Pharmacology > STUDY GUIDE > NR 565 Pharm midterm study guide (GRADED A) Question and Answer Solutions | Download To Score An A (All)
NR 565 Pharm midterm study guide (GRADED A) Question and Answer Solutions | Download To Score An A
Document Content and Description Below
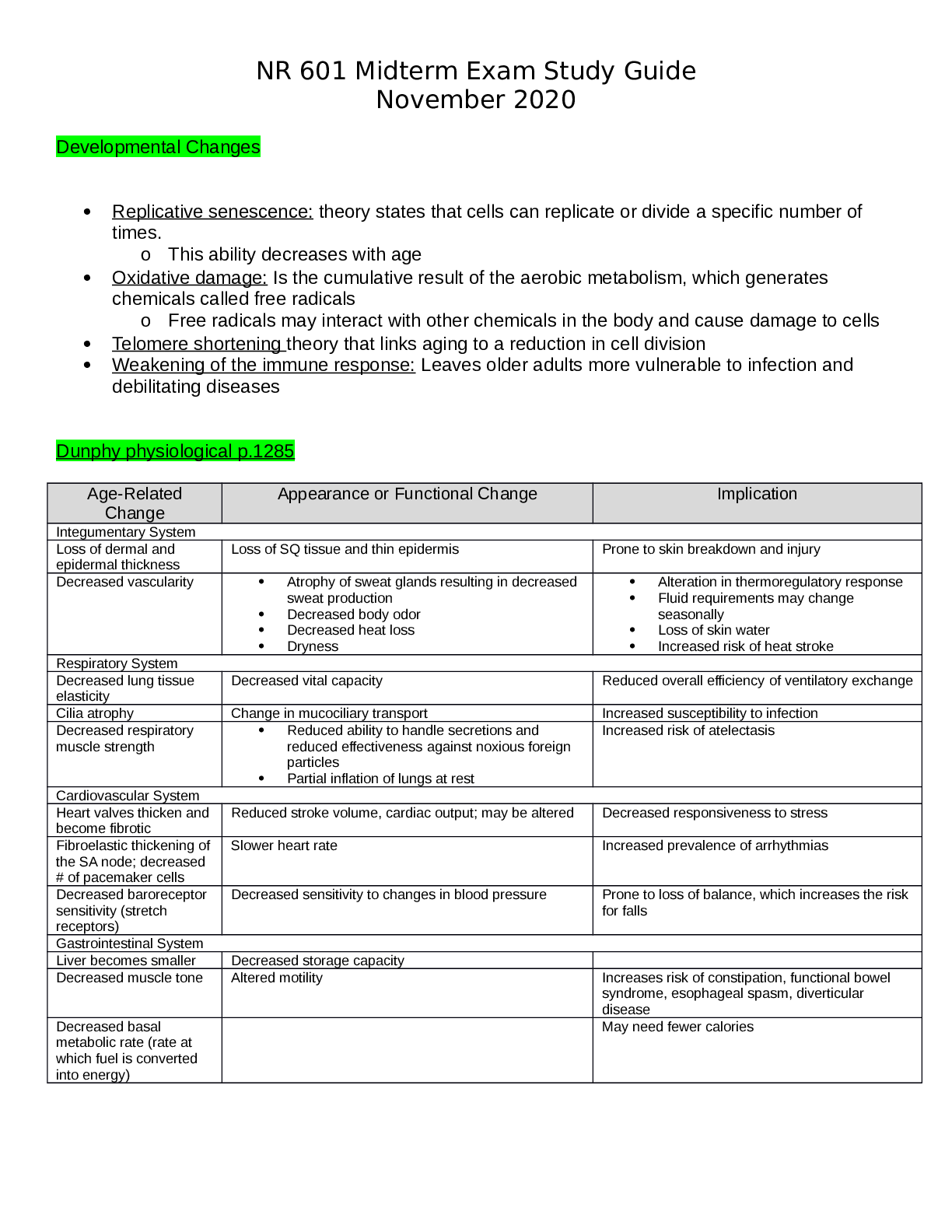
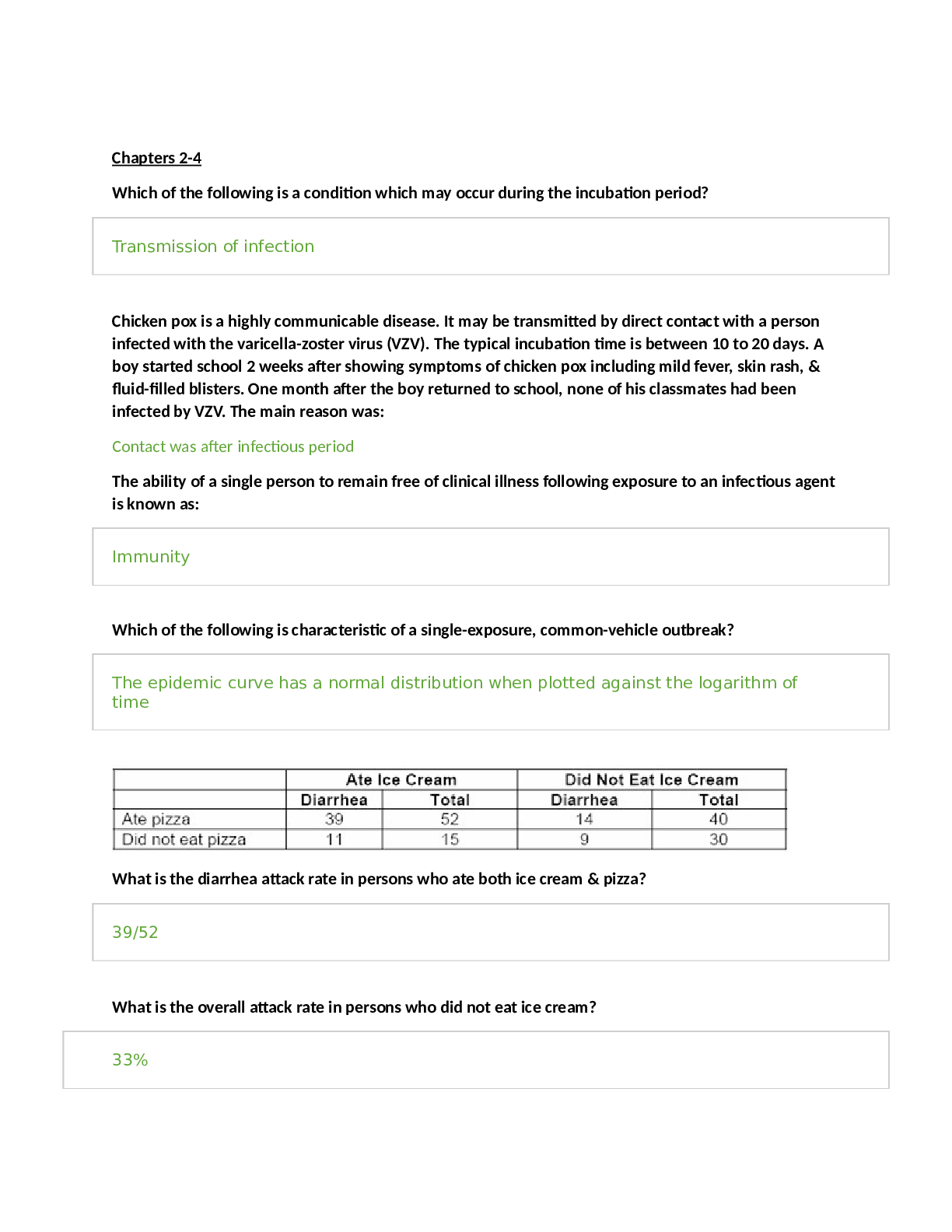
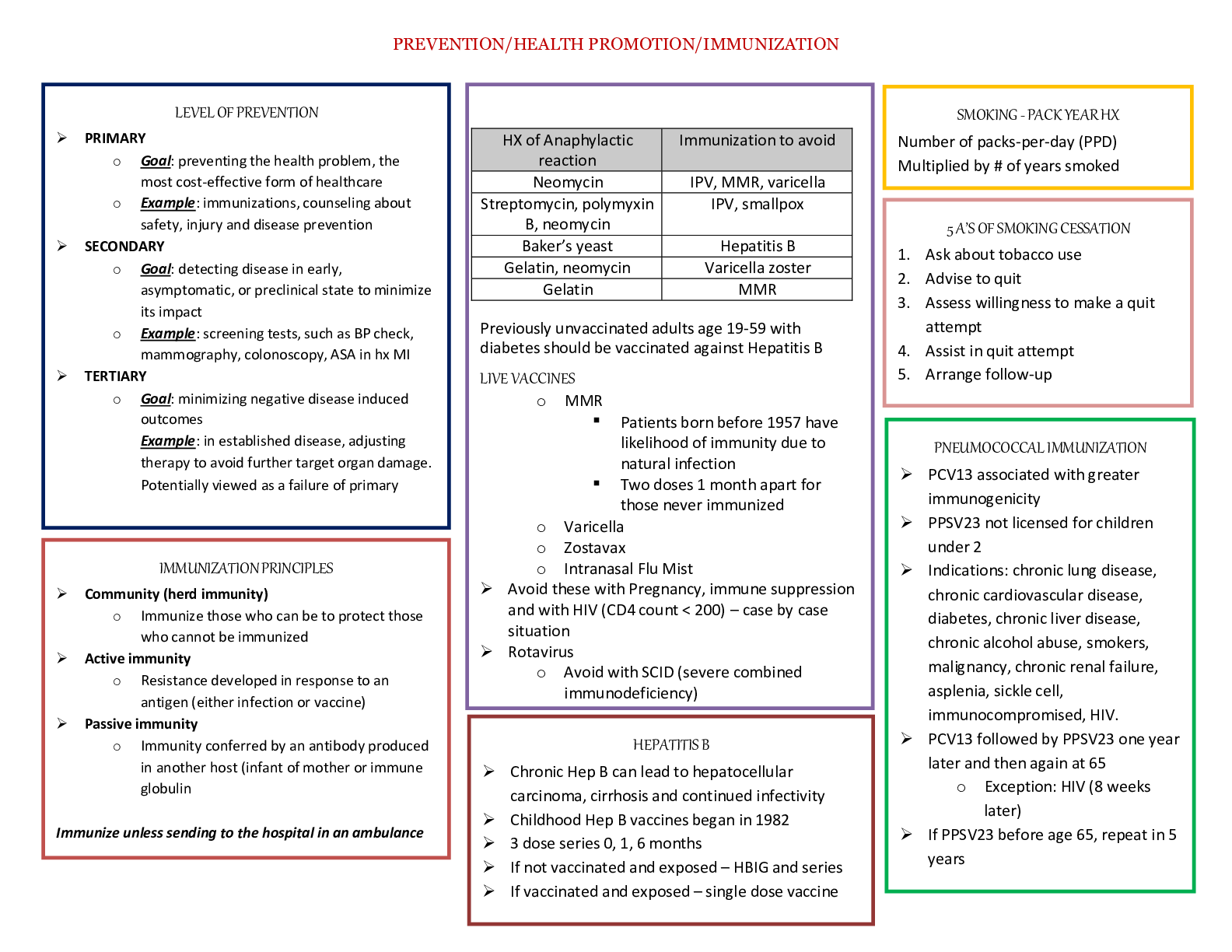
Chapter 2. Review of Basic Principles of Pharmacology 1. A patient’s nutritional intake and laboratory results reflect hypoalbuminemia. This is critical to prescribing because: Distribution of dru... gs to target tissue may be affected. 2. Drugs that have a significant first-pass effect: Are rapidly metabolized by the liver and may have little if any desired action 3.The route of excretion of a volatile drug will likely be the: Lungs 4. Medroxyprogesterone (Depo Provera) is prescribed intramuscularly (IM) to create a storage reservoir Increase the length of time a drug is available and active 5. The NP chooses to give cephalexin every 8 hours based on knowledge of the drug’s: Biological half-life 6. Azithromycin dosing requires that the first day’s dosage be twice those of the other 4 days of the prescription. This is considered a loading dose. A loading dose: Rapidly achieves drug levels in the therapeutic range 7. The point in time on the drug concentration curve that indicates the first sign of a therapeutic effect is the: Onset of action 8. Phenytoin requires that a trough level be drawn. Peak and trough levels are done: To determine if a drug is in the therapeutic range 9. A laboratory result indicates that the peak level for a drug is above the minimum toxic concentration. This means that the: Concentration will produce an adverse response 10. Drugs that are receptor agonists may demonstrate what property? Desensitization or downregulation with continuous use 11. Drugs that are receptor antagonists, such as beta blockers, may cause: An exaggerated response if abruptly discontinued 12. Factors that affect gastric drug absorption include: Lipid solubility of the drug 13. Drugs administered via IV: Begin distribution into the body immediately 14. When a medication is added to a regimen for a synergistic effect, the combined effect of the drugs is: Greater than the sum of the effects of each drug individually 15. Which of the following statements about bioavailability is true? Bioavailability issues are especially important for drugs with narrow therapeutic ranges or sustained-release mechanisms. 16. Which of the following statements about the major distribution barriers (blood-brain or fetal- placental) is true? The blood-brain barrier slows the entry of many drugs into and from brain cells. 17.Drugs are metabolized mainly by the liver via phase I or phase II reactions. The purpose of both of these types of reactions is to: Change drug molecules to a form that an excretory organ can excrete 18. Once they have been metabolized by the liver, the metabolites may be: More active than the parent drug Less active than the parent drug Totally “deactivated” so they are excreted without any effect 19. All drugs continue to act in the body until they are changed or excreted. The ability of the body to excrete drugs via the renal system would be increased by: Unbinding a nonvolatile drug from plasma proteins 20. Steady state is: When the amount of drug in the body remains constant 21. Two different pain medications are given together for pain relief. The drug—drug interaction Additive 22. Actions taken to reduce drug—drug interaction problems include all of the following EXCEPT: Prescribing a third drug to counteract the adverse reaction of the combination 23. Phase I oxidative-reductive processes of drug metabolism require certain nutritional elements. Which of the following would reduce or inhibit this process? Neither Protein malnutrition OR Iron-deficiency anemia 24. The time required for the amount of drug in the body to decrease by 50% is called: Half-life 25. An agonist activates a receptor and stimulates a response. When given frequently over time, the body may: Downregulate the numbers of that specific receptor 26. Drug antagonism is best defined as an effect of a drug that: Is modified by the concurrent administration of another drug 27. Instructions to a client regarding self-administration of oral enteric-coated tablets should include which of the following statements? “To achieve best effect, take the tablet with at least 8 ounces of fluid.” 