Chapter 9: End-of-Life Care Test Bank,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
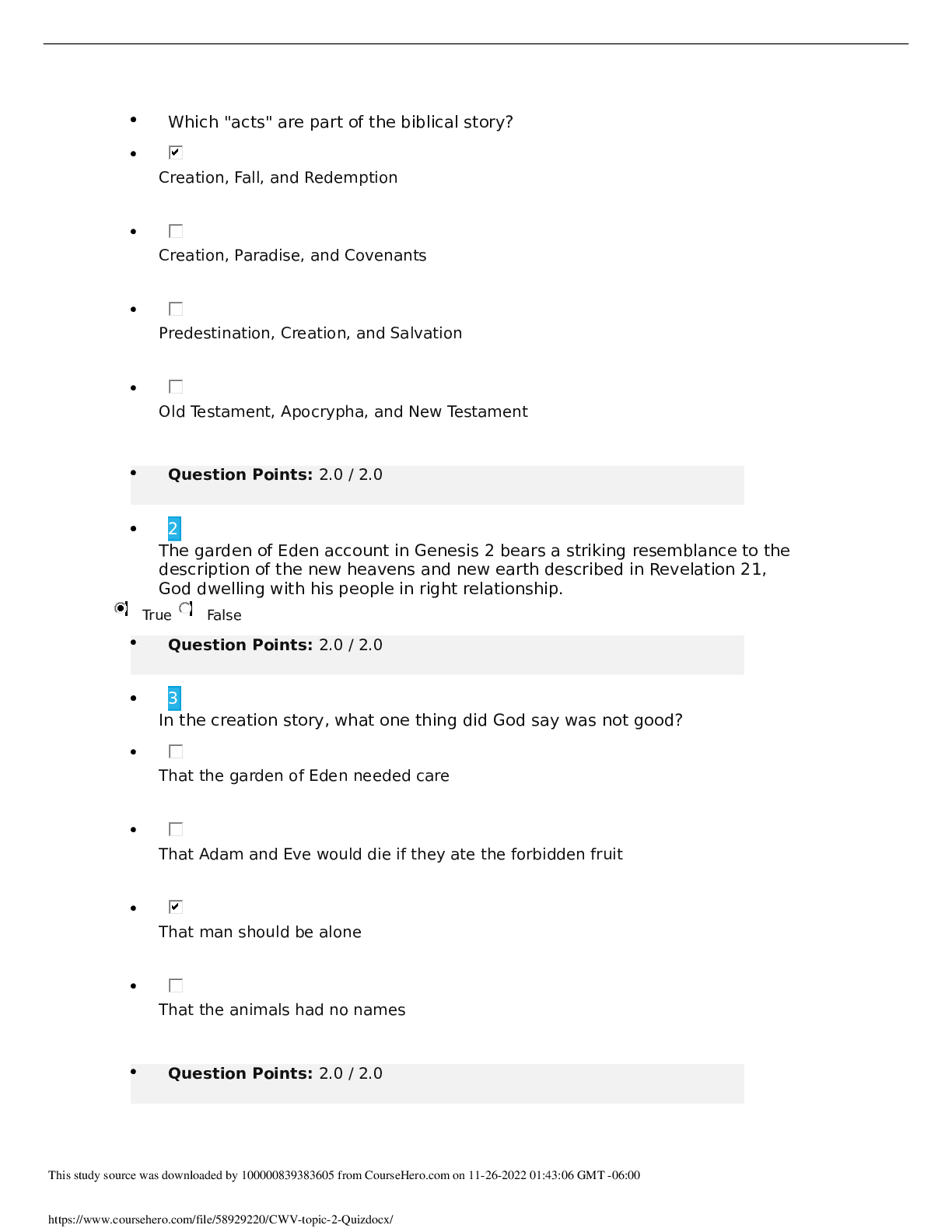
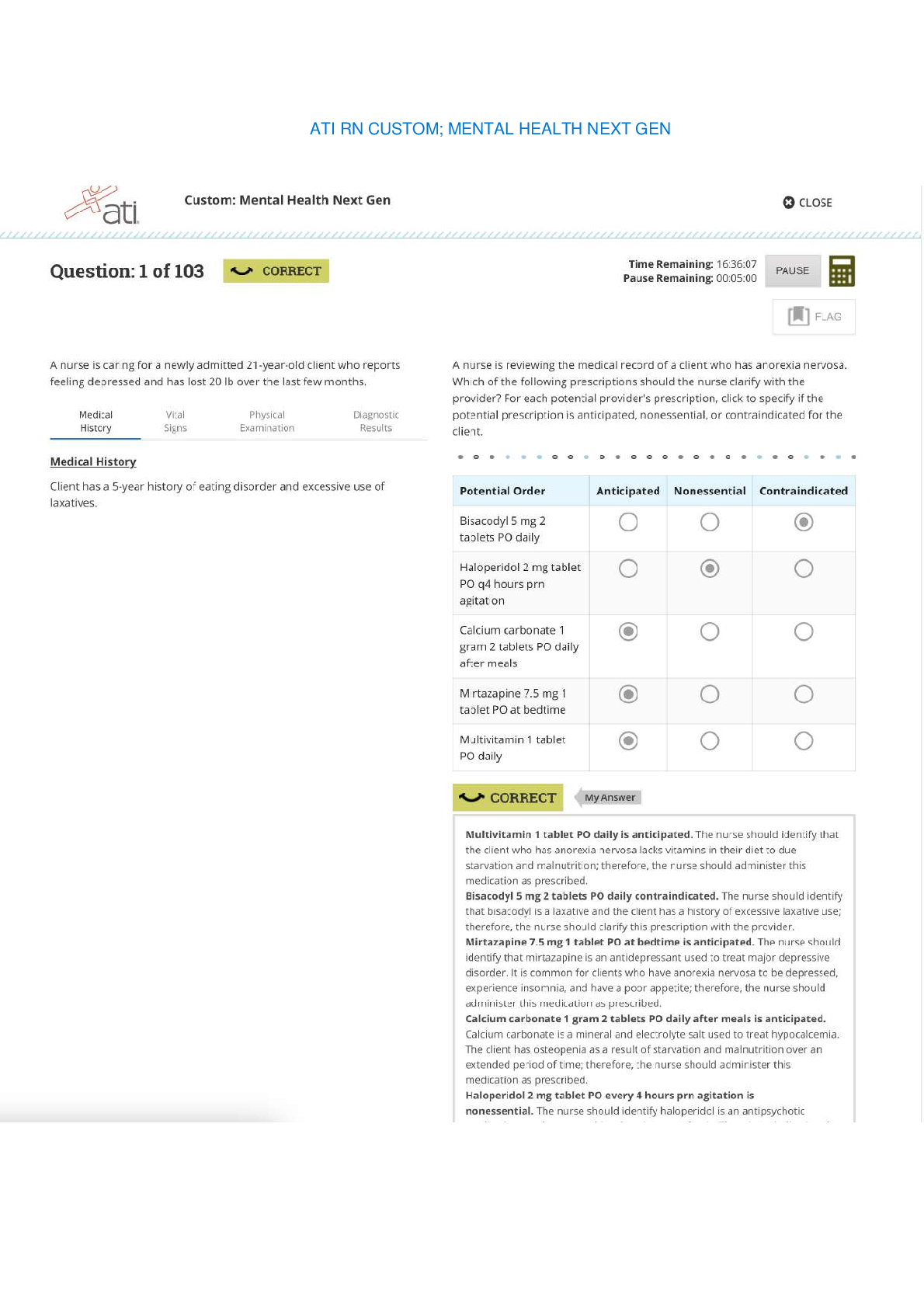
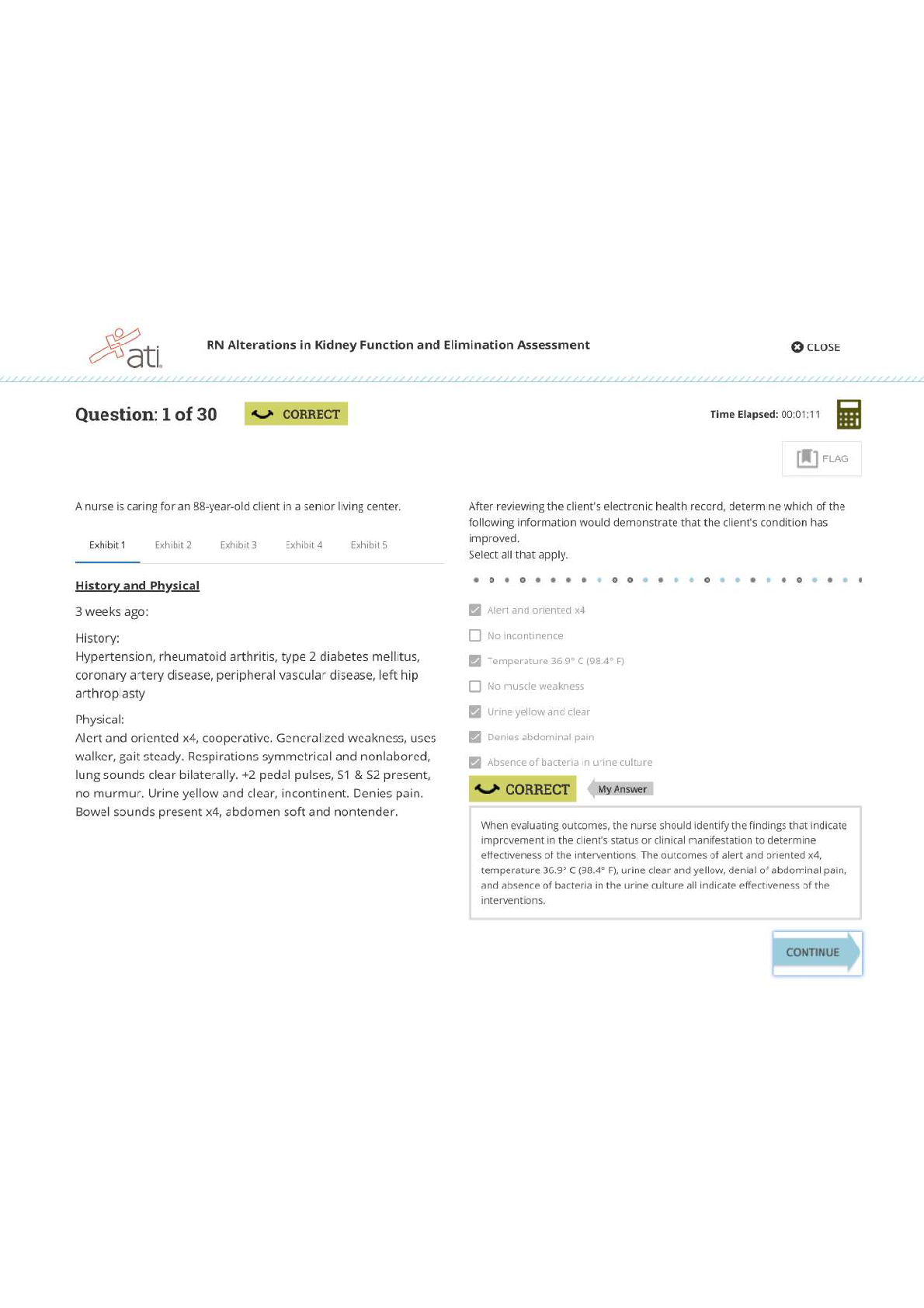
Chapter 9: End-of-Life Care Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The client tells the nurse that even though it has been 4 months since her sister’s death, she frequently finds herself crying uncont... rollably. The client is afraid that she is “losing her mind.” What is the nurse’s best response? a. “Most people move on within a few months. You should see a grief counselor.” b. “Whenever you start to cry, distract yourself from thoughts of your sister.” c. “You should try not to cry. I’m sure your sister is in a better place now.” d. “Your feelings are completely normal and may continue for a long time.” ANS: D Frequent crying is not an abnormal response. The nurse should let the client know that this is normal and okay. Although the client may benefit from talking with a grief counselor, it is not unusual for her to still be grieving after a few months. The other responses are not as therapeutic because they justify or minimize the client’s response. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (Therapeutic Communication) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 2. The nurse is discussing advance directives with a client. Which statement by the client indicates good understanding of the purpose of an advance directive? a. “An advance directive will keep my children from selling my home when I’m old.” b. “An advance directive will be completed as soon as I’m incapacitated and can’t think for myself.” c. “An advance directive will specify what I want done when I can no longer make decisions about health care.” d. “An advance directive will allow me to keep my money out of the reach of my family.” ANS: C An advance directive is a written document prepared by a competent individual that specifies what, if any, extraordinary actions a person would want taken when he or she can no longer make decisions about personal health care. It does not address issues such as the client’s residence in his or her own home. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding REF: p. 108 TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Management of Care—Advance Directives) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment) 3. The nurse is caring for a client who is considering being admitted to hospice. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “Hospice admission has specific criteria. You may not be a viable candidate, so we will look at alternative plans for your discharge.” b. “Hospice care focuses on a holistic approach to health care. It is designed not to hasten death, but rather to relieve symptoms.” c. “Hospice care will not help with your symptoms of depression. I will refer you to the facility’s counseling services instead.” d. “You seem to be experiencing some difficulty with this stage of the grieving process. Let’s talk about your feelings.” ANS: B As both a philosophy and a system of care, hospice care uses an interdisciplinary approach to assess and address the holistic needs of clients and families to facilitate quality of life and a peaceful death. This holistic approach neither hastens nor postpones death but provides relief of symptoms experienced by the dying client. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding REF: p. 108 TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 4. A hospitalized American Indian client is approaching death. Family members who are standing vigil in the client’s room begin to divide up his possessions among themselves as his symptoms progress. What is the nurse’s most important intervention? a. Ask the family members to step outside the room so the client cannot hear them. b. Tell the family that they are being insensitive and their behavior is inappropriate. c. Recognize that this is a culturally appropriate activity and document it in the chart. d. Report these activities to the client’s physician and the nursing supervisor. ANS: C American Indians often disperse material possessions before or after death to friends and family members. Recognizing this culturally appropriate activity would not be consistent with removing the family, stopping the activity, or reporting the client’s family’s behaviors. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (Cultural Diversity) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 5. The spouse of a dying client states that she is concerned that her husband is choking to death. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “Do not worry. The choking sound is normal during the dying process.” b. “I will administer more morphine to keep your husband comfortable.” c. “I can ask the respiratory therapist to suction secretions out through his nose.” d. “I will have another nurse assist me to turn your husband on his side.” ANS: D The choking sound or “death rattle” is common in dying clients. The nurse should acknowledge the spouse’s concerns and provide interventions that will reduce the choking sounds. Repositioning the client onto one side with a towel under the mouth to collect secretions is the best intervention. Morphine will assist with comfort but will not decrease the choking sounds. Nasal tracheal suctioning is not appropriate in a dying client. The nurse should not minimize the spouse’s concerns. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 6. The terminally ill client is prescribed morphine to help cope with increasing discomfort. A family member expresses concern that the client is on “too much morphine.” What is the nurse’s best response? a. “What has the physician told you about your family member’s illness?” b. “Don’t worry about that. We’re following the physician’s plan of care.” c. “Tell me more about what you mean by too much morphine.” d. “You should talk with your physician about this when he makes rounds.” ANS: C Asking family members to explain what they mean by “too much morphine” serves to gain more information for the nurse. The other questions will not help the nurse obtain more information about the client’s care or the family’s concerns. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (Therapeutic Communication) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring and Communication 7. The nurse is teaching a family member about various types of complementary therapies that might be effective for relieving the dying client’s anxiety and restlessness. Which statement by the family member indicates understanding of the nurse’s teaching? a. “Maybe we should just hire a round-the-clock sitter to stay with Grandmother.” b. “I have some of her favorite hymns on a CD that I could bring for music therapy.” c. “I don’t think that she’ll need pain medication along with her herbal treatments.” d. “I will burn therapeutic incense in the room so we can stop the anxiety pills.” ANS: B Music therapy is a complementary therapy that may produce relaxation by quieting the mind and removing a client’s inner restlessness. Complementary therapies are used in conjunction with traditional therapy. The complementary therapy would not replace pain or anxiety medication but may help decrease the need for these medications. Hiring an around-the-clock sitter does not demonstrate that the client’s family understands complementary therapies. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Basic Care and Comfort—Non- Pharmacological Comfort Interventions) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 8. A terminally ill client has just died in a hospital setting with family members at the bedside. The health care provider is also present. What should be the nurse’s priority intervention as postmortem care begins? a. Call for emergency assistance so that resuscitation procedures can begin. b. Ask the family members if they would like to spend time alone with the client. c. Ensure that a death certificate has been completed by the physician. d. Request family members to prepare the client’s body for the funeral home. ANS: B Before moving the client’s body to the funeral home, the nurse should ask family members if they would like to be alone with the client. Emergency assistance will not be necessary. Although it is important to ensure that a death certificate has been completed before the client is moved to the mortuary, the nurse first should ask family members if they would like to be alone with the client. The client’s family should not be expected to prepare the body for the funeral home. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 9. The nurse is providing care for a hospice client who is in the last stages of the dying process. The client develops a pressure ulcer on her sacrum, and family members tell the nurse that they would like a specialist consulted to treat the ulcer. When the nurse discusses this with the client, the client states that the ulcer does not bother her, that it is not causing her pain, and that she’d rather not have additional caregivers at this time. What should the hospice nurse do next? a. Tell the family the wound care specialist will be consulted and treatment will begin. b. Ask the social worker and the chaplain to talk with family members about the dying process. c. Explain the client’s desires to the family, emphasizing that the client will be made as comfortable as possible. d. Ask the agency mental health nurse to speak with the client about refusing treatment. ANS: C When palliative care is provided to the dying client, symptoms will be actively treated only if they are causing the client distress. In this case, the client has stated that the pressure ulcer is not causing her distress, and she does not want further intervention. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 10. The nurse is being trained in hospice care. Which intervention by the nurse is most compatible with the goals of end-of-life care for the client? a. Administer influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations. b. Prevent the client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease from smoking. c. Perform passive range-of-motion exercises to prevent contractures. d. Permit the client with diabetes mellitus to have a serving of ice cream. ANS: D When a client is near the end of life, nursing interventions should be focused toward facilitating peaceful death by granting the client’s wishes and identifying his or her needs. Allowing a client who wishes to have something that is not permitted in the diet can be comforting if he or she has a craving or a desire for that food. There is no reason to withhold it at this time. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 11. The nurse is assessing the dying client. Which manifestations of a dying client should the nurse assess to determine whether the client is near death? a. Level of consciousness b. Respiratory rate c. Bowel sounds d. Pain level on a 0 to 10 scale ANS: B All of these assessments should be performed during the dying process. As the peripheral circulation decreases, the client’s level of consciousness and bowel sounds decrease. The client is unable to provide a numeric number on a pain scale. The nurse should continue to assess respiratory rate throughout the dying process. As the rate drops significantly and breathing becomes agonal, death is near. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity (Physiological Adaptation—Pathophysiology) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment) 12. The wife is concerned because her terminally ill husband does not want to eat. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “Let him know that food is available if he wants it, but do not insist that he eat.” b. “A feeding tube can be placed in the nose to provide important nutrients.” c. “Force him to eat even if he does not feel hungry, or he will die sooner.” d. “He is getting all the nutrients he needs through his intravenous catheter.” ANS: A When family members understand that the client is not suffering from hunger and is not “starving to death,” they may allow the client to determine when, what, or if to eat. Often, as death approaches, metabolic needs decrease and clients do not feel the sensation of hunger. Forcing them to eat frustrates the client and the family. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 13. The family members of a client with a terminal illness tell a nurse that the client keeps asking if she is dying. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “Whenever she asks about dying, change the subject.” b. “Tell her the truth in as gentle a way as possible.” c. “Tell her that she will get better eventually.” d. “Ask her if she is afraid to die.” ANS: B Being honest and truthful at such a time is important. It helps the client develop trust in those caring for her. Changing the subject will frustrate the client and may make her distrustful. Providing false hope is not a realistic intervention. Asking a pointed question often will not elicit the information that you want from the client. It is better to ask open-ended questions. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 14. The client’s family members are concerned that the client should have a urinary catheter placed because of her decreasing urinary output. What is the hospice nurse’s best response? a. “A Foley catheter is inserted only if she is taking medications that affect output.” b. “I will insert a Foley catheter if her urinary output drops below 500 mL/day.” c. “A Foley catheter will be inserted if her bladder becomes distended.” d. “I will insert a Foley catheter if she becomes incontinent of urine.” ANS: C Insertion of an indwelling catheter is acceptable if the client is unable to void, has a distended bladder, and would be more comfortable not moving. The other statements are not appropriate uses for an indwelling catheter in a hospice setting. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 15. The health care provider suggests inpatient hospice for a client. The family members are concerned that their loved one will receive only custodial care. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “The goal of palliative care is to provide the greatest degree of comfort possible and help the dying person enjoy whatever time is left.” b. “Palliative care will release you from the burden of having to care for someone in the home. It does not mean that curative treatment will stop.” c. “A palliative care facility is like a nursing home and costs less than a hospital because only pain medications are given.” d. “Your relative is unaware of her surroundings and will not notice the difference between her home and a palliative care facility.” ANS: A Palliative care provides an increased level of personal care designed to manage symptom distress. The focus is on pain control and helping the relative die with dignity. DIF: Cognitive Level: Comprehension/Understanding REF: p. 110 TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 16. A dying client’s family members are spending time with the client. What instruction is best to give to family members regarding noise in the client’s room? a. “Remember that she cannot hear you.” b. “Try to get her to talk or respond to you.” c. “Avoid making any noise when you are with her.” d. “Talk in your normal speaking voice.” ANS: D The sense of hearing may remain intact, even when it appears that the client is totally unresponsive to any sort of stimuli. The family member should speak to the client as if she were fully aware. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 17. A client who is near death appears to be having difficulty breathing. What is the nurse’s highest-priority intervention? a. Teach the family how to perform nasotracheal suctioning. b. Request that the physician order morphine sulfate. c. Document the finding in the client’s chart. d. Call a respiratory therapist to intubate the client. ANS: B Morphine sulfate is the standard treatment for dyspnea near death; it relieves the psychological and physiologic distress that accompanies breathlessness. Suctioning or intubation may cause the client discomfort. Documentation is important, but it is not the priority intervention because it does nothing to relieve the client’s distress. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 18. The nurse is caring for a dying client who becomes very agitated. What is the nurse’s best response? a. Use music therapy to promote relaxation. b. Increase the dose of intravenous opioids. c. Provide a second antipsychotic medication. d. Assess the client for urinary retention. ANS: D Dying clients become agitated when they are in pain or have some discomfort. Before administering medications or other therapies to decrease discomfort, the nurse should assess for potential causes of discomfort including urinary retention. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 19. An experienced hospice nurse is training a new nurse in the practices of palliative care. What statement by the new nurse indicates understanding about drug therapy for end-of-life care? a. “I can administer as much pain medication as I want because the client is dying.” b. “The administration of these medications will hasten the client’s death.” c. “I can administer medication per the protocol to relieve the client’s symptoms.” d. “The purpose of palliative sedation is to relieve family members’ distress.” ANS: C Palliative care nurses follow protocols when administering medications. These protocols are standing prescriptions from the provider that identify the appropriate medication, dose, and situation for administration. The nurse cannot administer more than is prescribed. The medications are given to promote comfort and if administered per protocol will not hasten death. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Evaluation) 20. An older client was admitted to hospice owing to impending death in approximately 6 weeks. After 2 months, the family remains at the bedside but is becoming increasingly impatient and irritable. What is the best nursing intervention? a. Ask the family to leave and not return until they are calmer. b. Sit with the family and listen to their concerns and fears. c. Tell the family members not to worry, the client will die soon. d. Consult the chaplain to come and pray with the client’s family. ANS: B Death cannot be accurately predicted. The nurse should sit with the family and listen to their concerns. The nurse should not provide false hope or reassurance. Family members should remain with the client as long as they would like. The chaplain should be consulted if the family requests. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (Therapeutic Communication) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 21. An intensive care nurse is discussing withdrawal of care with a client’s family. The family expresses concerns related to discontinuation of therapy. What is the nurse’s best response? a. “I understand your concerns, but in this state, discontinuation of care is not a form of active euthanasia.” b. “You will need to talk to the provider because I am not legally allowed to participate in the withdrawal of life support.” c. “I realize this is a difficult decision. Discontinuation of therapy will allow the client to die a natural death.” d. “There is no need to worry. Most religious organizations support the client’s decision to stop medical treatment.” ANS: C The nurse should validate the family’s concerns and provide accurate information about the discontinuation of therapy. The other statements address specific issues related to the withdrawal of care but do not provide appropriate information about its purpose. If the client’s family asks for specific information about euthanasia, legal, or religious issues, the nurse should provide unbiased information about these topics. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The hospice nurse is caring for a dying client and her family members. What nursing interventions are appropriate to use? (Select all that apply.) a. Teach family members about physical signs of impending death. b. Encourage the management of adverse symptoms. c. Assist family members by offering an explanation for their loss. d. Encourage reminiscence by both client and family members. e. Avoid spirituality because the client’s and the nurse’s beliefs may not be congruent. f. Do not encourage hope for the terminally ill client. ANS: A, B, D The nurse should teach family members about the physical signs of death, because family members often become upset when they see physiologic changes in their loved one. Palliative care includes management of symptoms so that the peaceful death of the client is facilitated. Reminiscence will help both the client and family members cope with the dying process. The nurse is not expected to explain why this is happening to the family’s loved one. The nurse can encourage spirituality if the client is agreeable, regardless of whether her religion is the same. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 2. The nurse is providing care for a dying client. The nurse would place highest priority on treating which symptoms? (Select all that apply.) a. Anorexia b. Weight loss c. Pain d. Agitation e. Nausea f. Hair loss g. Dyspnea ANS: C, D, E, G Only symptoms that cause distress for a dying client should be treated. Such symptoms include pain, nausea and vomiting, dyspnea, and agitation. These problems interfere with the client's comfort. Even when symptoms, such as anorexia or weight loss, disturb the family, they should be treated only if the client is distressed by their presence. The nurse should provide education to the family and the client related to normal symptoms of dying. DIF: Cognitive Level: Application/Applying or higher REF: N/A TOP: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity (End-of-Life Care) MSC: Integrated Process: Caring 3. The nurse is admitting a new client to the hospital and needs to determine the plan of care. What criterion is required for the client to make his own medical decisions? (Select all that apply.) a. Can communicate his treatment preferences b. Is able to read and write at an 8th grade level c. Is oriented enough to received information d. Can evaluate and deliberate information e. Has completed an advance directive ANS: A, C, D To have decision-making ability, a person must be able to perform three tasks: receive information (but not necessarily oriented 4); evaluate, deliberate, and mentally manipulate information; and communicate a treatment preference. The client does not have to read or write at a specific level. Education can be provided at the client’s level, so that he can make the necessary decisions. The client does not need to complete an advance directive to make his own medical decisions. An advance directive will be necessary if he wants to designate someone to make medical decisions when he is unable to. DIF: Cognitive Level: Knowledge/Remembering REF: p. 107 TOP: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment (Management of Care—Advance Directives) MSC: Integrated Process: Nursing Process (Assessment) [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 08, 2021
Number of pages
10
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
22