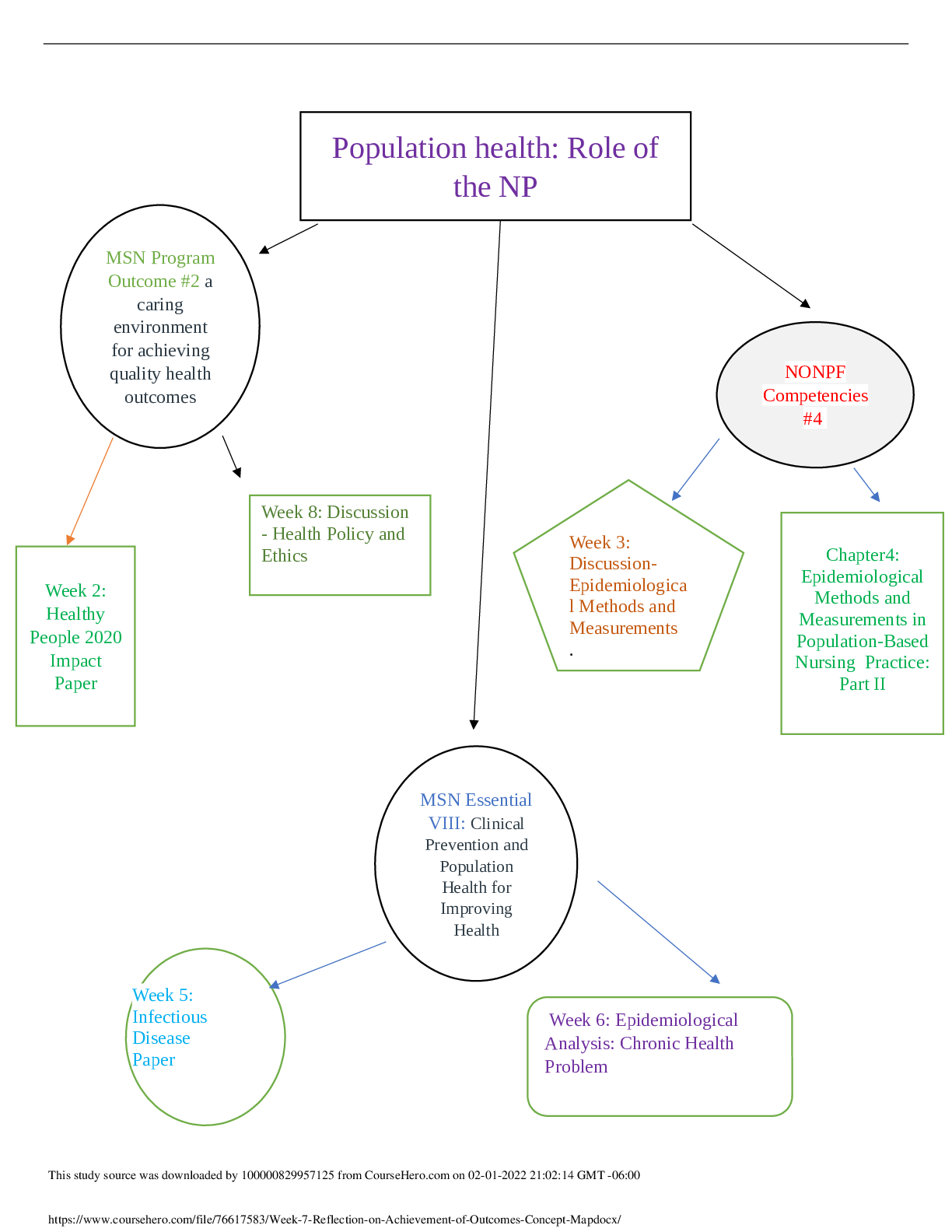
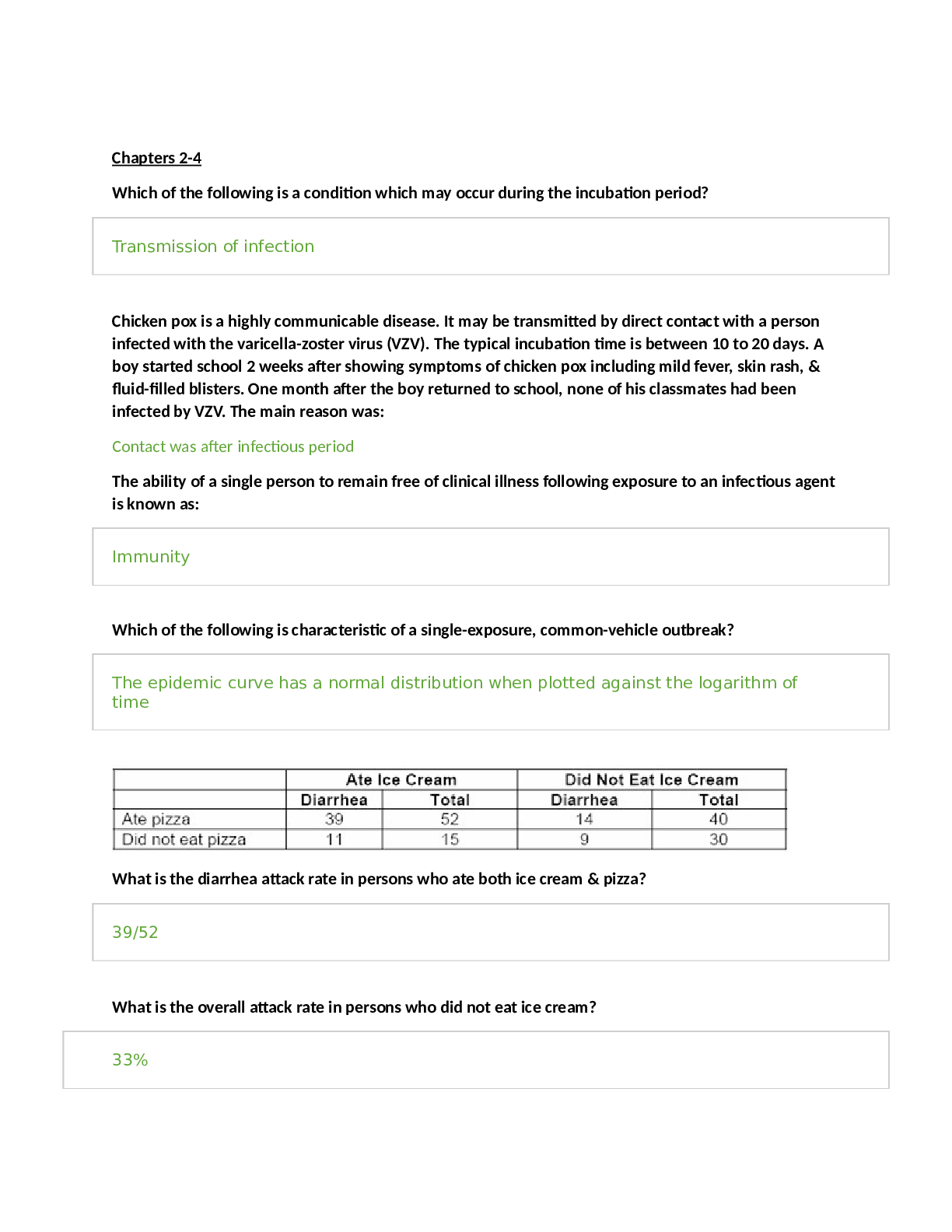
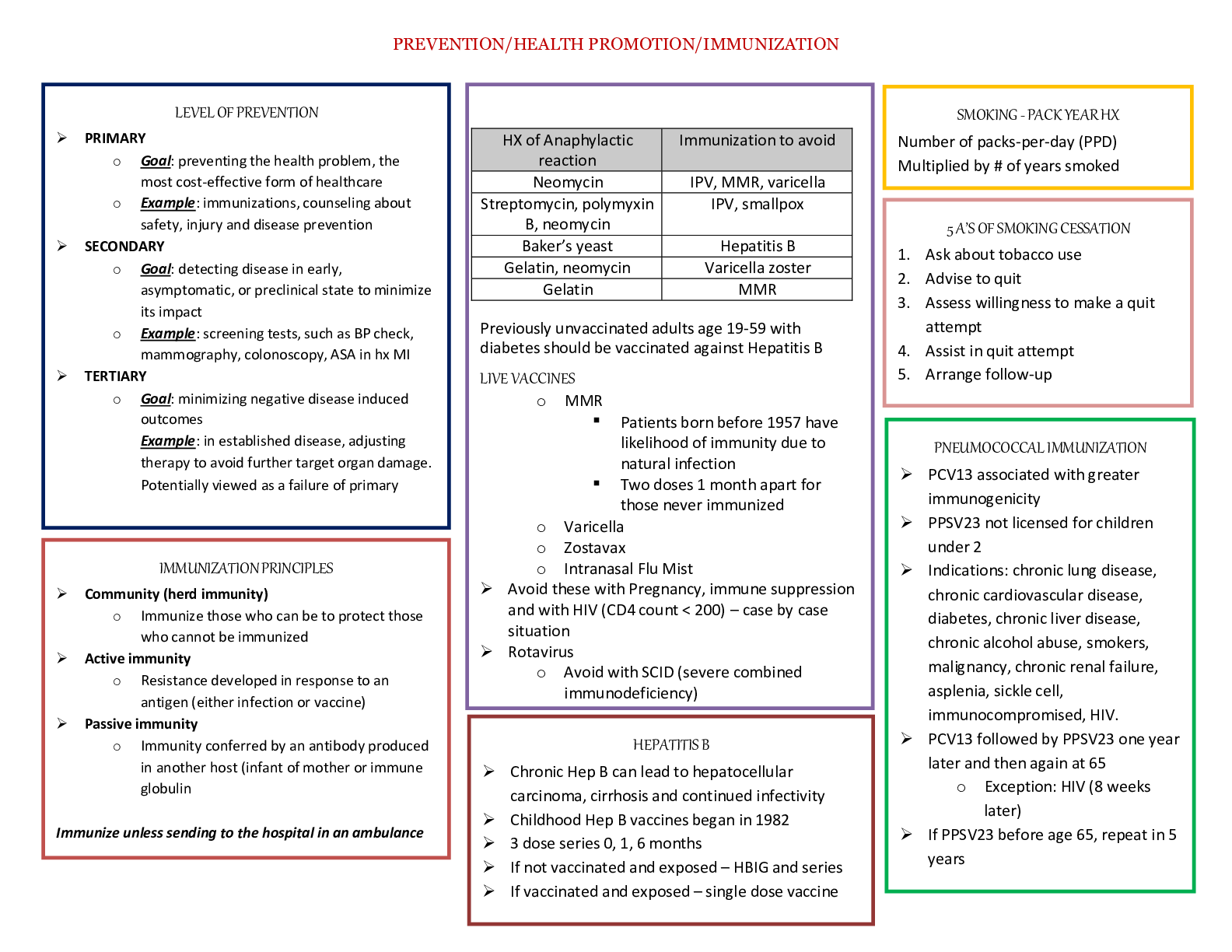
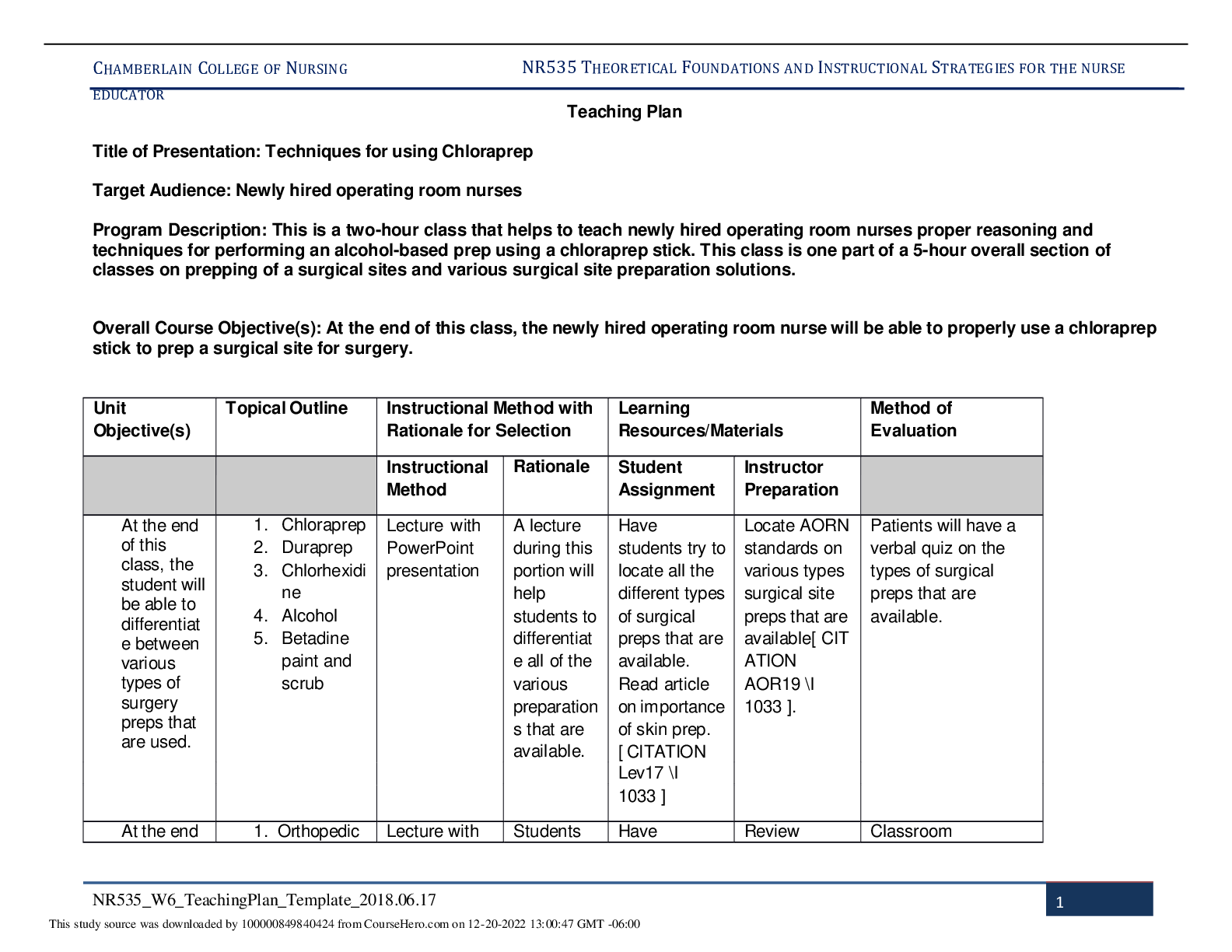
*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR 602 Week 4 Midterm Study Guide (Exam Points) | Already Graded A | Chamberlain College of Nursing (All)
NR 602 Week 4 Midterm Study Guide (Exam Points) | Already Graded A | Chamberlain College of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
NR 602 Week 4 Midterm Study Guide (Exam Points) A Bethesda System Pap smear report that reads LSIL is most consistent with which classification CIN 1 A single Pap smear reading of ASCUS in a pati... ent negative for HPV infection should have what as follow-up? Routine screening A female patient is 35 years old. She has never had an abnormal Pap smear and has had regular screening since age 18. If she has a normal Pap smear with HPV testing today, when should she have the next cervical cancer screening 5 years Lab results on your 26-year-old patient show a negative Pap smear with a positive HPV screen. Which procedure will be required next Repeat Pap and HPV screen 9yo female has completed course of amox for strep throat. LMP was 2wks ago, says it was normal. On exam, there's erythema of extern. genitalia w/small amount of white discharge. Micro wet prep reveals few clue cells, but many budding hyphae. No WBCs. Which one would be the most appropriate treatment? a. Metronidazole 500mg BID x7 days b. OTC hydrocortisone 1% cream TID c. Fluconazole tabs 150mg x1 dose d. Erythromycin 500mg TID x10 days Woman c/o vaginal itching, white discharge. She is in good health except for recent abx for strep throat. Pelvic reveals tender vulvovaginal area w/edema and nonmalodorous white patches. Which is the most likely cause? a. Bacterial vaginosis b. Trichomonas c. Lactobacillus overgrowth d. Candidiasis 18yo female c/o secondary amenorrhea. On exam, there is normal secondary sex characteristics and normal genitalia. Pregnancy is ruled out. What would necessitate further eval? a. Elevated blood cholesterol levels b. Androgen deficiency c. Galactorrhea d. Hirsutism Primary amenorrhea is best described as: a. Cessation of menstruation x6mo b. Failure of menstruation to occur by 17ho c. Failure of menstruation to occur by 13yo 25yo female c/o vaginal irritation and discharge. On exam, cervix is easily friable and erythematous. No adnexal tenderness. Wet prep reveals mobile protozoa on NS slide. This most likely represents: a. Trichomonas Treatment options for condyloma acuminatum include: a. Imiquimod (Aldera) 49yo female c/o dark, watery brown vaginal discharge. Which best describes what might be seen on physical exam in pt's with cervical cancer? a. Ulcerated firm cervix 22yo female c/o pelvic pain. Exam reveals cervical motion and uterine tenderness. Which supports PID dx? a. Temp <100F b. Absence of WBCs in vag fluid c. Mucopurulent vag discharge When a patin is diagnosed with PMS, which intervention would be recommended to help alleviate the symptoms? B. Eating a diet low in simple sugars and high in proteins. (Decrease caffeine, take diuretics but continue to consume fluids, regular exercise, and analgesics). is the condition in which functional endometrial tissue is found in ectopic sites outside the uterus. Endometriosis is the condition in which endometrial glands and stoma are found within the myometrium, interspersed between the smooth