Sophia history II milestone 2,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
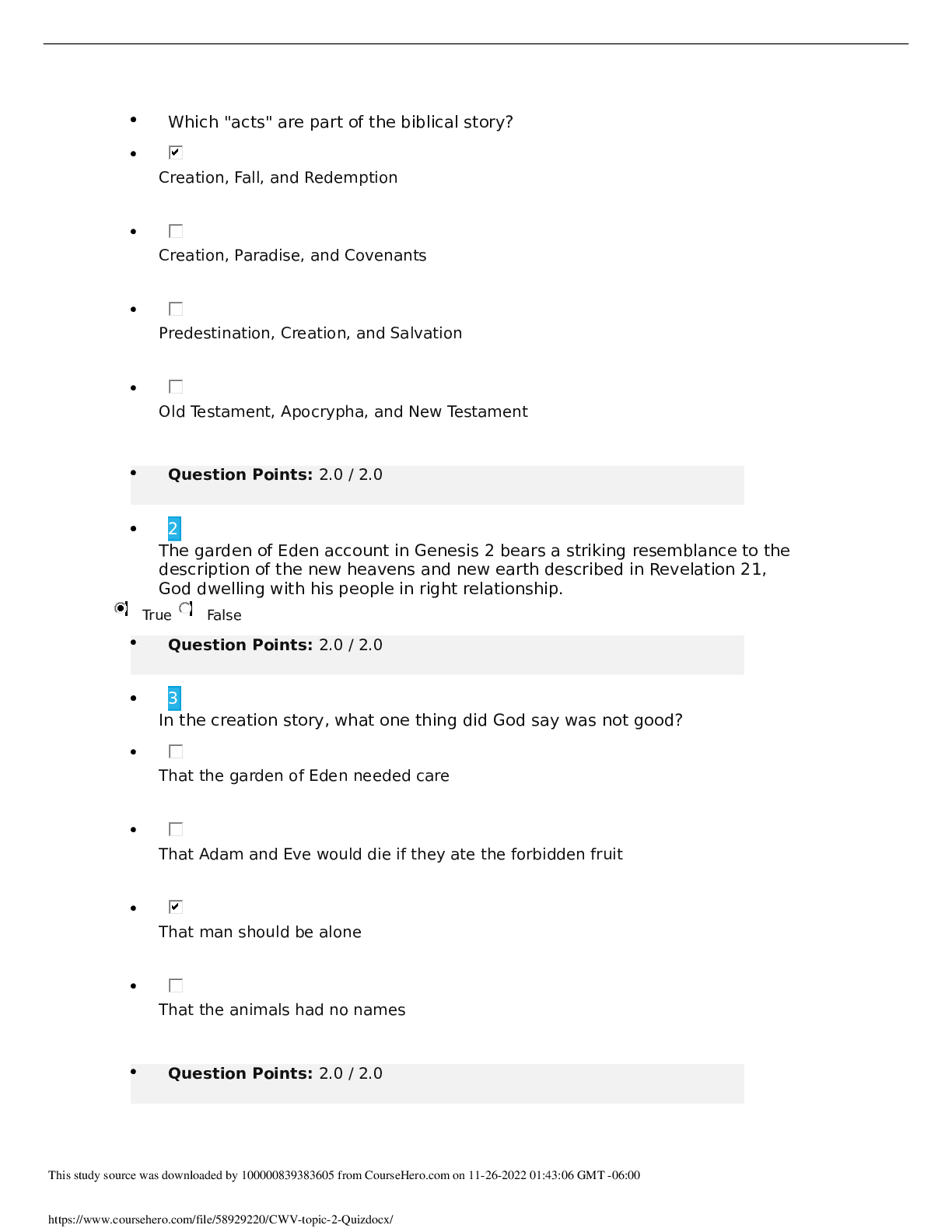
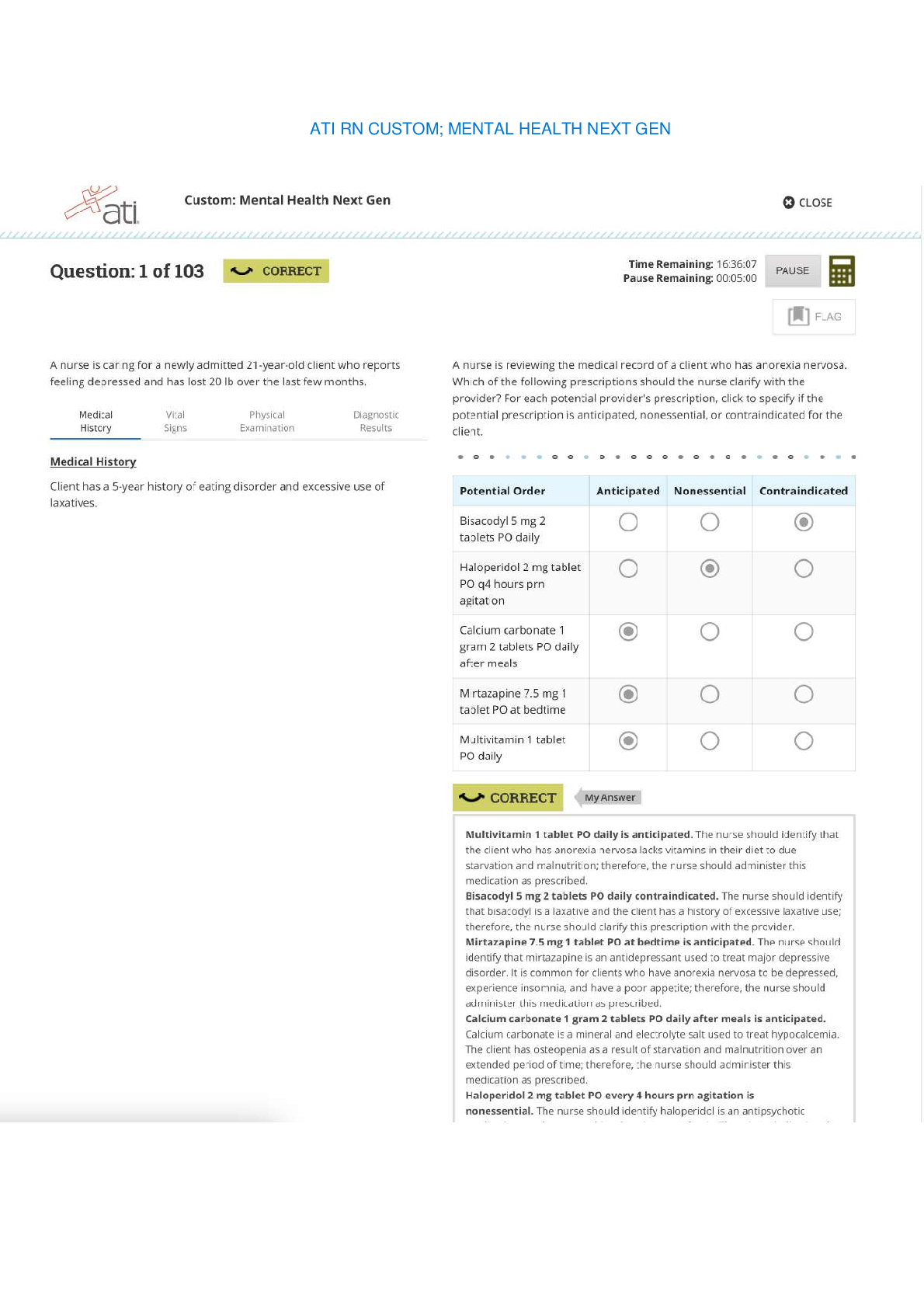
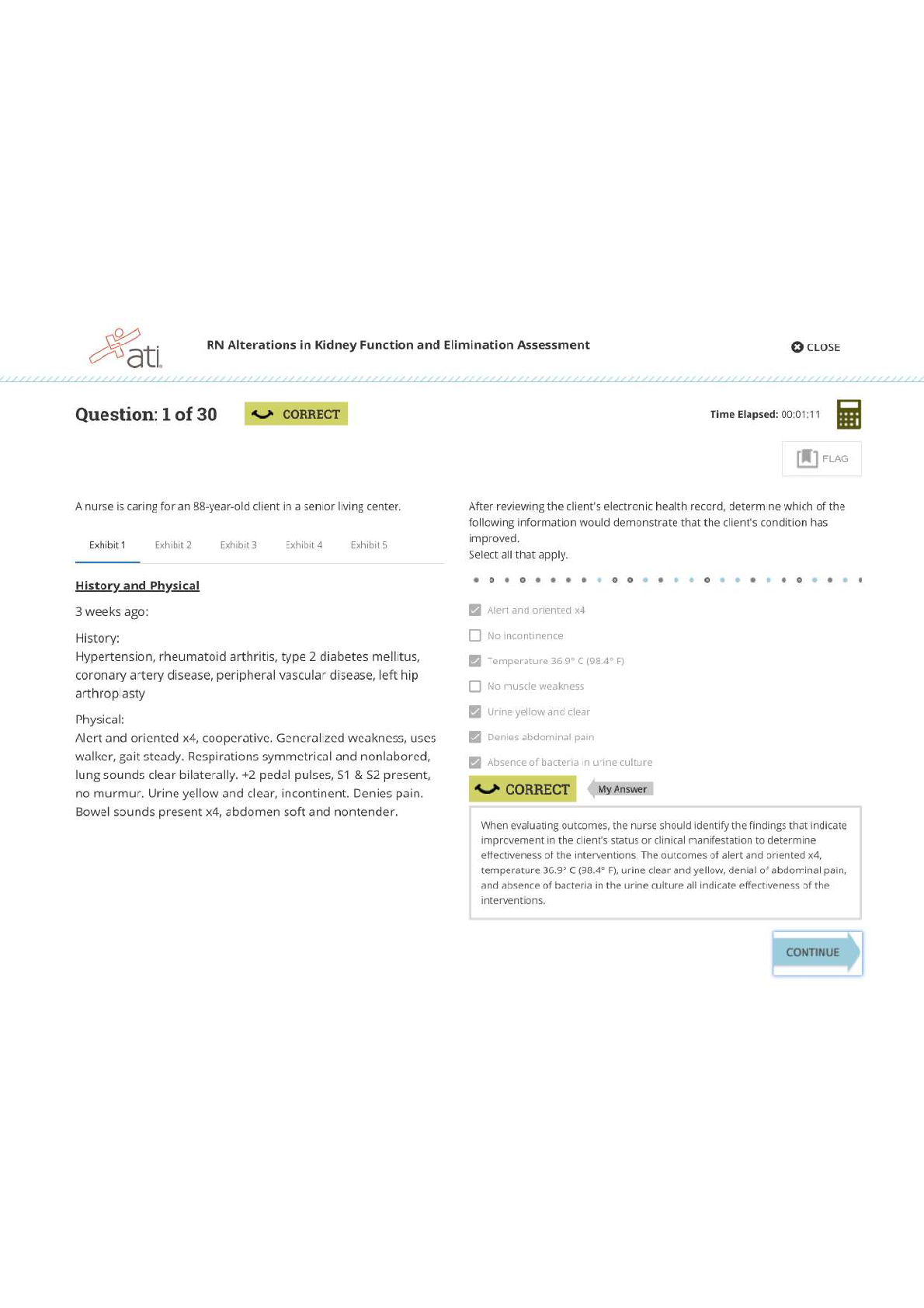
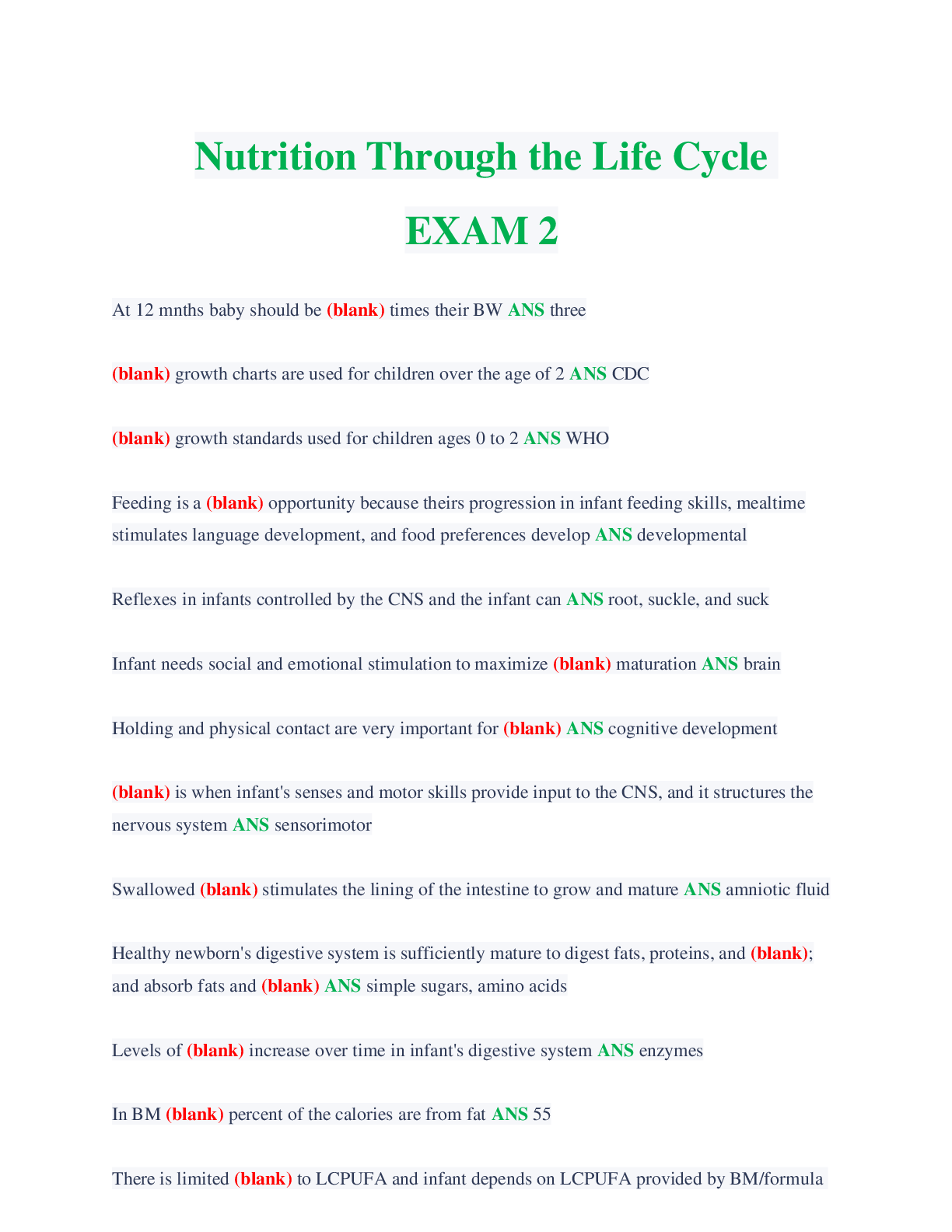
Which statement is NOT true of the Progressives? • They wanted to replace capitalism with a socialized economy. • They sought to improve industrial working conditions for men, women, and ... children. • They advocated the creation of more democratic election processes. • They relied on science and technology to improve governance. 2 Theodore Roosevelt’s “Square Deal” had three main components. Choose the action that was NOT included in his plan. • regulation of corporations • federal oversight of public lands • direct aid to the poor • consumer protections 3 President Franklin Roosevelt oversaw both a First New Deal and a Second New Deal to curb the Great Depression. Choose the action that was part of his First New Deal. • The National Labor Relations Act reformed labor relations by protecting American workers’ right to unionize and bargain collectively for wages and benefits. • The Works Progress Administration provided jobs for more than eight million unemployed workers over an eight-year span. • The Social Security Act established a permanent safety net to help the most vulnerable Americans, including the elderly, the disabled, and single parents. • To put Americans back to work quickly, the Public Works Administration contracted with private companies to build highways, bridges, and military bases. 4 President Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points revealed his plan for world peace following World War I. Wilson’s proposals included all of the following EXCEPT __________. • a call for free trade and freedom of the seas • a stipulation that Germany pay for the war • an end to secret treaties and negotiations • a reduction in armaments around the world 5 All of the following factors contributed to an American shift toward imperialism in the 1890s EXCEPT __________. • The federal government was seeking ways to ease labor conflict in the United