. Ophthalmic medications are readily absorbed into systemic circulation. All of these medications are used to treat glaucoma and may cause class-related adverse effects, but cholinergic drops are the only ones shown that will slow heart rate and accelerate GI motility. Question 19 1 out of 1 points Janice is a 19-year-old female who presents to the emergency department via ambulance. She is pale, diaphoretic, agitated, and convinced she is having a stroke. Her vital signs include a temperature of 98.9° F, pulse of 114 beats per minute, respirations of 32 breaths per minute, and a blood pressure of 110/74 mm Hg. Diagnostic evaluation is negative and Janice is diagnosed with an acute panic attack. The initial treatment of choice is: Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. A panic anxiety attack requires immediate intervention with a short acting benzodiazepine for immediate symptom control. A calm environment would be helpful, but is not adequate alone to manage acute episodes characterized by physical symptoms. Oxygen is not indicated in the absence of organic problems. The numb hands and feet, known as “stocking-glove paresthesia,” are characteristic of respiratory alkalosis consistent with tachypnea and will resolve once the patient slows her breathing and retains CO2. While cognitive behavioral therapy is an important part of chronic anxiety management, is has no role in acute management of acute panic attack. Question 20 0 out of 1 points Lorraine is a 41-year-old female who presents for an asthma follow-up visit. She says she feels very well, has almost no daytime symptoms, and is using her inhaled corticosteroid medication daily as prescribed. Her PEFR is 85% of her personal best. The best approach to this patient is to: Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. In accordance with EPR-3 guidelines, assessment of asthma follow-up must include a validated asthma questionnaire, such as the ACT. The information gathered so far is encouraging but incomplete and any decision about her care should be made based on a complete assessment. “A” and “B” are not correct as these are treatments that cannot be determined until her assessment is complete. “D” is incorrect because it is not required; at follow-up, objective airflow assessment may be completed with either PEFR or FEV1. Question 21 1 out of 1 points Mr. Owen is a 37-year-old patient who has been admitted for surgical resection of a malignant tumor in his lung. His physical recovery has been uneventful and he is being prepared for discharge. While discussing his ongoing cancer therapy with Mr. Owen, the AGACNP determines that he has experienced persistent, excessive anxiety and worry almost every day for more than one year. What other aspect of Mr. Owen's psychosocial history would be required to made a diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder? Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is an axis I disorder according to DSM-V. Diagnostic criteria require that the patient report both excessive anxiety and worry, and difficulty controlling that worry, for more days than not in the last six months. These two cardinal requirements are accompanied by three of at least six other findings, which may or may not include choices “A” through “C”; so while sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating and muscle tension may or may not occur, excessive anxiety and worry and difficulty controlling that worry are required for the diagnosis. Question 22 0 out of 1 points Kevin T. is a 49-year-old male who is being discharged after hospitalization for an acute inferior wall myocardial infarction. This is his first hospitalization and his first chronic medical diagnosis. Aside from his elevated cardiac isoenzymes and troponins, his laboratory profile was essentially within normal limits. The only apparent cardiac risk factor is an LDL cholesterol of 200 mg/dL. Initiating an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor is an example of which level of prevention for Kevin? Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. Controlling his LDL after a myocardial event is about trying to prevent further events or deterioration. “A” is not correct as primary prevention is about preventing disease—appropriate exercise in a healthy patient is primary prevention. “B” is not correct as secondary prevention is about screening for asymptomatic disease and intervening before disease develops—routine cholesterol screening that reveals an elevated before an MI would be secondary prevention. “D” is not correct as there is no “restorative” level of prevention. Question 23 1 out of 1 points You are evaluating a patient who has been admitted to the emergency room after being arrested for starting a fight in a local sports' bar. The patient is now being cooperative, but reports that he has been in treatment for PTSD for months. He has been prescribed fluoxetine but has not noticed any improvement in symptoms, and now has been arrested for violence. The AGACNP knows that the next step in medication management is likely to include: Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. While SSRIs, beta adrenergic antagonists, and even centrally acting antiadrenergic agonists (clonidine) are all used