muscle fibers. Adenomyosis Uterine are benign neoplasms of smooth muscle origin. Leiomyomas are firm, rubbery, sharply defined round masses in breast tissue. Fibroadenomas Endometriosis is the condition where endometrial tissue is found growing outside of the uterus in the pelvic cavity. What are risk factors for endometriosis? D. Periods longer than 7 days and increased menstrual pain. An 18 yr old woman presents at the clinic complaining new-onset breakthrough bleeding, even though she is on contraceptive. What contraceptive use, along with new onset-onset breakthrough bleeding, has been associated with pelvic inflammatory disease? B. Depo-Provera A woman with lobular carcinoma in situ has a relative risk of developing invasive breast cancer of 8.0 Pap smear results of atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance require which procedure next Follow-up Pap smear A 23-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a Pap smear. After the examination, the client confides that her mother had died of endometrial cancer one year ago and says that she is afraid that she would die of the same cancer. Which risk factor stated by the client after an education session on wrist factors indicate that brother teaching is needed Late onset menarche The frequency for cervical screening depends on the patient and her age. What is the longest recommended time interval between cervical screens for patients who are 65 years old or younger Five years Jenna was evaluated and diagnosed with condyloma acuminatum. Treatment options for Jenna will include all of the following except Topical acyclovir I can roll over grasp a rattly, and reach for things and have begun feeding myself finger foods, but i can't wave bye-bye yet. How old am I? 6 months I can walk well on tiptoes, my speech is 50% understandable, I know six body parts, but can't balance on one foot for 2 seconds. I am: 2 1/2 years old Most children can independently dress themselves by age 4 years A 35-year-old smoker is being evaluated for birth control choices. Patient has a history of pelvic inflammatory disease along with an embolic episode after her last pregnancy. Which of the following methods of birth control would you recommend Condoms and the vaginal sponge A 20-year-old woman visiting the clinic says that she wishes to begin using Depot Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo-Provera) as a form of birth control what important information said the nurse include when teaching the client about Depo-Provera Calcium intake and exercise should be increased because of the possible loss of bone mineral density with increasing duration of use A client seeking advice about contraception asked the nurse about how an Intrauterine device prevent pregnancy how should the nurse respond It produces a spermicidal intrauterine environment A nurse is teaching a group of women about the side effects of different types of contraceptives. What frequent side effect associated with the use of an IUD should the nurse discussed during the teaching session Excessive menstrual flow A nurse is teaching a female client about the side effects of estrogen in an oral contraceptive. Which common side effect identified by the client indicates to the nurse at the teaching was effective Nausea A nurse is canceling a female client with type one diabetes to request a contraceptive information. What contraceptive method should the nurse recommend