States. • Missionaries believed their work abroad would benefit people and help expand democratic principles. • Protestant religious leaders sought to increase Christian influences around the world. • American entrepreneurs and businessmen owned fruit and sugar plantations in Hawaii and Cuba. 6 In 1916, pressure from activists and the National Child Labor Committee contributed to the __________, which prohibited interstate trade of any goods produced by child labor. • passage of the Keating-Owen Act • creation of the National Consumers League • formation of the U.S. Children’s Bureau • Supreme Court ruling in Muller v. Oregon 7 Choose the false statement about the War of 1898. • Congress recognized Cuba’s independence and authorized the military to forcefully remove Spain. • During the war, the U.S. claimed Guam, Wake Island, and parts of the Samoan Islands. • The U.S. recognized the independence of Cuba, the Philippines, and other Spanish colonial holdings. • Newspapers reported the explosion on the U.S.S. Maine was the result of a Spanish attack. 8 A neighborhood in New York City, Harlem, became a center for a black political and cultural movement in the 1920s. Which of the following statements best describes the "New Negro" movement? • It advocated for black autonomy and, if necessary, a return to Africa. • It encouraged Southern blacks to relocate to Northern urban centers. • It promoted a black literary culture that celebrated its racial heritage. • It attempted to enforce the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution. 9 Why did President Theodore Roosevelt use the power of his office to advance Progressive reform? • His prior experiences led him to sympathize with many of the goals of the Progressive movement. • He believed that corporations should be the backbone of the U.S. economy. • The voting public desired a Progressive alternative to the policies of William McKinley. • He believed in granting more power to the individual states. 