as first line agents depending upon symptom presentation, patients who have more severe symptoms and do not respond to initial treatments often require management with atypical antipsychotics. This patient has been treated with an SSRI, reports no improvement, and has been arrested for his behavior; these circumstances are a clear indication for escalation to the nest level of therapy. Question 24 1 out of 1 points Mrs. Salter is an 81-year-old lady who presents for evaluation of near-syncopal episodes. Her 12-lead ECG, complete blood count, and comprehensive metabolic panel are all essentially normal. A urinalysis shows some trace protein but is otherwise normal. A 24- hour rhythm monitor demonstrates rare premature ventricular contractions. Mrs. Salter has been in good health and had her first episode at her aerobics class. She only gets lightheaded when she exerts herself. Her heart auscultates for a grade III/VI systolic crescendo-decrescendo murmur at the second intercostal space, right sternal border. The AGACP considers that the likely cause of the syncope is: Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. This is the classic murmur of aortic stenosis, which impedes cardiac output and as it progresses will produce a symptomatic decrease in carotid perfusion. “A” is not correct as there is no sign or symptom of seizure activity. “B” is not correct—the rare PVC is not likely to cause syncope. “D” is not correct—a blood pressure is not given and the proteinuria could come from any variety of causes. Question 25 1 out of 1 points Who among the following patients is at greatest risk for a pulmonary embolus? Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. The primary risk factor for pulmonary embolus is deep vein thrombosis, for which primary risks are polycythemia and stasis. “A” is not correct—the concentration of estrogen in most hormonal contraception is so low that it barely increases risk above that of the general circulation. Of the millions of women on hormonal contraception, only a handful develop DVT/PE. “B” is not correct—this patient is likely to have problems bleeding rather than clotting. “D” is not correct—while smoking is a risk factor for many things DVT is not among them. Question 26 1 out of 1 points Mrs. Birdsong is an 85-year-old female who has been admitted for surgical repair of a hip fracture. She is in remarkably good spirits and is quite talkative. She readily answers all of the questions on her intake assessment, and readily acknowledges information provided during her room orientation. Later while talking with the patient's son the AGACNP learns that the patient has had significant cognitive impairment for a few years. She has virtually no short term memory, but compensates by confabulating. Her son says she is generally very happy as long as there is no change in her day to day routine. This history is most consistent with which form of dementia? Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. Alzheimer’s dementia is statistically the most common form of dementia and is characterized by a long trajectory that progresses to include confabulation. Additionally, patients with this form of dementia are very reliant upon routine and may be distressed when it is disrupted. “A” is not correct; Lewy body dementia characteristically progresses much more quickly and produces an angry demeanor. “B” is incorrect because vascular dementia typically produces a more depressive affect and is not characterized by confabulation; additionally, patients with vascular dementia often have a medical history consistent with vascular risk factors. “D” is not correct as there is no apparent history of Parkinson’s disease. Question 27 1 out of 1 points Mrs. Radovich is an 80-year-old female with a variety of chronic medical conditions which are reasonably well controlled. She generally enjoys a good quality of life and is active with her family. Today her only concern is that she is having problems with her vision. She notices that while trying to look at pictures of her great grandchildren she can’t seem to focus on their faces. She also reports increased trouble reading—she cannot seem to see the words that she is looking at, and her reading glasses do not help. Further evaluation of Mrs. Radovich should include assessment with: Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. An Amsler grid is used to assess central vision and is used to assess symptoms of macular degeneration, an age-related disease that decreases central vision. “A” is not correct, a slit lamp assesses the anterior chamber of the eye and does not especially help in evaluation of macular symptoms. “B” is not correct as this assesses visual acuity and would not be especially helpful with the complaint is loss of central vision. “C” is not correct—a Wood’s lamp is an alternate light source used to visualize corneal abrasions. Question 28 0 out of 1 points R.J. is a 55-year-old female who presents with acute onset left sided facial pain and an inability to move the left side of her face. She cannot smile, raise her eyebrow or even close her left eye, The immediate approach to this patient should include: Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. This is the classic presentation of