Diaphragm with spermicide The client asked the nurse about the use of an IUD for contraception. What information should the nurse include in the response Explosion of the device, occasional dyspareunia, risk for perforation of the uterus Sylvia is 44-year-old woman with dysfunctional uterine bleeding and is an able to use oral contraceptives. Which of the following medications can be use for management of DUB Medroxyprogesterone Which is not a common cause of irregular menstrual bleeding Anovulation a na, 25-year-old, presents with dysmenorrhea. She states that her sister and mother have endometriosis, so she would like to be evaluated for it. Which of the following is consistent with a diagnosis of endometriosis Pelvic pain and dyspareunia A 16-year-old female is diagnosed with primary dysmenorrhea. She has taken over the counter ibuprofen 800 mg increments every eight hours during mentors for the past three months with minimal relief of symptoms. What intervention will provide greatest relief of dysmenorrhea symptoms Combined oral contraceptives My 24-year-old female presents to the practice with a painless 2 cm lobular mass in the right breast that is freely mobile and firm. This has noted on self breast examination, and she reports it has been unchanged for the past three months. The best course of action by the nurse practitioner would be to Order a diagnostic ultrasound or diagnostic mammogram A nurse is caring for a client who has contracted a trichomonal infection. Which oral drug should the nurse anticipate that the healthcare provider will most likely prescribe Metronidazole (Flagyl) For the patient with chronic bacterial vaginosis, the nurse practitioner will prescribe Metronidazole gel .75% vaginally 1-2 times a week for 4-6 months Women with a history of P ID have an increased risk for all of the following except Ovarian cyst Which of the following is the best method to diagnose a vaginal trichomonas infection Wet smear with microscopy A 30-year-old woman who is sexually active complains of a large amount of milk like vaginal discharge for several weeks. A micro scopic slide reveals a large number of cells that have blurred margins. Very few white blood cells are seen. The vaginal pH is at six. What is most likely Bacterial vaginosis A 25-year-old woman complains of dysuria, severe vaginal up your ride is, and a malodorous vaginal discharge. Pelvic examination reveals a strawberry colored cervix and frothy yellow discharge. Microscopic examination of the discharge reveals multiple organisms that have flagella. The correct pharmacological therapy for the condition is Oral Flagyl You are completing a pelvic exam on 32-year-old and Nancy. You detect a left adnexal mass on the bimanual exam. With an adnexal mass, the practitioner much always suspect Malignancy until proven otherwise A young woman presents to your practice with vaginal itching and white discharge. She denied sexual activity or douching. She has been in good health except for recurrent strep throat. Pelvic examination reveals a tender vulvovaginal area with edema and white patches, no odor is detected. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this problem Candidiasis after antibiotic treatment A 24-year-old female presents to the office with a complaint of vaginal itching in addition to thick mucoid discharge. She also has some mild urinary discomfort. The wet mount preparation using potassium hydroxide reveals a negative whiff test and few clue cells. There was no trichomonas visualized but the WBCs were too numerous to count. Which of the following would be the most likely diagnosis in the patient Chlamydia A 25-year-old woman comes to clinic complaining of increased vaginal discharge, milky gray in color with a fishy odor that both she and her husband have noticed. I wet smear is performed and the presence of clue cells confirmed. Which type of infection does the nurse suspect Bacterial vaginosis Which of the following statements is accurate regarding the usefulness of mammo in screening and detection of breast cancer? a. Mammo shouldn't be done if there is any breast pain or nipple retraction b. All women >40yo should have mammo on annual basis PMS occurs with greatest frequency and severity in the: a. Late luteal phase 28yo female c/o breast tenderness, fatigue, abd bloating, fluid retention, irritability 1wk before her menses onset. What is most important info to obtain from this pt to determine if the pt has PMS? a. Severity of symptoms b. Occurrence of symptoms in menstrual cycle What phase of menstrual cycle begins with menses cessation and ends w/ovulation? a. Ovulatory phase b. Follicular phase What phase of menstrual cycle begins with ovulation and ends w/menstruation? a. Ovulatory phase b. Follicular phase c. Proliferative phase 2. While the vital signs of a pregnant client in her third trimester are being assessed, the client complains of feeling faint, dizzy, and agitat ed. Which nursing intervention is appropriate? a. Have the client stand up and retake her blood pressure. b. Have the client sit down and hold her arm in a dependent position. c. Have the client turn to her left side and recheck her blood pressure in 5 minutes. d. Have the client lie supine for 5 minutes and recheck her blood pressure on both arms. A pregnant client has come to the emergency department with complaints of nasal congestion and epistaxis. Which is the correct inter pretation of these symptoms by the health care provider? Estrogen causes increased blood supply to the mucous membranes and can result in congestion and d. nosebleeds. 6. What is the reason for vascular volume increasing by 40% to 60% during pregnancy? a. Prevents maternal and fetal dehydration b. Eliminates metabolic wastes of the mother c. Provides adequate perfusion of the placenta d. Compensates for decreased renal plasma flow 7. Physiologic anemia often occurs during pregnancy because of: a. inadequate intake of iron. b. the fetus establishing iron stores. c. dilution of hemoglobin concentration. 12. A client in her first trimester complains of nausea and vomiting. She asks, Why does this happen? What is the nurses best response? a. It is due to an increase in gastric motility. b. It may be due to changes in hormones. 10. What is the most common symptom of vulvovaginal candidiasis? a. Fishy odor b. Fever c. Thin, grayish - white discharge d. Vulvar pruritis Chancroid treatment Tx- Abx azithromycin 1 g PO one time, ceftriaxone 250 mg IM 1 x, cipro 500 mg PO BID x3 days Syphilis treatment Penicillin G Trich treatment Tx-Metronidazole 2g PO single dose Candida treatment Tx- topical azole drugs or PO fluconazole bacterial vaginosis treatment Tx- metronidazole 500 mg PO x7 days, metronidazole gel 0.75 %x5 days, clinda cream 2% x3 nights PID treatment Tx- empirically with presumptive dx. Rocephin 250 IM +doxycycline 100 mg BID x14 + metronidazole 