10 Which statement best describes the international financial situation that contributed to the Great Depression? • American banks had extended private loans to European countries, but those countries defaulted on the loans. • Germany and Austria owed reparations to the U.S. government for starting World War I and refused to pay. • The U.S. government forgave numerous loans made to Great Britain and France during World War I. • Great Britain and France were able to pay their debts by using reparations from Germany and Austria. 11 Which statement reflects President Herbert Hoover’s response to the Great Depression? • “The American economy will recover, but only with active intervention on the part of the federal government." • "My administration's reforms will make our banking system stronger and more trustworthy." • “Farmers who have lost crops to drought will receive animal feed, and food for themselves.” • “The role of government is to encourage businesses to voluntarily help to sustain the economy.” 12 Although many young Americans in urban areas were associated with the "new generation" during the 1920s, the decade also witnessed the rise of the Lost Generation. All of the following describe aspects of the “Lost Generation” EXCEPT __________. • World War I and the Red Scare alienated some Americans from society. • Many intellectuals struggled with a sense of despair and disillusionment. • Many joined the Ku Klux Klan and other nativist groups to fight against radical ideologies and immigrants. • Authors created characters who had to display resilience amid constant struggle and failure. 13 Read the sentence from a Chicago newspaper account of a race riot during the Red Summer. White bathers at the Twenty-ninth street improvised beach saw a colored boy on a raft paddling into what they termed ‘white’ territory. A snarl of protest went up from the whites and soon a volley of rocks and stones were sent in his direction. Select the statement that accurately explains what is happening in this account. • The police had encouraged innocent white beachgoers to begin throwing rocks at black swimmers. • Whites were exercising their legal rights to use whatever means necessary to enforce segregation laws. • The black boy was intentionally making a political statement, which scared the whites and elicited a violent reaction. • Whites were willing to use violence to maintain an informal form of racial segregation in Chicago. 