28. The major reason for not crushing a sustained-release capsule is that, if crushed, the coated beads of the drugs could possibly result in: Toxicity 29. Which of the following substances is the most likely to be absorbed in the intestines rather than in the stomach? Sodium bicarbonate 30. Which of the following variables is a factor in drug absorption? A rich blood supply to the area of absorption leads to better absorption 31. An advantage of prescribing a sublingual medication is that the medication is: Absorbed rapidly 32. Drugs that use CYP 3A4 isoenzymes for metabolism may: Induce and inhibit the metabolism of another drug 33. Therapeutic drug levels are drawn when a drug reaches steady state. Drugs reach steady state: After four to five half-lives 34. Upregulation or hypersensitization may lead to: An exaggerated response if the drug is withdrawn Chapter 7. Cultural and Ethnic Influences in Pharmacotherapeutics 1. Cultural factors that must be taken into account when prescribing include(s): Who the decision maker is in the family regarding health-care decisions Attitudes regarding the use of drugs to treat illness The patient’s view of health and illness 2. Ethnic differences have been found in drug: Hepatic metabolism 3. The National Standards of Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services are required to be implemented in all: Organizations that receive federal funds 4. According to the National Standards of Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services, an interpreter for health care: Must be a professionally trained medical interpreter 5. According to the U.S. Office of Minority Health, poor health outcomes among African Americans are attributed to: Discrimination, cultural barriers, and lack of access to health care 6. The racial difference in drug pharmacokinetics seen in American Indian or Alaskan Natives are: Largely unknown due to lack of studies of this population 7. Pharmacokinetics among Asians are universal to all the Asian ethnic groups. False 8. Alterations in drug metabolism among Asians may lead to: Slower metabolism of antidepressants, requiring lower doses 9.Asians from Eastern Asia are known to be fast acetylators. Fast acetylators: Require higher doses of drugs metabolized by acetylization to achieve efficacy 10. Hispanic native healers (curanderas): Use herbs and teas in their treatment of illness Chapter 8. An Introduction to Pharmacogenomics 1. Genetic polymorphisms account for differences in metabolism, including: Poor metabolizers, who lack a working enzyme Intermediate metabolizers, who have one working, wild-type allele and one mutant allele Extensive metabolizers, with two normally functioning alleles 2. Up to 21% of Asians are ultra-rapid 2D6 metabolizers, leading to: Increased dosages needed of drugs metabolized by 2D6, such as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors 3. Rifampin is a nonspecific CYP450 inducer that may: Induce the metabolism of drugs, such as oral contraceptives, leading to therapeutic failure 4. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein by a drug such as quinidine may lead to: Increased levels of a coadministered drug, such as digoxin, that requires P-glycoprotein for absorption and elimination 5. Warfarin resistance may be seen in patients with VCORC1 mutation, leading to: Decreased response to warfarin 6. Genetic testing for VCORC1 mutation to assess potential warfarin resistance is required prior to prescribing warfarin. False 7. Pharmacogenetic testing is required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration prior to prescribing: Cetuximab 8. Carbamazepine has a Black Box Warning recommending testing for the HLA-B*1502 allele in patients with Asian ancestry prior to starting therapy due to: Increased risk for Stevens-Johnson syndrome in Asian patients with HLA-B*1502 allele 9. A genetic variation in how the metabolite of the cancer drug irinotecan SN-38 is inactivated by the body may lead to: Increased adverse drug reactions, such as neutropenia 10. Patients who have a poor metabolism phenotype will have: Slowed metabolism of a prodrug into an active drug, leading to accumulation of prodrug 11. Ultra-rapid metabolizers of drugs may have: Active drug rapidly metabolized into inactive metabolites, leading to potential therapeutic failure 12. A provider may consider testing for CYP2D6 variants prior to starting tamoxifen for breast cancer to: Reduce the likelihood of therapeutic failure with tamoxifen treatment Chapter 1. The Role of the Nurse Practitioner 1. Nurse practitioner prescriptive authority is regulated by: The State Board of Nursing for each state 2. The benefits to the patient of having an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) prescriber include: Nurses care for the patient from a holistic approach and include the patient in decision making regarding their care 3. Clinical judgment in prescribing includes: Factoring in the cost to the patient of the medication prescribed 4. Criteria for choosing an effective drug for a disorder include: Consulting nationally recognized guidelines for disease management 5. Nurse practitioner practice may thrive under health-care reform because of: The demonstrated ability of nurse practitioners to control costs and Improve patient outcomes Chapter 4. Legal and Professional Issues in Prescribing 1. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulates: The official labeling for all prescription and over-the-counter drugs 2. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval is required for: Medical devices, including artificial joints 3. An Investigational New Drug is filed with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Prior to human testing of any new drug entity 4. Phase IV clinical trials in the United States are also known as: Postmarketing research 5. Off-label prescribing is: Legal if there is scientific evidence for the use 6. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration: Registers manufacturers and prescribers of controlled substances 7. Drugs that are designated Schedule II by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration: May not be refilled; a new prescription must be written 8. Precautions that should be taken when prescribing controlled substances include: Using tamper-proof paper for all prescriptions written for controlled drugs 9. Strategies prescribers can use to prevent misuse of controlled prescription drugs include: Use of chemical dependency screening tools Firm limit-setting regarding prescribing controlled substances Practicing “just say no” to deal with patients who are pushing the provider to prescribe controlled substances 10. Behaviors predictive of addiction to controlled substances include: Stealing or borrowing another patient’s drugs 11. Medication agreements or “Pain Medication Contracts” are recommended to be used: Universally for all prescribing for chronic pain 12. A prescription needs to be written for: Legend drugs Most controlled drugs Medical devices Chapter 13. Over-the-Counter Medications 1. Michael asks you about why some drugs are over-the-counter and some are prescription. You explain that in order for a drug to be approved for over-the-counter use the drug must: Be safe and labeled for appropriate use Have a low potential for abuse or misuse Be taken for a condition the patient can reliably self-diagnose 2. In the United States, over-the-counter drugs are regulated by: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research 3. As drugs near the end of their patent, pharmaceutical companies may apply for the drug to change to over-the-counter status in order to: Continue to make large profits from their blockbuster brand-name drug 4. New over-the-counter drug ingredients must undergo the U.S. Food and Drug Administration New Drug Application process, just as prescription drugs do. True 5. The ailment that generates the greatest over-the-counter annual drug sales is: Cough and colds 6. Common over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen: Are harmful if taken in higher than recommended amounts 7. When obtaining a drug history from Harold, he gives you a complete list of his prescription medications. He denies taking any other drugs, but you find that he occasionally takes aspirin for his arthritis flare ups. This is an example of: A common misconception that intermittently taken over-the counter medications are not an important part of his drug history 8. The Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act, which is part of the 2006 U.S. Patriot Act: Restricts the sales of drugs that contain methamphetamine precursors, including a daily and 30-day limit on sales 9. When prescribing a tetracycline or quinolone antibiotic it is critical to instruct the patient: Not to take antacids while on these medications, as the antacid decreases absorption Chapter 25. Drugs Used in Treating Inflammatory Processes 1. Henry presents to clinic with a significantly swollen, painful great toe and is diagnosed with gout. Of the following, which would be the best treatment for Henry? Low-dose colchicine 2. Patient education when prescribing colchicine includes: Colchicine always causes some degree of diarrhea. 3. Larry is taking allopurinol to prevent gout. Monitoring of a patient who is taking allopurinol includes: BUN, creatinine, and creatinine clearance 4. Phil is starting treatment with febuxostat (Uloric). Education of patients starting febuxostat includes: Gout may worsen with therapy. 5. Sallie has been taking 10 mg per day of prednisone for the past 6 months. She should be assessed for: Osteoporosis 6. Patients whose total dose of prednisone will exceed 1 gram will most likely need a second prescription for: Omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor to prevent peptic ulcer disease 7. Daniel has been on 60 mg of prednisone for 10 days to treat a severe asthma exacerbation. It is time to discontinue the prednisone. How is prednisone discontinued? Develop a tapering schedule to slowly wean Daniel off the prednisone. 8. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis who are on chronic low-dose prednisone will need co- treatment with which medications to prevent further adverse effects? A bisphosphonate Calcium supplementation Vitamin D 9. Patients who are on or who will be starting chronic corticosteroid therapy need monitoring of: Serum glucose 10. Patients who are on chronic long-term corticosteroid therapy need education regarding: Reporting black tarry stools or abdominal pain 11. All nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) have an FDA Black Box Warning regarding: Potential for causing life-threatening GI bleeds 12. Jamie has fractured his ankle and has received a prescription for acetaminophen and hydrocodone (Vicodin). Education when prescribing Vicodin includes: He should not take any other acetaminophen-containing medications 13. When prescribing NSAIDS, a complete drug history should be conducted as NSAIDs interact with these drugs: Warfarin, an anticoagulant 14. Josefina is a 2-year-old child with acute otitis media and an upper respiratory infection. Along with an antibiotic she receives a recommendation to treat the ear pain with ibuprofen. What education would her parent need regarding ibuprofen? Josefina needs to be well-hydrated while taking ibuprofen. 15. Henry is 82 years old and takes two aspirin every morning to treat the arthritis pain in his back. He states the aspirin helps him to “get going” each day. Lately he has had some heartburn from the aspirin. After ruling out an acute GI bleed, what would be an appropriate course of treatment for Henry? Add an H2 blocker such as ranitidine to his therapy. 16. The trial period to determine effective anti-inflammatory activity when starting a patient on aspirin for rheumatoid arthritis is: 4 to 6 days 17. Patients prescribed aspirin therapy require education regarding the signs of aspirin toxicity. An early sign of aspirin toxicity is: Tinnitus 18. Monitoring a patient on a high-dose aspirin level includes: Salicylate level Complete blood count Urine pH 19. Patients who are on long-term aspirin therapy should have annually. Complete blood count Chapter 52. Pain Management: Acute and Chronic Pain 1. Different areas of the brain are involved in specific aspects of pain. The reticular and limbic systems in the brain influence the: Motivational aspects of pain 2. Patients need to be questioned about all pain sites because: Patients tend to report the most severe or important in their perception. 3. The chemicals that promote the spread of pain locally include: Neurokinin A 4. Narcotics are exogenous opiates. They act by: Attaching to receptors in the afferent neuron to inhibit the release of substance P 5. Age is a factor in different responses to pain. Which of the following age-related statements about pain is NOT true? Preterm and newborn infants do not yet have functional pain pathways. 6. Which of the following statements is true about acute pain? Referred pain is present in a distant site for the pain source and is based on activation of the same spinal segment as the actual pain site. 7. One of the main drug classes used to treat acute pain is NSAIDs. They are used because: Inflammation is a common cause of acute pain. 8. Opiates are used mainly to treat moderate to severe pain. Which of the following is NOT true about these drugs? Opiates stimulate only mu receptors for the control of pain. 9. If interventions to resolve the cause of pain (e.g., rest, ice, compression, and elevation) are insufficient, pain medications are given based on the severity of pain. Drugs are given in which order of use? Non-opiate, increased dose of non-opiate, opiate 10. The goal of treatment of acute pain is: Reduction or elimination of pain with minimum adverse reactions 11. Which of the following statements is true about age and pain? Acetaminophen is especially useful in both children and adults because it has no effect on platelets and has fewer adverse effects than NSAIDs. 12. Pain assessment to determine adequacy of pain management is important for all patients. This assessment is done to: Determine if the diagnosis of source of pain is correct Determine if the current regimen is adequate or different combinations of drugs and non- drug therapy are required Determine if the patient is willing and able to be an active participant in his or her pain management 13. Pathological similarities and differences between acute pain and chronic pain include: Chronic pain has a predominance of C-neuron stimulation. 14. A treatment plan for management of chronic pain should include: Negotiation with the patient to set personal goals for pain management Discussion of ways to improve sleep and stress An exercise program to improve function and fitness 15. Chronic pain is a complex problem. Some specific strategies to deal with it include: Scheduling return visits on a regular basis rather than waiting for poor pain control to drive the need for an appointment 16. Chemical dependency assessment is integral to the initial assessment of chronic pain. Which of the following raises a “red flag” about potential chemical dependency? Multiple times when prescriptions are lost with requests to refill 17. The Pain Management Contract is appropriate for: Patients with chronic pain who will require long-term use of opiates Chapter 14. Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System 1. Charlie is a 65-year-old male who has been diagnosed with hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Doxazosin has been chosen to treat his hypertension because it: Relaxes smooth muscle in the bladder neck 2. To reduce potential adverse effects, patients taking a peripherally acting alpha1 antagonist should do all of the following EXCEPT: Monitor their blood pressure and skip a dose if the pressure is less than 120/80. Patients should Take the dose at bedtime, Sit up slowly and dangle their feet before standing, & Weigh daily and report weight gain of greater than 2 pounds in one day 3. John has clonidine, a centrally acting adrenergic blocker, prescribed for his hypertension. He should Not miss a dose or stop taking the drug because of potential rebound hypertension 4. Clonidine has several off-label uses, including: Alcohol and nicotine withdrawal Post-herpetic neuralgia 5. Jim is being treated for hypertension. Because he has a history of heart attack, the drug chosen is atenolol. Beta blockers treat hypertension by: Reducing vascular smooth muscle tone 6. Which of the following adverse effects are less likely in a beta1-selective blocker? Impaired insulin release 7. Richard is 70 years old and has a history of cardiac dysrhythmias. He has been prescribed nadolol. You do his annual laboratory work and find a CrCl of 25 ml/min. What action should you take related to his nadolol? Extend the dosage interval. 8. Beta blockers are the drugs of choice for exertional angina because they: Decrease myocardial oxygen demand by decreasing heart rate and vascular resistance 9. Adherence to beta blocker therapy may be affected by their: Effects on the male genitalia, which may produce impotence 10. Beta blockers have favorable effects on survival and disease progression in heart failure. Treatment should be initiated when the: Left ventricular dysfunction is diagnosed 11. Abrupt withdrawal of beta blockers can be life threatening. Patients at highest risk for serious consequences of rapid withdrawal are those with: Angina Coronary artery disease 12. To prevent life-threatening events from rapid withdrawal of a beta blocker: The dosage should be decreased by one-half every 4 days. 13. Beta blockers are prescribed for diabetics with caution because of their ability to produce hypoglycemia and block the common symptoms of it. Which of the following symptoms of hypoglycemia is not blocked by these drugs and so can be used to warn diabetics of possible decreased blood glucose? Diaphoresis 14. Combined alpha-beta antagonists are used to reduce the progression of heart failure because they: Vasodilate the peripheral vasculature 15. Carvedilol is heavily metabolized by CYP2D6 and 2C9, resulting in drug interactions with which of the following drug classes? Histamine 2 blockers Quinolones Serotonin re-uptake inhibitors 16. Alpha-beta blockers are especially effective to treat hypertension for which ethnic group? African American 17. Bethanechol: Increases detrusor muscle tone to empty the bladder 18. Clinical dosing of Bethanechol: Starts at 5 mg to 10 mg PO and is repeated every hour until a satisfactory clinical response is achieved 19. Patients who need to remain alert are taught to avoid which drug due to its antimuscarinic effects? Diphenhydramine 20. Anticholinesterase inhibitors are used to treat: Myasthenia gravis 21. Which of the following drugs used to treat Alzheimer’s disease is not an anticholinergic? Memantine 22. Taking which drug with food maximizes it bioavailability? Rivastigmine 23. Which of the following drugs should be used only when clearly needed in pregnant and breastfeeding women? Pyridostigmine 24. There is a narrow margin between first appearance of adverse reaction to AChE inhibitors and serious toxic effects. Adverse reactions that require immediate action include: Fasciculations of voluntary muscles 25. Adherence is improved when a drug can be given once daily. Which of the following drugs can be given once daily? Donepezil 26. Nicotine has a variety of effects on nicotinic receptors throughout the body. Which of the following is NOT an effect of nicotine? Vasodilation and decreased heart rate Effects of nicotine include: Increased secretion of gastric acid and motility of the GI smooth muscle, Release of dopamine at the pleasure center & Stimulation of the locus coeruleus 27. Nicotine gum products are: Bound to exchange resins so the nicotine is only released during chewing 28. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT): Delays healing of esophagitis and peptic ulcers 29. Success rates for smoking cessation using NRT: Vary from 40% to 50% at 12 months 30. Cholinergic blockers are used to: Counteract the extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) effects of phenothiazines Control tremors and relax smooth muscle in Parkinson’s disease Inhibit the muscarinic action of ACh on bladder muscle 31. Several classes of drugs have interactions with cholinergic blockers. Which of the following is true about these interactions? Drugs with a narrow therapeutic range given orally may not stay in the GI tract long enough to produce an action. 