500 mg BID x14 Amenorrhea Primary Primary (no menses by 13 w/o 2ndary sex characteristics OR 15 w/ secondary sex; Vulvar Carcinoma symptoms Sx- vulvar itching, mass, vulvar bleeding/pain and tumor found incidentally during pelvic -Chlamydia: purulent discharge, red, congested cervix, urethritis, salpingitis, UTI sx,(Tx: azithromycin). NAAT test -Trich: Foamy, greenish-white discharge, strawberry-like appearance covers the endocervix and may extend to vaginal mucosa, double hairpin capillaries, flagellated organisms , friable, red cervix. protozoa (Tx: metronidazole) -Ghon: thick, creamy discharge, inflamed cervix, urethritis, UTI sx, ( Tx: Cefixime, or ceftriaxone) - Bac. vaginosis: gray or white d/c, "clue cells", fishy odor, pH >4.5, gram stain for dx, (Tx- metronidazole) - Syphilis: Trep. pallidum, painless sore (indurated, papule or ulcer with raised borders) then 6 weeks later more appear, painless regional lymphadenopathy. spirochetes (Tx-penicillin parenterally) Jarisch-herxheimer reaction Tier 2 Birth Control Fail rate 2-3%; OCP, COC's, transdermals, cervical ring. Tier 1 Birth Control Fail rate <1%; IUD, DMPA (Depo), Progestin implant, sterilization Pelvic mass - Benign: unilateral, mobile, cystic, smooth, < 10cm, calcification, gravity dependent layering of cyst contents - Malignant: bilateral, fixed, solid/firm, nodular, multiple septations <2mm, ascites - enlarging mass or with pain= immediate evaluation - ascites or upper abd mass, abd distention= ovarian CA - Ultrasound= benign or malignant, color flow doppler studies= vascular pattern, surgery is needed for malignancy histology PID -Tx: Ceftriaxone 250mg IM single dose, plus Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x 14 days, with or without Metronidazole 500mg PO BID x 14 days -met for recent gyn. instrumentation or BV Amenorrhea simply means absence of menses and is part of the spectrum of ovulatory disorders classified as AUB-O. The most common causes of amenorrhea are pregnancy, hypothalamic amenorrhea, and PCOS No menses by age 14 in the absence of growth or development of secondary sexual characteristics No menses by age 16 regardless of the presence of normal growth and development of secondary sexual characteristics In women who have menstruated previously, no menses for an interval of time equivalent to a total of at least three previous cycles, or 6 months Secondary amenorrhea is defined as 3 months without a menses once menses has been established. The question “Have you had any bleeding from the vagina?” can assist in determining primary, secondary, and potential causes. exercise-induced amenorrhea is complex and most likely due to the combination of low body fat and diminished secretion of GnRH. Lower GnRH levels result in fewer luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle- stimulating hormone (FSH) pulses, which in turn decreases the amount of estrogen produced by the ovaries. Treat= All women with anovulation require management of this condition: If left untreated, endometrial cancer can occur, regardless of the woman’s age. Typically treatment consists of inducing menses using a progestogen such as medroxyprogesterone acetate 5 to 10 mg daily for the first 12 to 14 days of the cycle or OC to induce menstrual cycle. primary dysmenorrhea is a diagnosis of EXCLUSION, in other words, secondary causes must be ruled out before rendering the diagnosis. Primary dysmenorrhea is likely based on