14 Study the political cartoon published in Judge in 1905. Which of the following is the best example of Theodore Roosevelt's use of "The New Diplomacy? • The U.S. Navy intervened in the Panamanian revolution to secure American access to a canal site in Central America. • The Roosevelt Corollary reversed the Monroe Doctrine by allowing European nations to intervene in Latin American affairs. • The U.S. Army participated in a joint operation with Spanish forces to put down an insurrection in Cuba. • U.S. Marines occupied Nicaragua after that country refused to accept loans from American banks to pay off its debts. 15 President Wilson’s stance on American neutrality in World War I changed between 1914 and 1917. Which event occurred most proximate to Wilson's request to Congress to declare war? • Britain suffered massive causalities in the Battle of the Somme. • Germany broke its promise to restrict its use of submarine warfare and sank the Laconia. • The value of American exports to the Allied powers reached $3 billion. • Germany launched attacks on military and merchant ships around Great Britain. 16 When the United States entered World War I, anti-alcohol groups saw the opportunity to enact a national Prohibition amendment for all of the following reasons EXCEPT ______. • State anti-liquor laws already affected a significant number of Americans. • The enactment of Prohibition as a wartime emergency created sufficient precedent for an national amendment. • Anti-liquor advocates organized hunger strikes outside of the White House. • They thought grain should not be used to make beer and liquor when soldiers overseas needed food. 17 "Article X diminishes American independence by taking away Congress’s power to declare war." Choose the person or group that held this belief regarding the proposed League of Nations, particularly Article X. • President Wilson • Reservationists • Irreconcilables • Democrats 18 All of the following statements can be attributed to W. E. B. Du Bois EXCEPT __________. • “I