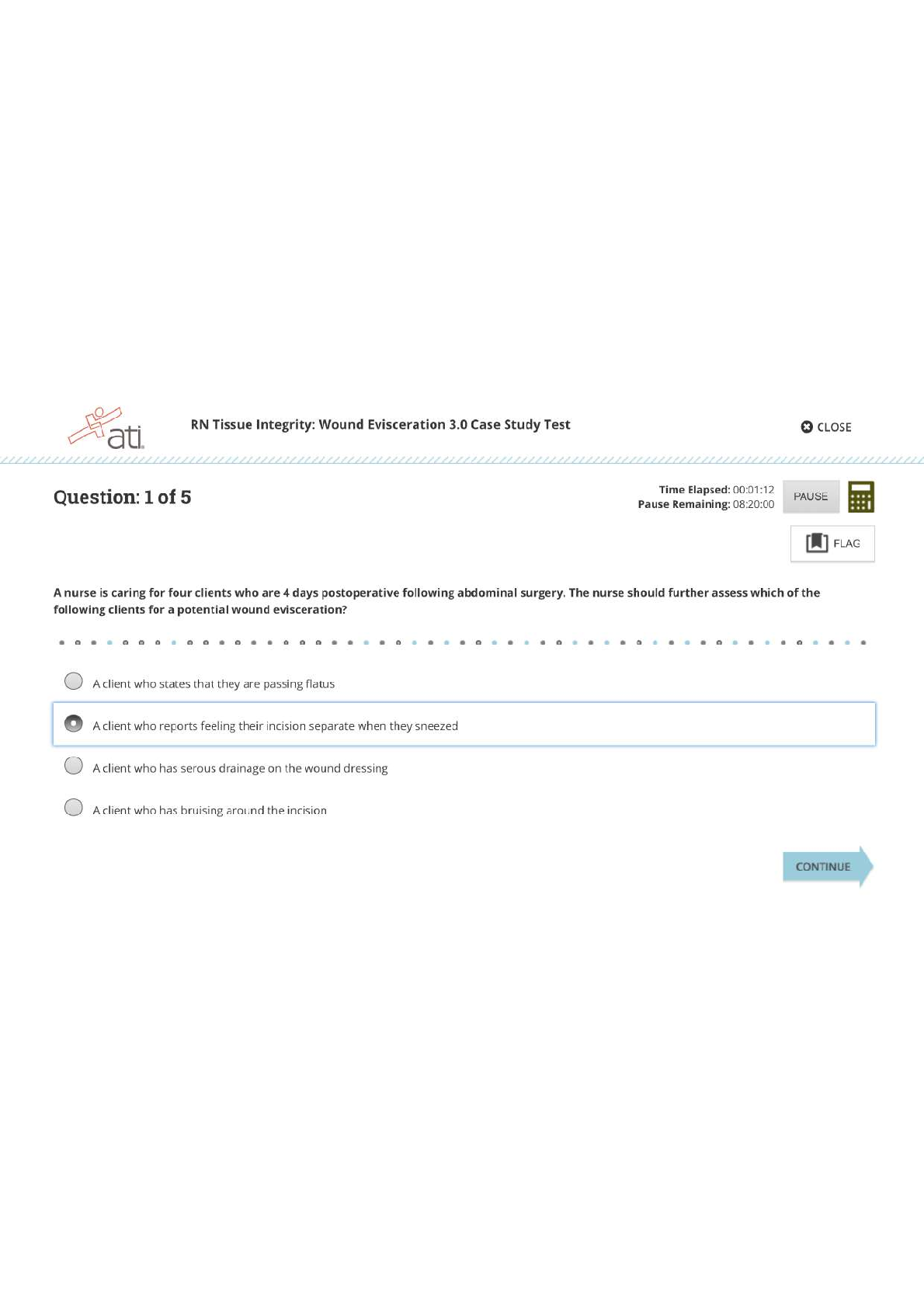
*NURSING > ATI MEDICAL SURGICAL > MEDSURG ATI 2019B,100% CORRECT (All)
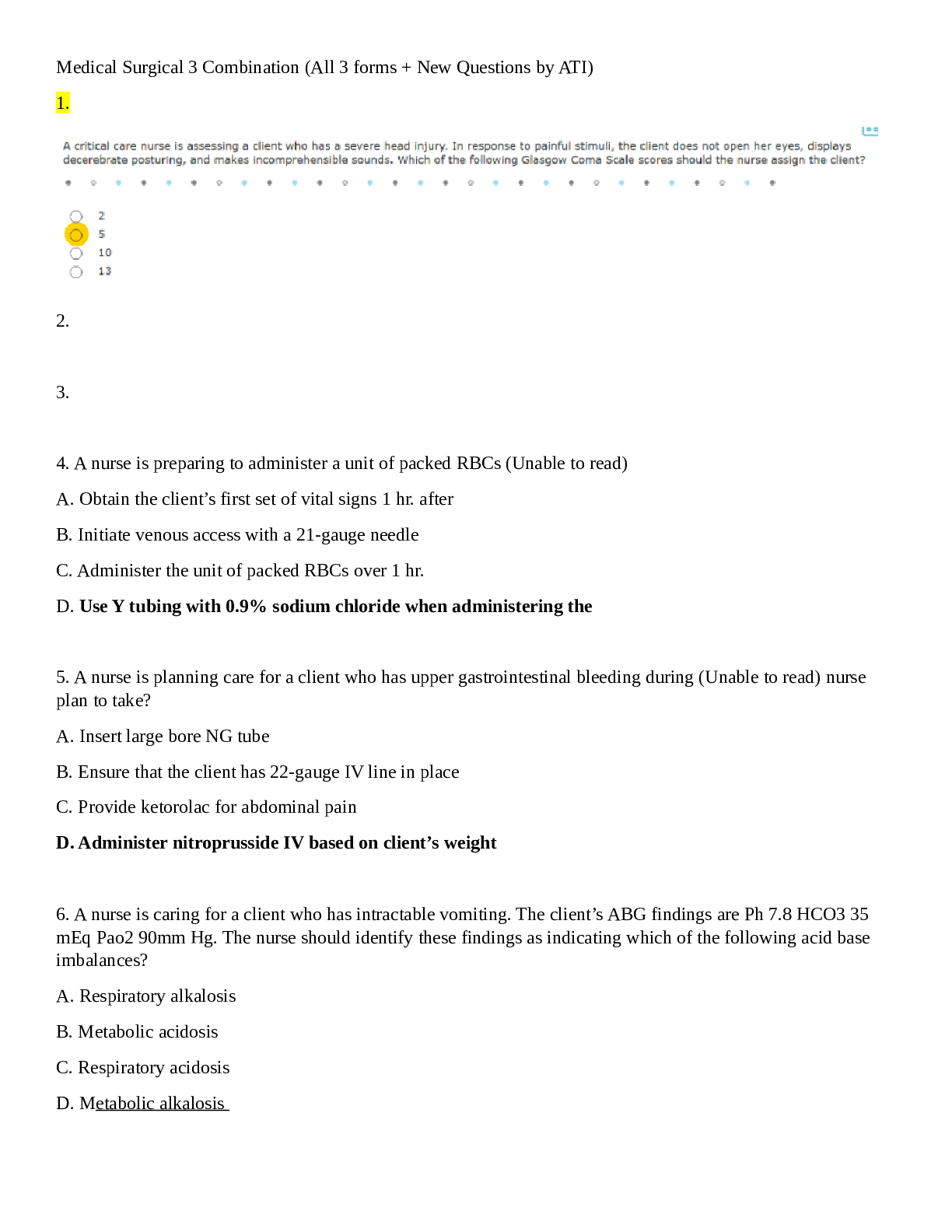
MEDSURG ATI 2019B,100% CORRECT
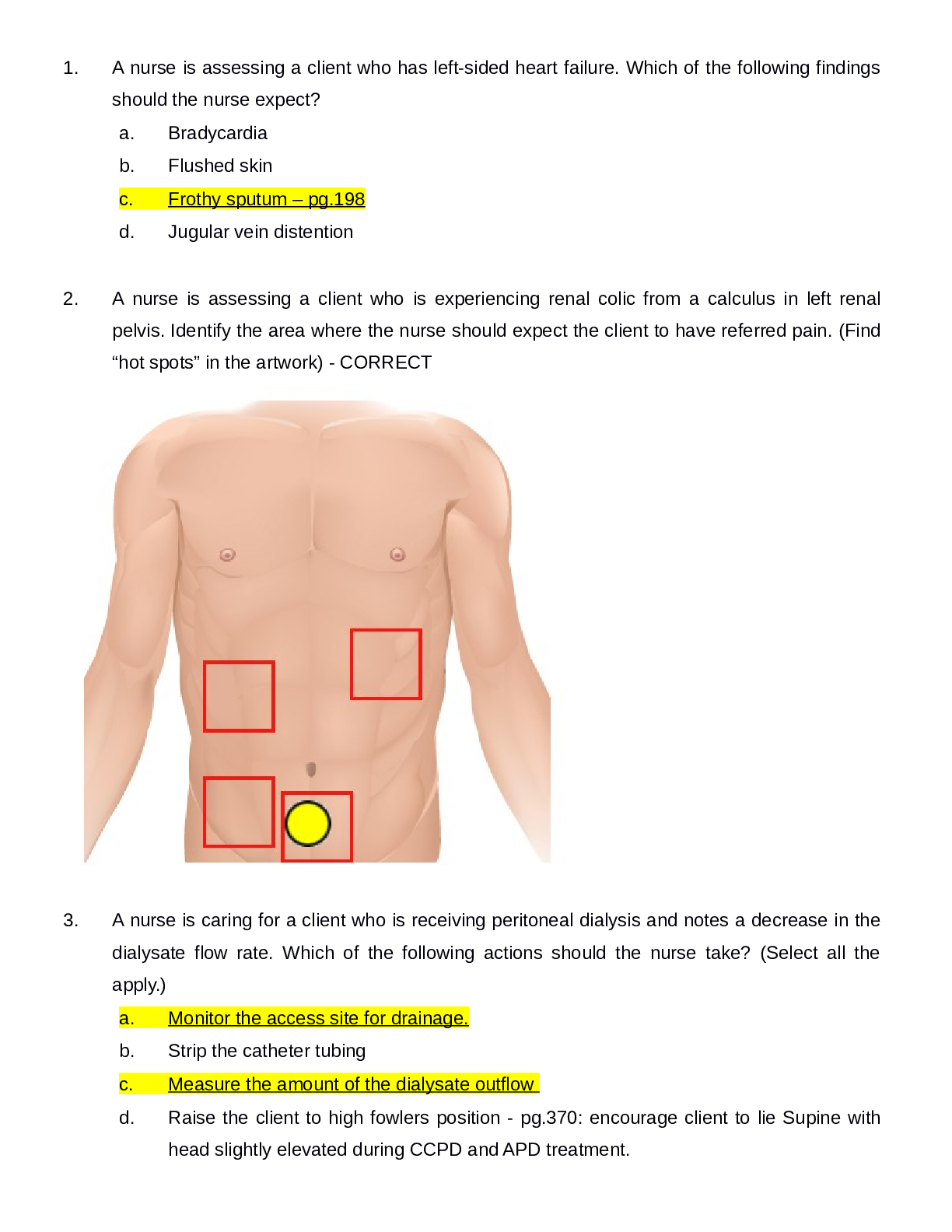
Document Content and Description Below
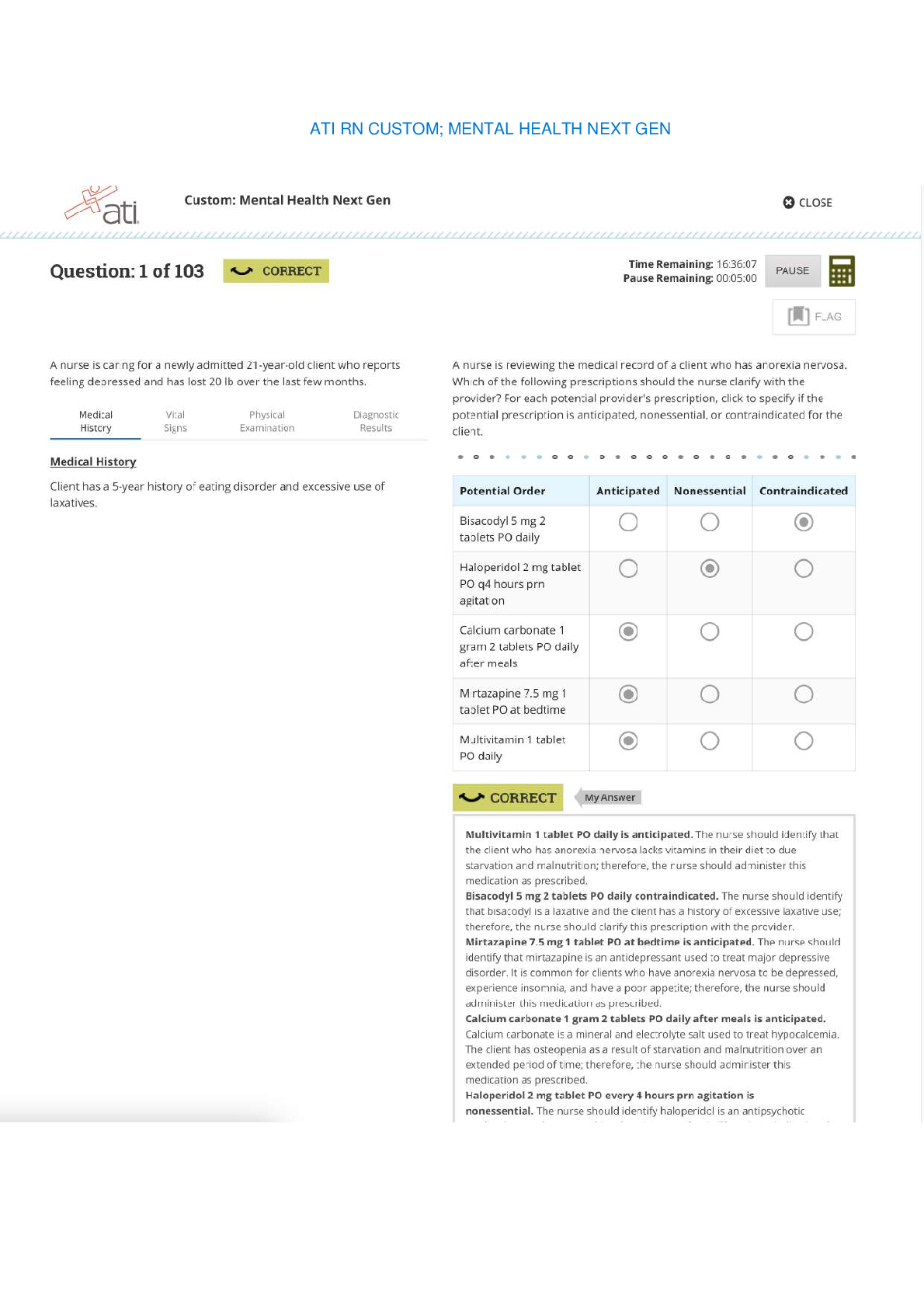
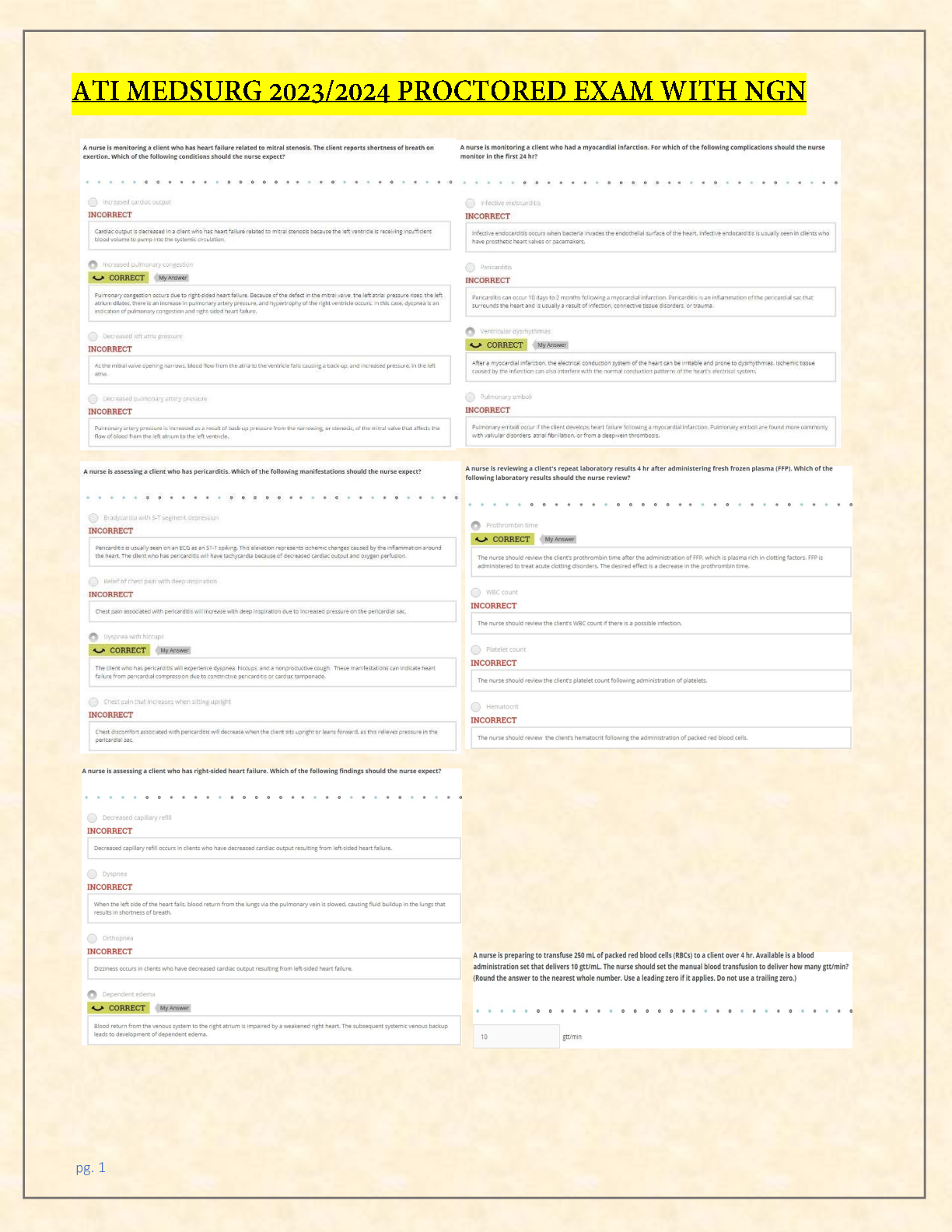
1) Inflammatory Bowel Disease: DietaryRecommendations (583) • low fiber • increased protein • decreased calories Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease • Eat foods high in protein and c... alories, and low in fiber • Identify foods that trigger clinical manifestations • Avoid caffeine and alcohol, take multivitamin w/ iron • Eat small frequent meals • Dietary supplements high in protein and low in fiber • Monitor for electrolyte imbalance especially potassium • Vitamin B12 Diverticulitis • Consume clear liquid until manifestations subside • Add fiber when solid foods are tolerated • Avoid seeds or indigestible material that can block diverticula (nuts popcorn) • Avoid alcohol. Limit fat intake to 30%, adequate fluids, bulk forming laxatives 2) Respiratory Management and MechanicalVentilation: Need for Suctioning • Suction secretions to maintain airway and tube patency 3) Disorders of the Eye: Expected Findings (122) • Retinal detachment- flashes of light and blind spotscurtain closing over eyes • Glaucoma- increased IOP causing gradual vision loss • Injury. Disease process, aging process • Macular degeneration(#1 cause of vision loss in ppl over 60), cataracts, glaucoma • MD: lack of depth perception, object distortion, blurred vision, loss of central vision, blindness • Cataracts: decreased visual acuity, blurred vision, diplopia, photo sensitivity, halo around lights, visible opacity, absent red reflex • Glaucoma: headache, mild eye pain, loss of peripheral vision, inc. IOP, photophobia, pupils non reactive to light 4) Disorders of the Eye: Analyzing Findings • IOP: 10-21 mm/Hg • Monitor for IOP • -monitor for decreased vision and light sensitivity • -Assess pt for aching or discomfort around the eye • -Tx severe plain and nausea with analgesics and antiemetics 5) Arthroplasty: Prevent complication- DVT, anemia, -Older adults @ higher risk CPM Prevent pressure ulcers Using a Continuous PassiveMotion Machine • Promote motion and prevent scar tissue formation • Avoid flexion of hip greater than 90 degrees, don’t cross legs, abduction pillow, raised toilet seat • -Full extention to perscribedamt of flexion • -Placed and initiated right after surgery • -stopped for meals 6) Cancer Disorders (981) Laryngeal Cancer andBody Image Disturbance Consult speech language path. for clients who have difficulty speaking -Provide comfort to pt who have permenant loss of voice or disfigurment -Refer to counseling servcies as needed 7) Burns: Prioritizing Emergency Interventions (829) Airway -fluid and electrolyte -thermoregulation -infection • Maintain Airway and Ventilation (cough deep breathe, suction, elevate head of bed, oxygen), • monitor vitals • maintain cardiac output (IV access, fluid replacement in first 24 hours, rapid replacement during emergent phase, isotonic crystalloid solutions such as NaCl or Lactated Ringers, colloids such as albumin or synthetic plasma expanders after first 24 hours. Maintain urine output, possible administration of blood products), • monitor for shock, pain management (avoid IM or Sc administration, IV opioid analgesics, monitor