history as well as an unremarkable physical exam and a negative pregnancy test. The most common MISDIAGNOSIS of primary dysmenorrhea is secondary dysmenorrhea due to endometriosis. Like endometriosis, fibroids can be associated with menorrhagia, infertility and bowel and bladder complaints. Uterine fibroids are the most common indication for hysterectomy in the United States. The most common symptom is post-menopausal bleeding. Therefore, providers should assume that ALL women with post-menopausal bleeding OR women ≥ 45 years with AUB have endometrial cancer UNTIL proven otherwise with endometrial biopsy AUB are based on the cause and may include pharmacologic measures such as contraceptives, GnRHs, NSAIDs and antifibrinolytics. Non-pharmacological interventions typically include surgical methods such as endometrial ablation, thermal endometrium destruction, uterine artery embolization and hysterectomy. Referral is indicated for an unidentified cause of AUB, complicated cases, refractory treatment, and surgery. Biopsy is required to definitively ascertain whether a mass is solid versus cystic, and benign versus malignant. A fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a minimally invasive way to differentiate solid and cystic masses, and provides for cytologic evaluation of a palpable mass. VC characteristic pseudohyphae may be seen on a wet smear done with normal saline, Gnorrhea The first stage is characterized by bacteremia with chills, fever, and skin lesions; it is followed by the second stage during which the patient experiences acute septic arthritis with characteristic effusions, most commonly in the wrists, knees, and ankles Many functional cysts will resolve within 3 months Asymptomatic simple ovarian cysts less than 10 cm in diameter, including functional cysts and benign neoplasms, have a low probability of malignancy and can be followed with serial imaging. There is little evidence-based guidance for timing of repeat ultrasounds, but they are generally obtained at 3-or 6-month intervals to establish stability hormonal contraceptives can be used to control repeated episodes of symptomatic functional cysts. Tests appropriately ordered in primary care while specialist consultation is pending include cancer antigen 125 (CA-125), alpha fetoprotein (AFP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) Nationally reportable infections chancroid, chlamydia, gonorrhea, hepatitis, HIV, and syphilis Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASCUS) o Reflex testing for HPV on abnormal PAP results and repeat testing is based on those results Atypical Glandular Cells (AGCs) o More common in older women (ages 40-69 years) o 1/3 of cases are associated with pre-malignancy or malignancy o Risk of cancer increases with age o Refer for Endometrial Biopsy Low-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (LSIL) o Cervical cells are mildly abnormal o Usually caused by a low risk HPV infection o Appropriateness of repeat screening vs. referral for diagnostic testing is largely dependent upon whether or not the woman is HPV + and age High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HSIL) o Abnormal cervical cells which are more likely to be associated with premalignancy and malignancy. o Refer immediately for cervical biopsy and treatment (Colposcopy or LEEP procedure) PID experience vary widely. Historically, the abrupt onset of acute lower abdominal pain following