call for immediate and uncompromising activism for African American civil rights in order to achieve social progress.” • “We must demand an end to Jim Crow segregation and the convict lease system, and we must support universal suffrage.” • “I believe we must protest and demand change to protect our African American communities and our very lives.” • “The burden of change is upon us, the African American community; we are responsible for our own success.” 19 Which of the following aspects of the Progressive era is considered by historians to contain elements of BOTH social justice and social control? • "As members of the Niagara Movement, we call for immediate political equality for all." • "State laws that separate facilities for blacks and whites have been deemed constitutional." • "Attempts to monitor segregation of whites and blacks in the South systematize white supremacy." • "Muller v. Oregon, which limited working hours, was a victory for female workers, but it cited studies that suggested women were the weaker sex. 20 One trend of the 1920s that associated the decade with a “new generation” was young urban women who wore short skirts, had short hair, and smoked and drank in public. These women were called __________. • flappers • manly • unconventionals • new consumers 21 The New Deal transformed the Democratic Party. Choose one example of this transformation. • Democratic leadership in individual states assumed responsibility for their own economic stability and prosperity. • Party dominance by white Southerners was challenged by new members, including Northern liberals and African Americans. • President Franklin Roosevelt formally approached Congress to act on civil rights, including enacting a federal antilynching law. • The Democratic Party embraced the ideas of small government, fewer regulations, and individual responsibilities. 22 Consider the photograph titled, “One of the pioneer women of the Oklahoma Panhandle dust bowl,” taken by Arthur Rothstein in April 1936. Why does the photographer call the woman in the image a “pioneer”? • She reinforces the traditional American values of persistence and hard work in the face of adversity. • She symbolizes those Americans leaving their homes and starting over elsewhere. • She epitomizes the plight of American farmers on the Great Plains. • She represents the greed associated with overfarming and land speculation. 