Bell’s palsy, and rapid administration of corticosteroids can decrease the intensity and duration of symptoms, as well as reduce the likelihood of residual pain. “B” is not indicated; it does not contribute to the diagnosis. “C” may be used as there is a theory that herpes virus causes Bell’s palsy, but this is equivocal and not uniformly practiced. “D” may become necessary at some point to prevent corneal abrasion but the immediate approach should be corticosteroids. Question 29 1 out of 1 points A 78-year-old male present for a physical examination. He has no discomfort or complaints other than a general decrease in vision, but it helps when he puts things under a bright light to read. He admits that while driving at night the streetlights appear to be a bit distorted and his night vision is pretty poor. Given the likely diagnosis, the AGACNP expects which of the following physical findings? Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. This scenario is consistent with cataracts, a common abnormality seen in older adults. The presence of the cataract diminishes the red reflex and ultimately will obliterate it. “A” is not correct, injected conjunctiva are more consistent with inflammation. “B” is not correct—a sluggish pupil response may occur in response to a variety of conditions, including drug toxicities and poisonings, neurological, or ocular disease, but not with cataracts. “D” is not correct; white spots in the macula is most often suggestive of macular degeneration. Question 30 0 out of 1 points Jason is a 46-year-old male who is being managed for sepsis. He has HIV/AIDS and has had a prolonged hospitalization characterized by a variety of complications. He was extubated 3 days ago but continues gastric decompression with a nasogastric tube(NGT), total parenteral nutrition and antibiotic therapy via a central venous catheter, and urinary drainage via a Foley catheter. He continues to demonstrate consistent low grade fevers but all points of insertion of his tubes are normal to inspection, a chest radiograph demonstrates improvement of his pneumonia, and his urinalysis shows no bacteria, leukocytes, or nitrites. The AGACNP should next order: Response Feedback : “C” is the correct answer. The incidence of bacterial sinusitis is significantly higher in patients with AIDS as compared to the general population and the long term NGT is a risk factor for sinus infection. A maxillofacial CT scan should be considered in any patient with AIDS to rule it out in the setting of persistent fever, especially when risk factors exist. “A” is not correct—gastric drainage can be expected to grow bacteria and will not contribute to the diagnosis. “B” is not correct; urine that has no bacteria or leukocytes is unlikely to be infected. “D” is not the correct answer—while it may be indicated further along in the diagnostic pathway, sinusitis is more likely and “C” should be ordered first. Question 31 0 out of 1 points The interpretation of a chest radiography should follow a systematic approach to ensure that all vital structures are evaluated and important clinical findings are not missed. The last thing to be assessed when looking at chest radiography should be the _____________: Response Feedback : “A” is the correct answer. The lungs are the last thing to be examined; when not properly taught, new may clinicians go right to the heart and lungs and may miss important information. Like the nursing process (assess, diagnose, plan, intervene, evaluate) and the system for ECG interpretation (rate, rhythm, intervals, axis, morphology) the system for interpretation of the chest radiograph should proceed from assessing patient identification, patient rotation, level of inspiration, film exposure to an assessment of the film proceeding in this order: Mediastinum and hila, thoracic cage, extrathoracic bones and soft tissues, and finally lungs. Using a systematic approach helps eliminate the risk of missing vital findings. Question 32 1 out of 1 points The Short Confusion Assessment Method (Short-CAM) is a widely used four item tool that assesses delirium in the hospitalized patient. It includes observation of all of the following except: Response Feedback : “D” is the correct answer. The tool was developed to improve identification and recognition of delirium, not to diagnose causation. The four items observed with the Short-CAM method are (1) acuity of onset, (2) inattention, (3) disorganized thinking, and (4) level of consciousness. Once delirium is recognized, then clinical diagnosis of underlying cause is indicated. Question 33 1 out of 1 points Ms. Yang has been hospitalized for 5 days for the management of a gastrointestinal bleeding. She appears to have stabilized hemodynamically, but today she had a temperature of 101.9° F and chest radiography demonstrates a diagnosis of pneumonia. The AGACNP knows that the diagnostic evaluation for hospital acquired pneumonia for all patients must include: [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 35 pages
.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 01, 2022
Number of pages
35
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 01, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
43


.png)

.png)






.png)



.png)



.png)

.png)