for respiratory depression, meds before dressing change, nonpharm pain management), • prevent infection (restrict visitors, no plants or flowers, no fresh fruits or vegetables), • nutritional support( may need increased calories up tp 5,000, increase protein, may need TPN, ) • Restore mobility, • psychosocial support 8) Electrolyte Imbalances: (472) Safety, abc’s Evaluation ofPotassium Chloride Therapy - hypokalmeia Never administer by bolus, 5-10 mEq/hr Assess for phlebitis Monitor urine output Diminished respirations and breath sounds Monitor cardiac rhythm (especially pts taking Digoxin), LOC, bowel sounds, kidney function, mg ca phosphorus, provide assistance with ADLs 9) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and TherapeuticProcedures: (294) Assessing Arterial Line (296) check placement -keep pressure -flush before between and after meds -watch for clotting Assess integrity of arterial waveform, monitor circulation in the limb with the line( cap refill, temp, color). Monitor respiratory and cardiac status, placement, prevent infection and blood clots 10) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and TherapeuticProcedures: (349) ECG Abnormalities FollowingMyocardial Infarction (351) Angina- ST depression/ T wave inversion indicates ischemia MI- T wave inversion indicates ischemia, ST segment elevation indicates injury, abnormal Q waves indicates necrosis 11) Head Injury: Monitoring CSF Leakage • Leakage from nose or ears • "halo" sign- yellow stain surrounded by blood on a paper towel, • fluid tests positive for glucose -report to dr 12)Diabetes Mellitus Management: (914) ClientEducation Regarding Medications Rotate injection sites, don’t aspirate for blood Eat at regular intervals, avoid alcohol intake, adjust insulin to exercise Take even if can't eat. -Clear-cloudy-cloudy- clear pull in short acting first then long acting -Must eat after injection or will have hypoglycemia 13) Tuberculosis: Client Teaching Regarding Medication Therapy Must take for 6-12 months No alcohol, may interfere with BC, report yellowing skin, drink lots of water, notify provider with vision or hearing changes 14) Aneurysms: 434 Signs and Symptoms ofAortic Dissection Aortic Aneurysm Gnawing feeling in abdomen, flank or back pain, Pulsating abdominal mass (do not palpate) Bruit. Increased BP -Severe back pain -Hoarsness, cough, SOB, difficulty swallowing -Decreased urinary output Aortic Dissection Sudden stabbing, tearing, ripping, abdominal or back pain Hypovolemic shock (diaphoresis, nausea, vomiting, faintness, apprehension) decreased or absent peripheral pulses, neuro deficits, hypotension and tachycardia (initially) 15) Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis:Complications(640) Hemodialysis: clotting, air bubbles, temperature of dialysate, regulation of ultrafiltration, hypotension, cramping, vomiting, bleeding, contamination, hypovolemia, disequilibrium syndrome. clotting/Infection of access site -Disequilibrium syndrome -use slow exchange rate - Administer anticonvulsant/barbituates if needed -Hypotensoin -IV fluids -Decreased HOB -Anemia -Monitor labs and provide blood products as needed -Infectious Diseases Peritoneal Dialysis: peritonitis, infection at access site, leakage, reflux, protein loss, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obstruction 16) Peptic Ulcer Disease: Complications (549) Perforation/Hemorrhage: severe epigastric pain spreading across