32. Scopolamine can be used to prevent the nausea and vomiting associated with motion sickness. The patient is taught to: Swallow the tablet 1 hour before traveling where motion sickness is possible 33. You are managing the care of a patient recently diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). He is taking tamsulosin but reports dizziness when standing abruptly. The best option for this patient is: Discontinue the tamsulosin and start doxazosin. 34. You are treating a patient with a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The patient’s wife mentions difficulty with transportation to the clinic. Which medication is the best choice? Donepezil 35. A patient presents with a complaint of dark stools and epigastric pain described as gnawing and burning. Which of the medications is the most likely cause? Bethanechol 36. Your patient calls for an appointment before going on vacation. Which medication should you ensure he has an adequate supply of before leaving to avoid life-threatening complications? Carvedilol 37. Activation of central alpha2 receptors results in inhibition of cardioacceleration and centers in the brain. Vasoconstriction Chapter 15. Drugs Affecting the Central Nervous System 1. Sarah, a 42-year-old female, requests a prescription for an anorexiant to treat her obesity. A trial of phentermine is prescribed. Prescribing precautions include: Anorexiants may cause tolerance and should only be prescribed for 6 months 2. Before prescribing phentermine to Sarah, a thorough drug history should be taken including assessing for the use of serotonergic agents such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and St John’s wort due to: The risk of serotonin syndrome 3. Antonia is a 3-year-old child who has a history of status epilepticus. Along with her routine antiseizure medication, she should also have a home prescription for to be used for an episode of status epilepticus. Rectal diazepam (Diastat) 4. Rabi is being prescribed phenytoin for seizures. Monitoring includes assessing: For phenytoin hypersensitivity syndrome 3 to 8 weeks after starting treatment 5. Dwayne has recently started on carbamazepine to treat seizures. He comes to see you and you note that while his carbamazepine levels had been in the therapeutic range, they are now low. The possible cause for the low carbamazepine levels include: Carbamazepine auto-induces metabolism, leading to lower levels in spite of good compliance. 6. Carbamazepine has a Black Box Warning due to life-threatening: Dermatologic reaction, including Steven’s Johnson and toxic epidermal necrolysis 7. Long-term monitoring of patients who are taking carbamazepine includes: Complete blood count every 3 to 4 months 8. Six-year-old Lucy has recently been started on ethosuximide (Zarontin) for seizures. She should be monitored for: Blood dyscrasias, which are uncommon but possible 9. Sook has been prescribed gabapentin to treat neuropathic pain and is complaining of feeling depressed and having “strange” thoughts. The appropriate initial action would be: Assess for suicidal ideation 10. Selma, who is overweight, recently started taking topiramate for seizures and at her follow- up visit you note she has lost 3 kg. The appropriate action would be: Reassure her that this is a normal side effect of topiramate and continue to monitor her weight. 11. Monitoring of a patient on gabapentin to treat seizures includes: Recording seizure frequency, duration, and severity 12. Scott’s seizures are well controlled on topiramate and he wants to start playing baseball. Education for Scott regarding his topiramate includes: He should monitor his temperature and ability to sweat in the heat while playing 13. Cara is taking levetiracetam (Keppra) to treat seizures. Routine education for levetiracetam includes reminding her: To wear sunscreen due to photosensitivity from levetiracetam 14. Levetiracetam has known drug interactions with: Few, if any, drugs 15. Zainab is taking lamotrigine (Lamictal) and presents to the clinic with fever and lymphadenopathy. Initial evaluation and treatment includes: Ruling out a hypersensitivity reaction that may lead to multi-organ failure 16. Samantha is taking lamotrigine (Lamictal) for her seizures and requests a prescription for combined oral contraceptives (COCs), which interact with lamotrigine and may cause: Reduced lamotrigine levels, requiring doubling the dose of lamotrigine 17. The tricyclic antidepressants should be prescribed cautiously in patients with: Heart disease 18. A 66-year-old male was prescribed phenelzine (Nardil) while in an acute psychiatric unit for recalcitrant depression. The NP managing his primary health care needs to understand the following regarding phenelzine and other monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): He should not be prescribed any serotonergic drug such as sumatriptan (Imitrex) MAOIs interact with many common foods, including yogurt, sour cream, and soy sauce Symptoms of hypertensive crisis (headache, tachycardia, sweating) require immediate treatment 19. Taylor is a 10-year-old child diagnosed with major depression. The appropriate