menses ). Substantial clinical improvement should occur within 72 hours of beginning treatment. Women who do not respond within this time frame should be reevaluated to confirm the diagnosis of PID; ceftrianone 250 im, doxy 100 mg 14 days, flagyl 500 mg bid x 14 day An increased risk of PID is seen in the first 21 days after IUD insertion Infant length increases an average of 2.5 cm (1 inch) a month during the first 6 months the infant should be going to the breast 8 to 12 times (or every 2 to 3 hours) in 24 hours for approximately 20 to 45 minutes at each feeding. 6 wet diapers in 24 hours Head circumference: Head Circumference Like the rest of the growing infant, head circumference growth is rapid. During the first 6 months of life, head circumference increases approximately 1.5 cm (0.6 inches) per month. During the second 6 months of age, head circumference slows to only 0.5 cm (0.2 inches) per month. On average, the head circumference is 43 cm (17 inches) at 6 months and increases to 46 cm (18 inches) by 12 months, which represents a 33% increase from birth. During this time, the cranial sutures close. The posterior fontanel closes between 6 and 8 weeks of age while the anterior fontanel closes around 14 months, with a range between 12 and 18 months of age. During the first 12 months of life, the brain size increases by 2.5 times. Developmental milestone achievement illustrates brain growth and differentiation. Smiling at you: By 3 months, the infant has a social smile, and smiles in response to their parent’s voice. 4-5 months Infants spontaneously smile and visually follow their parent by turning their head. Throwing ball: 12 months – rolls a ball, 24 months kicks ball,s 36 months – catches a ball 48 months- throws ball underhand Gun safety- knowing friends Teaching about gun safety is always critical. Working to strengthen the developmental competencies of youth includes educating youths at an early age about violence and its prevention, teaching anger management and strategies for preventing a fight (role-playing), and promoting self-defense strategies, such as learning a martial art and discussing ways to manage difficult or potentially violent situations Suggest discussions with friends about ways to handle potential situations in which a gun or knife might be brandished. Breast cancer screening guidelines Mammogram every 2 years for women aged 50–74 (grade: B). Decisions regarding biennial screening for women aged 40–49 should be made on an individual basis (grade: C). Insufficient evidence to recommend for or against screening after age 74 (I Statement). Recommends against teaching self-breast examination (grade: D). Hpv infections: Mom passing immunity and vaccination of child: Maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies provide the fetus with passive immunity. Promote exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life to promote passive immunity and guard against exposure to contaminated food and water. which provides immunity for approximately 3 months postdelivery. Between 1 and 3 months, infants begin to synthesize IgG that reaches 40% of adult levels by 1 year of age. At birth, the newborn produces significant amounts of immunoglobulin M (IgM), which reaches adult levels by 9 months of age. Secretory IgA is absent at birth but is present in saliva and tears by 5 weeks. During infancy, the function and quality of T-lymphocytes, lymphokines, interferon-γ, interleukins, tumor