abdomen, rigid board like abdomen, hyperactive to diminished bowel sounds, rebound tenderness Pernicious anemia: pallor, glossitis, fatigue, paresthesia. Will need B12 injections. Dumping syndrome: syncope, pallor, palpitations, dizziness, headache -Heartburn, bloating, N&V -Pain, bloddyemisis or stools -weight loss, med. side effects 17) Fluid Imbalances: (473) PrioritizingAssessment Findings Safey, abc’s 18) Hemodynamic Shock: Ventricular Fibrillation (423) can cause cardiogenic shock -Dx- ECG, Ech, CT, Cardiac cath, chest x ray -Tx- Cardiac cath, Anticoagulants, defib shock to fix rythem 19) Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney (674) Disease: Evaluating Client Understanding Drink2 to 3 L, stop smoking, lose weight, NSAIDS with caution, diabetic and HTN control, take prescribed antibiotics. High protein diet, restriction during oliguric phase, potassium and sodium restriction according to stage of disease -Instruct pt to take ALL prescribed meds and ATB -Decreased dietary potassium, phosphate, and mag. -Increase protein, possible TPN 20) Gastrointestinal Therapeutic Procedures: (523) Teaching Colostomy Care Educate and a support person Odor causing foods: fish, eggs, asparagus, garlic, beans, and dark green leafy vegetables Gas causing foods: dark green leafy vegetables, beer, carbonated drinks, dairy products, and corn. Yogurt may decrease gas Ostomy involving small intestine: avoid high fiber foods for first 2 months, chew food well, increase fluids, and evaluate for blockage with addition of fiber Filters, deodorizers, or breath mint can minimize odor when pouch is open Encourage client to look at and touch stoma Normal stoma appearance, symptoms of blockage 21) Respiratory Management andMechanical Ventilation: (199) ComplicationsFollowing Extubation RR > 30/min or <8/min -BP or HR changes >20% baseline -SaO2 <90% -Dysrhythmias, increased ST segment -Sig. decrease in tidal volume -Labored resp. and increased use of accessory muscles -Restlessness, anxiety, decreased LOC -Monitor for resp. destress or airway obstruction such as ineffective cough, dyspnea, and stridor 22) Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema: 361 Manifestations of Left-Sided Heart Failure Dyspnea, orthopnea, fatigue Displaced apical pulse, S3 heart sounds Pulmonary congestion(dyspnea, cough, pink frothy sputum) Altered mental status Manifestations of organ failure such as oliguria 23) Postoperative Nursing Care: Using anIncentive Spirometer (1104) Use at least every 2 hours. Promotes lung expansion, prevents atelectasis 24) Peripheral Vascular Diseases: (394) ClinicalManifestations of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Discoloration of hand, arm pain and swelling, blood clots, lack of color in hand or arm, weak or no pulses, arm fatigue, numbness or tingling in fingers, weakness of arm or neck, lump near collarbone, weakening grip Neck, shoulder, and arm pain, numbness -Impaired circulation and flushed sensations to the extremities -Symptoms are reproduced when arm is positioned above the shoulder or extended 25) Cancer Treatment Options: (999) DietaryConsiderations for a Client who has Stomatitis Use non-alcoholic glycerin based mouth wash Discourage consumption of salty, spicy, acidic foods Eat soft, bland foods high in calories (mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, cooked cereal, milk shakes, ice cream, frozen yogurt, bananas, breakfast mixes) Oral hygiene