*NURSING > EXAM > TEST BANK FOR PRIMARY CARE ART AND SCIENCE OF ADVANCED PRACTICE NURSING – AN INTERPROFESSIONAL APP (All)
TEST BANK FOR PRIMARY CARE ART AND SCIENCE OF ADVANCED PRACTICE NURSING – AN INTERPROFESSIONAL APPROACH 5TH EDITION
Document Content and Description Below
Description Table of Contents I. CARING-BASED NURSING: THE ART 1. Primary Care in the Twenty-First Century: A Circle of Caring 2. Caring and the Advanced Practice Nurse 3. Health Promotion 4. The Art ... of Diagnosis and Treatment 5. Evidence-Based Practice II. CARING-BASED NURSING: THE SCIENCE Section 1. Neurological Problems 6. Common Neurological Complaints 7. Seizure Disorders 8. Degenerative Disorders 9. Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke) 10. Infectious and Inflammatory Neurological Disorders Section 2. Skin Problems 11. Common Skin Complaints 12. Parasitic Skin Infestations 13. Fungal Skin Infections 14. Bacterial Skin Infections 15. Viral Skin Infections 16. Dermatitis 17. Skin Lesions Section 3. Eye Problems 18. Common Eye Complaints 19. Lid and Conjunctival Pathology 20. Visual Disturbances and Impaired Vision Section 4. Ear, Nose, and Throat Problems 21. Common Ear, Nose, and Throat Complaints 22. Hearing and Balance Disorders 23. Inflammatory and Infectious Disorders of the Ear 24. Inflammatory and Infectious Disorders of the Nose, Sinuses, Mouth, and Throat 25. Epistaxis 26. Temporomandibular Disorders 27. Dysphonia Section 5. Respiratory Problems 28. Common Respiratory Complaints 29. Sleep Apnea 30. Infectious Respiratory Disorders 31. Inflammatory Respiratory Disorders 32. Lung Cancer 33. Smoking Addiction Section 6. Cardiovascular Problems 34. Common Cardiovascular Complaints 35. Cardiac and Associated Risk Disorders 36. Dysrhythmias and Valvular Disorders 37. Disorders of the Vascular System Section 7. Abdominal Problems 38. Common Abdominal Complaints 39. Infectious Gastrointestinal Disorders 40. Gastric and Intestinal Disorders 41. Gallbladder and Pancreatic Disorders 42. Cirrhosis and Liver Failure Section 8. Renal Problems 43. Common Urinary Complaints 44. Urinary Tract Disorders 45. Kidney and Bladder Disorders Section 9. Gender-Related Health Problems 46. Common Reproductive System Complaints 47. Breast Disorders 48. Vaginal, Uterine, and Ovarian Disorders 49. Prostate Disorders 50. Penile and Testicular Disorders 51. Sexually Transmitted Infections Section 10. Musculoskeletal Problems 52. Common Musculoskeletal Complaints 53. Spinal Disorders 54. Soft-Tissue Disorders 55. Osteoarthritis and Osteoporosis Section 11. Endocrine and Metabolic Problems 56. Common Endocrine and Metabolic Complaints 57. Glandular Disorders 58. Diabetes Mellitus 59. Metabolic Disorders Section 12. Hematological and Immunological Problems 60. Common Hematological and Immunological Complaints 61. Hematologic Disorders 62. Immunological Disorders 63. Infectious Disorders Section 13. Psychosocial Problems 64. Common Psychosocial Complaints 65. Substance Use Disorders 66. Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders 67. Mood Disorders 68. Anxiety, Stress, and Trauma-Related Disorders 69. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders 70. Behavioral Disorders Related to Physical/Physiological Disturbances 71. Neurodevelopmental Disorders Section 14. Urgent Care Problems 72. Common Urgent Care Complaints 73. Common Injuries 74. Toxic Exposures 75. Environmental Exposures III. CARING-BASED NURSING: THE PRACTICE 76. Sports Physicals 77. Primary Care of Older Adults 78. Palliative Care and Pain Management 79. Ethical and Legal Issues of a Caring-Based Practice 80. The Business of Advanced Practice Nursing 81. The 15-Minute Hour: Practical Approaches to Behavioral Health for Primary Care 82. Putting Caring Into Practice: Caring for Self rimary Care: Art and Science of Advanced Practice Nursing - An Interprofessional Approach 5th edition Dunphy Test Bank Chapter 1. Primary Care in the Twenty-First Century: A Circle of Caring 1. A nurse has conducted a literature review in an effort to identify the effect of handwashing on the incidence of nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections in acute care settings. An article presented findings at a level of significance of <0.01. This indicates that A) the control group and the experimental group were more than 99% similar. B) the findings of the study have less than 1% chance of being attributable to chance. C) the effects of the intervention were nearly zero. D) the clinical significance of the findings was less than 1:100. Ans: B Feedback: The level of significance is the level at which the researcher believes that the study results most likely represent a nonchance event. A level of significance of <0.01 indicates that there is less than 1% probability that the result is due to chance. 2. A nurse has read a qualitative research study in order to understand the lived experience of parents who have a neonatal loss. Which of the following questions should the nurse prioritize when appraising the results of this study? A) How well did the authors capture the personal experiences of these parents? B) How well did the authors control for confounding variables that may have affected the findings? C) Did the authors use statistical measures that were appropriate to the phenomenon in question? D) Were the instruments that the researchers used statistically valid and reliable? Ans: A Feedback: Qualitative studies are judged on the basis of how well they capture and convey the subjective experiences of individuals. Statistical measures and variables are not dimensions of a qualitative methodology. 3. A nurse has expressed skepticism to a colleague about the value of nursing research, claiming that nursing research has little relevance to practice. How can the nurses colleague best defend the importance of nursing research?A) The existence of nursing research means that nurses are now able to access federal grant money, something that didnt use to be the case. B) Nursing research has allowed the development of masters and doctoral programs and has greatly increased the credibility of the profession. C) The growth of nursing research has caused nursing to be viewed as a true profession, rather than simply as a trade or a skill. D) The application of nursing research has the potential to improve nursing practice and patient outcomes. Ans: D Feedback: The greatest value of nursing research lies in the potential to improve practice and, ultimately, to improve patient outcomes. This supersedes the contributions of nursing research to education programs, grant funding, or the public view of the profession. 