first-line antidepressant for children is: Fluoxetine 20. Suzanne is started on paroxetine (Paxil), a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), for depression. Education regarding her antidepressant includes: SSRIs may take 2 to 6 weeks before she will have maximum drug effects 21. Cecilia presents with depression associated with complaints of fatigue, sleeping all the time, and lack of motivation. An appropriate initial antidepressant for her would be: Duloxetine (Cymbalta) 22. Jake, a 45-year-old patient with schizophrenia, was recently hospitalized for acute psychosis due to medication noncompliance. He was treated with IM long-acting haloperidol. Besides monitoring his schizophrenia symptoms, the patient should be assessed by his primary care provider: With the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) for extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) 23. Anticholinergic agents, such as benztropine (Cogentin), may be given with a phenothiazine to: Potentiate the effects of the drug 24. Patients who are prescribed olanzapine (Zyprexa) should be monitored for: Insomnia 25. A 19-year-old male was started on risperidone. Monitoring for risperidone includes observing for common side effects, including: Bradykinesia, akathisia, and agitation 26. In choosing a benzodiazepam to treat anxiety the prescriber needs to be aware of the possibility of dependence. The benzodiazepam with the greatest likelihood of rapidly developing dependence is: Alprazolam (Xanax) 27. A patient with anxiety and depression may respond to: Buspirone (Buspar) and an SSRI combined 28. When prescribing temazepam (Restoril) for insomnia, patient education includes: Temazepam should not be used more than three times a week for less than 3 months. 29. Patients should be instructed regarding the rapid onset of zolpidem (Ambien) because: Zolpidem should be taken just before going to bed. 30. One major drug used to treat bipolar disease is lithium. Because lithium has a narrow therapeutic range, it is important to recognize symptoms of toxicity, such as: Drowsiness and nausea 31. Tom is taking lithium for bipolar disorder. He should be taught to: Eat a diet with consistent levels of salt (sodium) 32. Cynthia is taking valproate (Depakote) for seizures and would like to get pregnant. What advice would you give her? Valproate is a known teratogen but may be taken after the first trimester if necessary. 33.When prescribing an opioid analgesic such as acetaminophen and codeine (Tylenol #3), instructions to the patient should include: The medication may cause sedation and they should not drive. Constipation is a common side effect and they should increase fluids and fiber Patients should not take any other acetaminophen-containing medications at the same time. 34. Kirk sprained his ankle and is asking for pain medication for his mild-to-moderate pain. The appropriate first-line medication would be: Ibuprofen (Advil) 35. Kasey fractured his ankle in two places and is asking for medication for his pain. The appropriate first-line medication would be: Acetaminophen with hydrocodone (Vicodin) 36. Jack, age 8, has attention deficit disorder (ADD) and is prescribed methylphenidate (Ritalin). He and his parents should be educated about the side effects of methylphenidate, which are: Insomnia and decreased appetite 37. Monitoring for a child on methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) includes: ADHD symptoms Routine height and weight checks Amount of methylphenidate being used 38. When prescribing Adderall (amphetamine and dextroamphetamine) to adults with ADHD the nurse practitioner will need to monitor: Blood pressure Chapter 29. Anxiety and Depression 1. Common mistakes practitioners make in treating anxiety disorders include: Thinking a partial response to medication is acceptable 2. An appropriate first-line drug to try for mild to moderate generalized anxiety disorder would be: Buspirone (Buspar) 3. An appropriate drug to initially treat panic disorder is: Diazepam (Valium) 4. Prior to starting antidepressants, patients should have laboratory testing to rule out: Hypothyroidism 5. David is a 34-year-old patient who is starting on paroxetine (Paxil) for depression. David’s education regarding his medication would include: He may experience sexual dysfunction beginning a month after he starts therapy 6. Jamison has been prescribed citalopram (Celexa) to treat his depression. Education regarding how quickly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants work would be: Appetite and concentration improve in the first 1 to 2 weeks. 