before and after meals 26) Blood and Blood Product Transfusions: (450) Infusion of Autologous Salvaged Blood 5 weeks up to 72 hours in advance Salvaged blood from surgery can be recycled through cell-saver machine and transfused prescribed 27) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and TherapeuticProcedures: Cardiac CatheterizationPostoperative Care (294) Apply an initial dressing of gauze and replace with transparent dressing w/i 24 hr -x ray to ensure placement -assess q8hr - Use 10mL or < syringe to flush -Clean port for 3 seconds and allow to dry -flush before, between, and after meds - no BP on arm with PICC 28) Disorders of the Male Reproductive System: Delegation of Postoperative Care FollowingProstate Surgery vitals 29) Electrocardiography and DysrhythmiaMonitoring: Monitoring a Client for Risk ofPulmonary Embolism Caused by dysrythmia -dyspnea, chest pain, air hunger, decreased o2 30) Noninflammatory Bowel Disorders: Self‑Management Strategies High fiber diet reduce stress Instruct pt to limit irritating foods Keep food diary 31) Emergency Nursing Principles and Management: Mass Casualty Triage Red- emergent Yellow- need care soon Green- walking wounded Black- expected to die 32) Renal Diagnostic Procedures: IV Urography 33) Hyperthyroidism: Postoperative Carefollowing a Thyroidectomy Keep trach @ bedside Vitals, assess for bleeding, laryngeal 34) Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Prioritizing Interventions Class I: Pt exhibits no symptoms with activity Class II: Pt has symptoms with ordinary exertion Class III: Pt displays symptoms with minimal exertion Class IV: Pt symptoms @ rest BASIC CARE AND COMFORT (6) 35) Peptic Ulcer Disease: Prevention ofDumping Syndrome instruct pt to avoid foods that cause distress -Monitor for orthostatic changes in v/s and tachycardia at these findings are suggestive of gastrointestinal bleeding -Have pt lie supine after eating 36) Renal Calculi: Dietary Restrictions Limit food high in animal protine -reduce calcium intake 37)Mobility and Immobility: Quad Cane Usewith Hemiplegia Use cane on uneffected side -Advance cane at same time as affected limb -Stairs- -Up with the good and down with the bad 38) Postoperative Nursing Care: ProphylacticDVT Care assess and compare peripheral pulses -Caused by dehydreation, obesity, trauma, malignacy, Hx of thrombosis, hormones, and use of indwelling cath -Nursing actions: prevention, avaoid dangling pt for long periods, anticoagulants, provide adequate hydration 39) Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic KidneyDisease: Planning Dietary Restrictions possible fluid restrictions -Restrict K+, phosphate, & magnesium Potassium and sodium regulated -High protein and possible TPN 40) Disorders of the Male Reproductive System: Preventing Complications following aTransurethral Resection of the Prostate Urine should be light pink. If red increase irrigation -If cath becomes obstructed turn of CBL and irrigate with 50mL -Record amt. of irrigation and sub. from total to get true output -Instruct pt not to urinate around cath-it will cause bladder spasem -Monitor vitals and bleeding HEALTH PROMOTION AND MAINTENANCE (2) 41) Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: Safer Sex Practices Abstienence is best -Use condoms -Get tested regularly 42) Health, Wellness, and Illness: Health Screening -Physical assessment -Evaluating health perceptions -Identifying risks to health/wellness -identify