23 Many historians have argued that the New Deal changed American politics and governance. All of the following statements support this argument EXCEPT __________. • Under Franklin Roosevelt, the executive branch became the focus of new ideas and actions to safeguard American citizens. • Franklin Roosevelt’s “fireside chats” explained complicated issues and inspired the public’s faith in the presidency. • The Franklin Roosevelt administration’s willingness to use the powers of the office transformed the presidency. • Franklin Roosevelt’s weak political skills were offset by the combined manpower and expertise of his “brain trusts.” 24 The Red Scare was a period following World War I in which Americans suppressed radical dissent. Which event is NOT considered a cause of the Red Scare? • The tsar’s regime in Russia was overturned by Communists, and some Americans feared labor unions in the United States were being infiltrated by these revolutionaries. • Laborers who had originally agreed not to strike in support of the war effort participated in nearly 3,000 strikes in 1919. • Race riots revealed that white Americans were willing to use violence and intimidation to maintain positions of supremacy in Northern cities. • A bomb explosion damaged the home of Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer in June 1919. 25 What was one purpose of the Glass-Steagall Act as a part of Franklin Roosevelt’s First New Deal? • to allow banks to form independent financial holding companies • to require federal agencies to assess and evaluate banking practices • to prohibit commercial banks from engaging in investment banking • to place commercial banks under temporary federal jurisdiction [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 21, 2020
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 21, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
83