necrosis factor and complement are reduced resulting in the infant’s inability to optimally respond to infectious bacteria and viruses. The levels of IgA, IgD, and IgE are reduced and do not mature until after infancy. Chlamydia slide: The USPSTF recommends using nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) to diagnose chlamydia and gonorrhea infections, both of which can be tested using the same specimen. Increased numbers of white blood cells in addition to the presence of clue cells suggest a concurrent vaginitis or coinfection with trichomoniasis, chlamydia, or candidiasis. Yeast infection slide: VC < 4.5 (usually) With KOH: pseudohyphae with yeast buds Thick or thin, white, curd-like (“cottage cheese”), adherent Yes, swelling, excoriation, redness, may have skin cracking in servere cases. Vaginal itching, burning, and/or discharge BV slide: Immediately after obtaining the vaginal secretions (whether by clinician collection or a woman’s self-swab as described in Appendix 6-B), mix one sample with normal saline solution, and a second sample with a 10% solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH). Candida albicans, Trichomonas vaginalis, clue cells (epithelial cells with indistinct borders due to adherent bacteria) associated with bacterial vaginosis, and white blood cells can be seen in normal saline solution. Microscopy has poor sensitivity for T. vaginalis detection; NAAT testing is recommended if trichomoniasis is suspected (see Appendix 6-B and Chapter 19) (CDC, 2015). Potassium hydroxide lyses trichomonads, white blood cells, and most bacteria, making visualization of Candida species easier. The presence of an amine or fishy odor with the addition of KOH to the vaginal secretions should be noted (whiff test), and is associated with, but not diagnostic for, bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis. With saline solution: positive for clue cells, decreased lactobacilli Thin, homogenous, grayish- white, adherent, fishy odor, Mild itching, if present at all,vaginal odor is often worse after intercourse. Bartholiins: 25yo female c/o tender area near her introitus and to the L of her perineum. Very painful sex was first sign. Initially bump was very small, but now is ping-pong ball size. On exam, abscess is present on L medial side of labia minora and there's edema extending into perineum. What is dx? a. Lipoma b. Dermoid cyst c. Bartholin's cyst d. Skene's duct cyst Cervical ca screen: Pap test every 3 years for all women aged 21–65 (grade: A). Co-testing with Pap test and HPV testing for women aged 30–65 who wish to extend the screening interval (grade: A). Recommends against screening women younger than age 21. Recommends against screening women older than age 65 if they have had adequate prior screening and are otherwise not at risk for cervical cancer. Recommends against screening women who have had a total hysterectomy for benign disease. Recommends against screening women younger than age 30 with HPV testing alone or with Pap test. Stanger anxiety age Social smile age, 6 weeks? Trich and HIV- medications, relations ship between hiv and trich HSV medications Pincher grasp age LH role in menstruation- released progesterone Day # of menstruation [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 06, 2021
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 06, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
69