access to healthcare -Identify obsticals to compliance and adhearance -Belief in prescribed therapy -Availibility of support system -financial restricitions PHARMACOLOGICAL AND PARENTERAL THERAPIES (23) 43) Miscellaneous Pain Medications: Medication Teaching for Allopurinol (Zyloprim) Steven- Johnsons syndrom, joint pain, pain or blood in urine, yellow skin or eyes -drowsiness -N&V diarrhea 44) Growth Factors: EvaluatingEpoetin Alfa (Epogen) Effectiveness Monitor hematocrit lab values 45) Blood and Blood Product Transfusions: Evaluating Therapeutic Response Monitor Vitals I&O and Labs 46) Gastrointestinal Therapeutic Procedures: Evaluating Client’s Understanding of TPN Must monitor glucose lvls closely durring TPN infusion -Given through PICC or Central Line 47) Blood and Blood Product Transfusions: Allergic Transfusion Reactions Stop infusion Change tubing start IV of 0,9% sodium chloride. Keep tubing, bags to send back to lab Mild- Itching, urticaria, flushing- Administer benadryl Anaphylactic- wheezing, dyspnea, chest tightness, cyanosis, hypotension -maintain airway, admin. 02, IV fluids, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and vasopressors 48) Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: Medication Adverse Effects Avoid antimicrobial, NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors, IV contrast dye -Monitor Digoxin lvl& administer post dialysis -kayexalate to increase elimination of serum potassium -epogen, procrit, to increase RBS stimulation -Iron supplement -Lasix -Amphojel- taken to stop phsophate absorption -take 2 hr before or after digoxin 49) Medications Affecting Coagulation: Self‑Administering Enoxaparin (Lovenox) -Injection given in R or L abdomen -Take only as directed -may inhibit blood clotting 50) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Complications of IV Therapy fluid overload thrombophlebitis, infiltration extravasation PHARMACOLOGICAL AND PARENTERAL THERAPIES (continued) 51) Diabetes Mellitus Management: Administering Insulin check glucose before meds if take insulin must eat after 52) Hypertension: Recognizing Side Effectsof Medications -Hypotension -edema -ACE-unproductive cough -monitor potassium 53) Gastrointestinal Therapeutic Procedures: Calculating Protein Intake 0.8-/kg 54) Opioid Agonists and Antagonists: Hypersensitivity to Morphine Narcan- antagonist Older pt do not metabolize as well If Resp. rate falls below 8/min stop opioid and give narcan 55) Posterior Pituitary Disorders: Plan of Care forClient who has Diabetes Insipidus monitor Vitals and labs -weigh daily -IV therapy -Fall precautions -Add bulk foods and fruit juices -Assess skin turgor and mucous membranes -provide skin and mouth care -encourage pt to drink in response to thirst 56) Opioid Agonists and Antagonists: ExpectedFindings Following Administration ofNaloxone (Narcan) Increased respirations, pain returns, increased HR, increased BP 57) Seizures and Epilepsy: Client Teaching aboutPhenytoin (Dilantin) -If one med doesn't work dose is increased or another med is added -Therapeutic lvl determined by blood test -Med taken same time each day -No oral contraception or warfarin Dilantin Therapeutic Lvl 10-20 58) Medications Affecting Blood Pressure: Monitoring Initial Dose of Lisinopril (Zestril) may make pt feel dizzy -Monitor BP, HR, and keep on falls precautions -Remind pt top ask for assistance to get up and to move slowly 59) Blood and Blood Product