7. An appropriate drug for the treatment of depression with anxiety would be: Escitalopram (Lexapro) 8. An appropriate first-line drug for the treatment of depression with fatigue and low energy would be: Venlafaxine (Effexor) 9. The laboratory monitoring required when a patient is on a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor is: There is no laboratory monitoring required 10. Jaycee has been on escitalopram (Lexapro) for a year and is willing to try tapering off of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. What is the initial dosage adjustment when starting a taper off antidepressants? Reduce dose by 50% for 3 to 4 days 11. The longer-term Xanax patient comes in and states they need a higher dose of the medication. They deny any additional, new, or accelerating triggers of their anxiety. What is the probable reason? They have become tolerant of the medication, which is characterized by the need for higher and higher doses. 12. What “onset of action” symptoms should be reviewed with patients who have been newly prescribed a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor? They can feel a bit of nausea, but this resolves in a week. 13. Which of the following should not be taken with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor? Alcohol 14. Why is the consistency of taking paroxetine (Paxil) and never running out of medication more important than with most other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)? It has a shorter half-life and withdrawal syndrome has a faster onset without taper. 15. The patient shares with the provider that he is taking his Prozac at night before going to bed. What is the best response? Have you noticed that you are having more sleep issues since you started that? Chapter 35. Headaches 1. Paige has a history of chronic migraines and would benefit from preventative medication. Education regarding migraine preventive medication includes: The goal of treatment is to reduce migraine occurrence by 50%. 2. A first-line drug for abortive therapy in simple migraine is: Naproxen (Aleve) 3. Vicky, age 56 years, comes to the clinic requesting a refill of her Fiorinal (aspirin and butalbital) that she takes for migraines. She has been taking this medication for over 2 years for migraines and states one dose usually works to abort her migraine. What is the best care for her? Assess how often she is using Fiorinal and refill her medication. 4. When prescribing ergotamine suppositories (Wigraine) to treat acute migraine, patient education would include: They may need premedication with an antinausea medication. 5. Migraines in pregnancy may be safely treated with: Acetaminophen with codeine (Tylenol #3) 6. Xi, a 54-year-old female, has a history of migraines that do not respond well to OTC migraine medication. She is asking to try Maxalt (rizatriptan) because it works well for her friend. Appropriate decision making would be: Prescribe Maxalt and arrange to have her observed in the clinic or urgent care with the first dose. 7. Kelly is a 14-year-old patient who presents to the clinic with a classic migraine. She says she is having a headache two to three times a month. The initial plan would be: Prescribe NSAIDs as abortive therapy and have her keep a headache diary to identify her triggers 8. Jayla is a 9-year-old patient who has been diagnosed with migraines for almost 2 years. She is missing up to a week of school each month. Her headache diary confirms she averages four or five migraines per month. Which of the following would be appropriate? Prescribe propranolol (Inderal) to be taken daily for at least 3 months. 9. Amber is a 24-year-old patient who has had migraines for 10 years. She reports a migraine on average of once a month. The migraines are effectively aborted with naratriptan (Amerge). When refilling Amber’s naratriptan, education would include: Naratriptan will interact with antidepressants, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and St John’s wort, and she should inform any providers she sees that she has migraines. Continue to monitor her headaches, if the migraine is consistently happening around her menses there is preventive therapy available. Pregnancy is contraindicated when taking a triptan 10. When prescribing for migraines, patient education includes: Stress reduction and regular sleep are integral to migraine treatment. 11. Juanita presents to the clinic with a complaint of headaches off and on for months. She reports they feel like someone is “squeezing” her head. She occasionally takes Tylenol for the pain, but usually just “toughs it out.” Initial treatment for tension headache includes asking her to keep a headache diary and a prescription for: Naproxen (Aleve) 12. Nonpharmacologic therapy for tension headaches includes: Biofeedback Stress management Massage therapy 13. James has been diagnosed with cluster headaches. Appropriate acute therapy would be: Oxygen 100% for 15 to 30 minutes 14. Preventative therapy for cluster headaches includes: Ergotamine nightly before bed 15. When prescribing any headache therapy, appropriate use of medications needs to be discussed to prevent medication-overuse headaches. A clinical characteristic of medication-overuse headaches is that they: Recur when medication wears off [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 28, 2022
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 28, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
62













.png)