Transfusions: Interventions for Transfusion Reaction Acute hemolytic › Immediate - This reaction may be mild or life-threatening. - Clinical findings include chills, fever, low back pain, tachycardia, flushing, hypotension, chest tightening or pain, tachypnea, nausea, anxiety, and hemoglobinuria. - This reaction may cause cardiovascular collapse, kidney failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation, shock, and death. febrile › 30 min to 6 hr after transfusion - Clinical findings include chills, fever, flushing, headache, and anxiety. - Use WBC filter. Administer antipyretics. Mild allergic › During or up to 24 hr after transfusion - Clinical findings include itching, urticaria, and flushing. - Administer antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl). Anaphylactic › Immediate - Clinical findings include wheezing, dyspnea, chest tightness, cyanosis, and hypotension. - Maintain airway; administer oxygen, IV fluids, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and vasopressors. Stop infusion, run normal saline in separate line, keep bag and line for testing 60) Electrolyte Imbalances: (494) TreatingHypomagnesemia less than 1.3 -DC mag-losing meds (loop diuretics) -Administer oral or IV mag sulfIm can cause pain and tissue damage, oral can cause diarrhea and increase mag depletion eIncourage food high in mag: dairy, dark green leafy veggies 61) Menstrual Disorders and Menopause: AdverseEffects of Medications ,Menopausal Hormone Therapy - increased risk for blood clots - long term use increases cancer risk 62) Vitamins, Minerals, and Supplements: Adverse Effects of Garlic Therapy Effect blood clotting, inhibits platelet formation Increased bleeding with lovenox, odor in colostomy 63) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Verifying Tip Placement ofPICC Line x ray verification prior to use Use 10mL or < syringe Tape cath hub to minimize manipulation Remove dressing from distal to proximal note length to help detect cath. migration 64) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Accessing Implanted Port Local anesthetic, Palpate port body septum to ensure accurate insertion of needle. Alcohol for 2-3 seconds, use non-coring (Huber) needle x ray to confirm placement -document cath placement @ beg. and end of shift (and any time py is moved) -check readings for hemodynamic cath -use 0.9% sodium chloride of flushing no heparin -Avoid air embolisim -risk for pneumothorax -Risk for dysrhythmias with insertion/movement of line 65) Cardiac Glycosides and Heart Failure: Evaluating Client Understanding ofDigoxin Administration (361) Apical HR for one full minute Hold if apical HR is <60bpm per min -Watch for N&V -Monitor ECG, BP -Take same time each day -take 2 hr before or after antacids If you miss dose take it as soon as you remember Therapeutic level 0.5-2.0 REDUCTION OF RISK POTENTIAL (21) 66) Pulmonary Embolism: Interventions (258) • Administer O2 therapy • High fowlers • initiate and maintain IV therapy • administer meds (anticoagulants and thrombolytic therapy) • Provide emotional support • Monitor changes in LOC and mental status 67) Cardiovascular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Postoperative Expected FindingsFollowing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (294) • Splint incision with deep breathing and coughing • Consult resp. services • Continually monitor HR and rythem • Hypertension and Hypotension • Chest tube dreain>150mL/hr could mean hemorrage • control plan • Monitor fluid and electrolyte 68) Inflammatory Bowel Disease: (580) InterpretingLaboratory Results • HGB & HCT decreased • ESR Increased • WBC increased • Platelet count increased • Serum albumin decreased • K, Mg, C decreased 69) Arthroplasty: Postoperative Care Following aKnee Arthroplasty (759) Prevent complication- DVT, anemia, -Older adults @ higher risk CPM, avoid pillows behind knees, keep heels off of bed, analgesics, antibiotics, anticoagulant, ice , neurovascular status Prevent pressure ulcers 70) Hyperthyroidism: (868) MonitoringLaboratory Results • Serum TSH test- decreased • -FTI and T3 increased • -Thyroid-releasing hormone- failure of expected rise 71) Diabetes Mellitus Management: GlycosylatedHemoglobin Test 4-6% normal target <7%, good glycemic control Indicates Blood sugar for last 120 days 72) Cancer Screening and Diagnostic Procedures: Assessing the Need for Intervention (990) CEA PSA AFP 73) Postoperative Nursing Care: (1104) Recognizing RiskFactors for Atelectasis Snoring, Stridor, Monitor Blood o2 lvl 74) Tuberculosis: Interpreting a Mantoux Skin Test (249) Red spot- no reaction Raised red bump- reaction 48-72 hours after injection More than 10mm induration, positive. Confirm with chest xray 75) Electrocardiography and Dysrhythmia Monitoring:Priority Analysis of an ECG Strip (312) MI (chest pain and ST depression or elevation) 76)Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: Recognizing Priority Laboratory Values Serum creatinine gradual increases 1-2mL/dL q 24-48 hr or 1-6 in ine week BUN increased to 80-100 w/i week Urine specific gravity >1-1.01 77) Diabetes Mellitus Management: (912) Evaluating Client Teaching Regarding Foot Care Keep feet clean and dry Wear shoes always Inspect feet daily Wear socks Wash with mild soap and warm water, test water with hands first Nailcare after showering Separate overlapping toes Leather shoes preferred, no open toed or open heel shoes Cotton or wool socks Avoid prolonged sitting, standing, or crossing legs 78) Angina and Myocardial Infarction: Monitoring for Complications (349) Acute MI- Decreased cardiac output Cardiogenic shock/HF: tachycardia, hypotension, dec. urinary output, altered LOC, res. Distress, dec pulses, cool clammy skin Ventricular aneurysm/rupture d/t necrotic tissue result of MI: sudden chest pain, dysrhythmia, sever hypotension Dysrythmia- Ischemic mitral regurgitation-development of new cardiac murmur 79) Gastrointestinal Therapeutic Procedures: Appropriate Client Teaching about Paracentesis (523) Explain procedure and purpose -Local anesthetics at insertion site -Pressure or pain when needle is inserted Assess client’s knowledge of procedure 80) Chest Tube Insertion and Monitoring: (191) Observing the Water-Seal Chamber for anAir Leak Continuous bubbling means there is an air leak Intermediate bubbling is normal Continuous bubbling in suction chamber only REDUCTION OF RISK POTENTIAL (continued) 81) Coagulation Disorders: (467) Thrombocytopenia ITP- Autoimmune where lifespan of platelets is decreased can result in severe hemorrhage Unusual spontaneous bleeding 82) Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis: Assessing an Arteriovenous (AV) Graft (640) Check for palpable thrill, auscultate bruit, distal pulses, circulation) 83) Preoperative Nursing Care: Recognizing Deviations in Laboratory Values (1082) CBC: WBC (4,500-11,000), RBC(4.2-6.1), Platelets (150,00-450,00) Hgb: 12-18 Hct: 35-52 Serum electrolyte: K (3.5-5), Na (135-145), Cl (98-106), C (8.6-10), P(2.7-4.5), Mg(1.6-2.6) Serum creatinine (0.5-1.3) BUN (8-25) ABGs: ph (7.35-7.45), PaCO2 (35-45), HCO3(22-26), PaO2(80-100) 84) Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: Interpreting Laboratory Values (674) AKI Serum creatinine gradual increases 1-2mL/dL q 24-48 hr or 1-6 in one week BUN increased to 80-100 w/i week Urine specific gravity >1-1.01 CKD Hematuria, proteinuria, decreased specific gravity BUN as high as 180 to 200 Creatinine, 4 over time. As high s 15 to 30 Decreased Na and Ca, Increased K, P, Mg Decreased H&H 85) Spinal Cord Injury: Assessment of a Client who has a Cervical Injury C4 or above poses risk for impaired spontaneous ventilation because of the involvement of the phrenic nerve Bladder management for spastic bladder (catheter) Glucocorticoids, plasma expanders, H2 agonists, vasopressors, muscle relaxants, antimuscarinic, stool softeners, analgesics, anticaogulants Oxygen, incentive spirometer, cough and deep breathe 86) Respiratory Management and Mechanical Ventilation: Choosing Appropriate Oxygen Equipment (199) Nasal Cannula- 24-44%, 1-6L/min Simple face mask- 40-60% at 1-6L/min. 5l/min to flush CO2 from mask Partial rebreather- 60-70% at 6-11L/min Nonrebreather- 80-90% at 10-15Lmin Venturi-mask- 24 to 55% at 2 to 10L/min, for clients with chronic lung disease Aerosol mask-24-100% at leas 10L/min. for facial trauma, burns, or thick secretions T piece-24-100% at least 10L/min. For pt with tracheostomy, laryngectomy, or ET SAFETY AND INFECTION CONTROL (4) 87) Seizures and Epilepsy: Recognizing At-Risk Client (62) Genetic predisposition (absence seizures more common in children) -Acute febrile state -Head trauma -Cerebral edema -Abrupt cessation of antiepileptic drugs -Infection -Metabolic disorder -Brain tumor Exposure to toxins -Hypoxia -Acute drug & alcohol withdrawal -Fluid and electrolyte imbalances Older adult: cerebrovascular disease Triggering factors: excessive stress, inc physical activity, hyperventilation, fatigue, alcohol ingestion, excessive caffeine, flashing lights, cocaine aerosols inhaling glue 88) Infection Control: Evaluating Appropriate Use 89) Cancer Treatment Options: Planning Care for Client Undergoing Brachytherapy private room warning sign dosimeter visitors can stay for 30 minutes, must be at least 6 feet away pregnant or under 16b cannot enter If it falls out put in lead lined container using tongs Remain in position to prevent dislodgement Call for assistance with elimination 90) Cancer Treatment Options: Precautions for Client who is Immunocompromised (999) Avoid crowds -Take Temp daily -Avoid food that could contain bacteria (fresh fruits and veggies, undercooked meat, fish, eggs, pepper, paprika -Avoid yard work, pet litter -Avoid FLuids that have set out at room temp for more than 1 hour -Was dishes in hot soapy water, after one use -Wash toothbrush in dish washer or with bleach -Do not share toiletry Monitor temp and wbc Fever greater than 37.8(100) should be reported \ Monitor skin and mucous membranes for infection Cultures before antimicrobial therapy Neutropenic precautions when wbcs are less than 1000 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 19, 2020
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 19, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
76
















 – Chamberlain College of Nursing.png)