4. Tracy is a nurse with a baccalaureate degree who works in the labor and delivery unit of a busy urban hospital. She has noticed that many new mothers abandon breast-feeding their babies when they experience early challenges and wonders what could be done to encourage more women to continue breast-feeding. What role is Tracy most likely to play in a research project that tests an intervention aimed at promoting breast-feeding? A) Applying for grant funding for the research project B) Posing the clinical problem to one or more nursing researchers C) Planning the methodology of the research project D) Carrying out the intervention and submitting the results for publication Ans: B Feedback: A major role for staff nurses is to identify questions or problems for research. Grant applications, methodological planning, and publication submission are normally carried out by nurses who have advanced degrees in nursing. 5. A patient signed the informed consent form for a drug trial that was explained to patient by a research assistant. Later, the patient admitted to his nurse that he did not understand the research assistants explanation or his own role in the study. How should this patients nurse respond to this revelation? A) Explain the research process to the patient in greater detail. B) Describe the details of a randomized controlled trial for the patient.C) Inform the research assistant that the patients consent is likely invalid. D) Explain to the patient that his written consent is now legally binding. Ans: C Feedback: Just as the staff nurse is not responsible for medical consent, the staff nurse is not responsible for research consent. If patients who have agreed to participate exhibit ambivalence or uncertainty about participating, do not try to convince them to participate. Ask the person from the research team who is managing consents to speak with concerned patients about the study, even after a patient has signed the consent forms. Multiple Selection 6. A nurse leader is attempting to increase the awareness of evidence-based practice (EBP) among the nurses on a unit. A nurse who is implementing EBP integrates which of the following? (Select all that apply.) A) Interdisciplinary consensus B) Nursing tradition C) Research studies D) Patient preferences and values E) Clinical expertise Ans: C, D, E Feedback: Fineout-Overholt, Melnyk, Stillwell, and Williamson define EBP as a problem-solving approach to the delivery of healthcare that integrates the best evidence from studies and patient care data with clinician expertise and patient preferences and values. Multiple Choice 7. Mrs. Mayes is a 73-year-old woman who has a diabetic foot ulcer that has been extremely slow to heal and which now poses a threat of osteomyelitis. The wound care nurse who has been working with Mrs. Mayes applies evidence-based practice (EBP) whenever possible and has proposed the use of maggot therapy to debride necrotic tissue. Mrs. Mayes, however, finds the suggestion repugnant and adamantly opposes this treatment despite the sizable body of evidence supporting it. How should the nurse reconcile Mrs. Mayes views with the principles of EBP? A) The nurse should explain that reliable and valid research evidence overrides the patients opinion. B) The nurse should explain the evidence to the patient in greater detail.C) The nurse should integrate the patients preferences into the plan of care. D) The nurse should involve the patients family members in the decision-making process. Ans: C Feedback: Patient preferences should be integrated into EBP and considered alongside research evidence and the nurses clinical expertise; evidence does not trump the patients preferences. The family should be involved, but this is not an explicit dimension of EBP. Similarly, explaining the evidence in more detail is not a demonstration of EBP. [Show More]
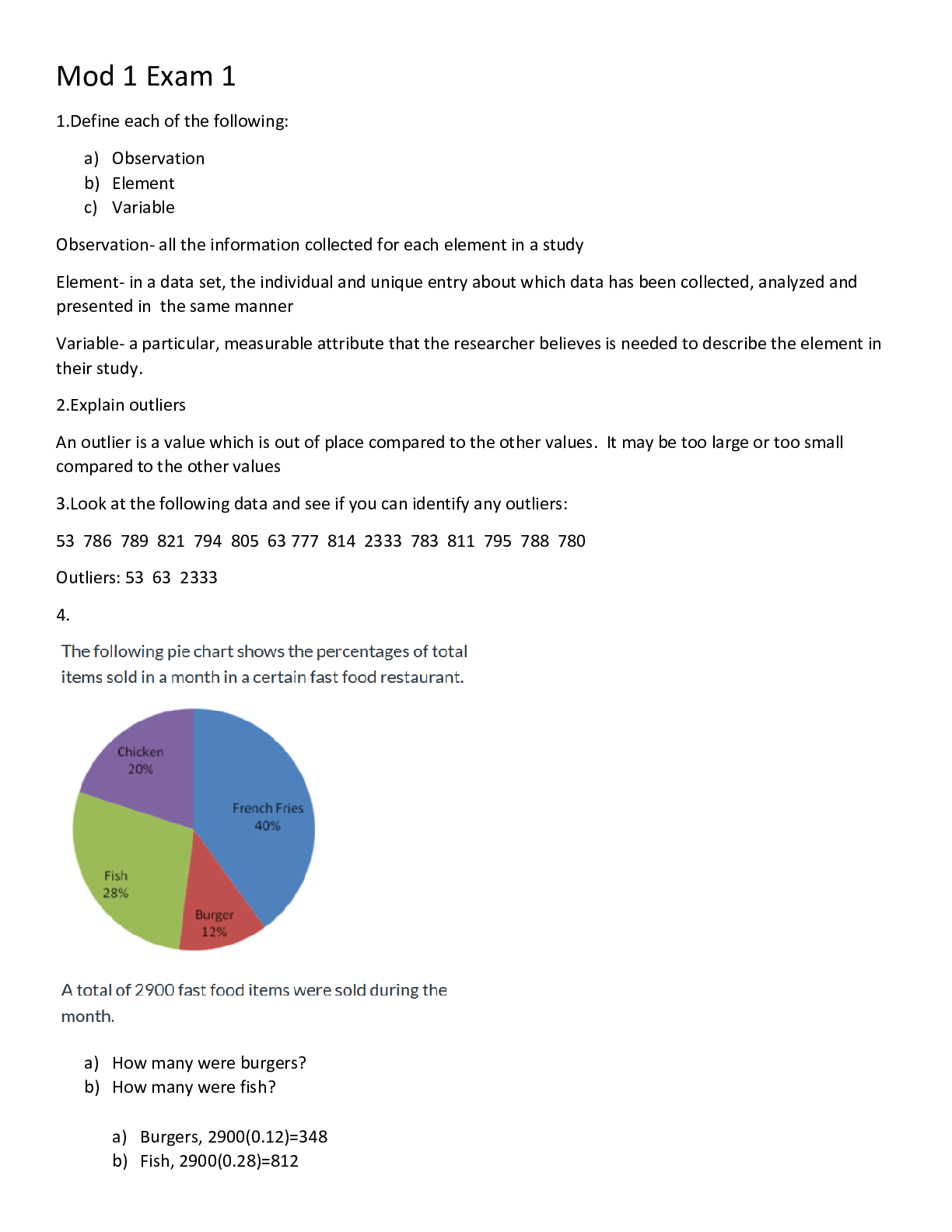
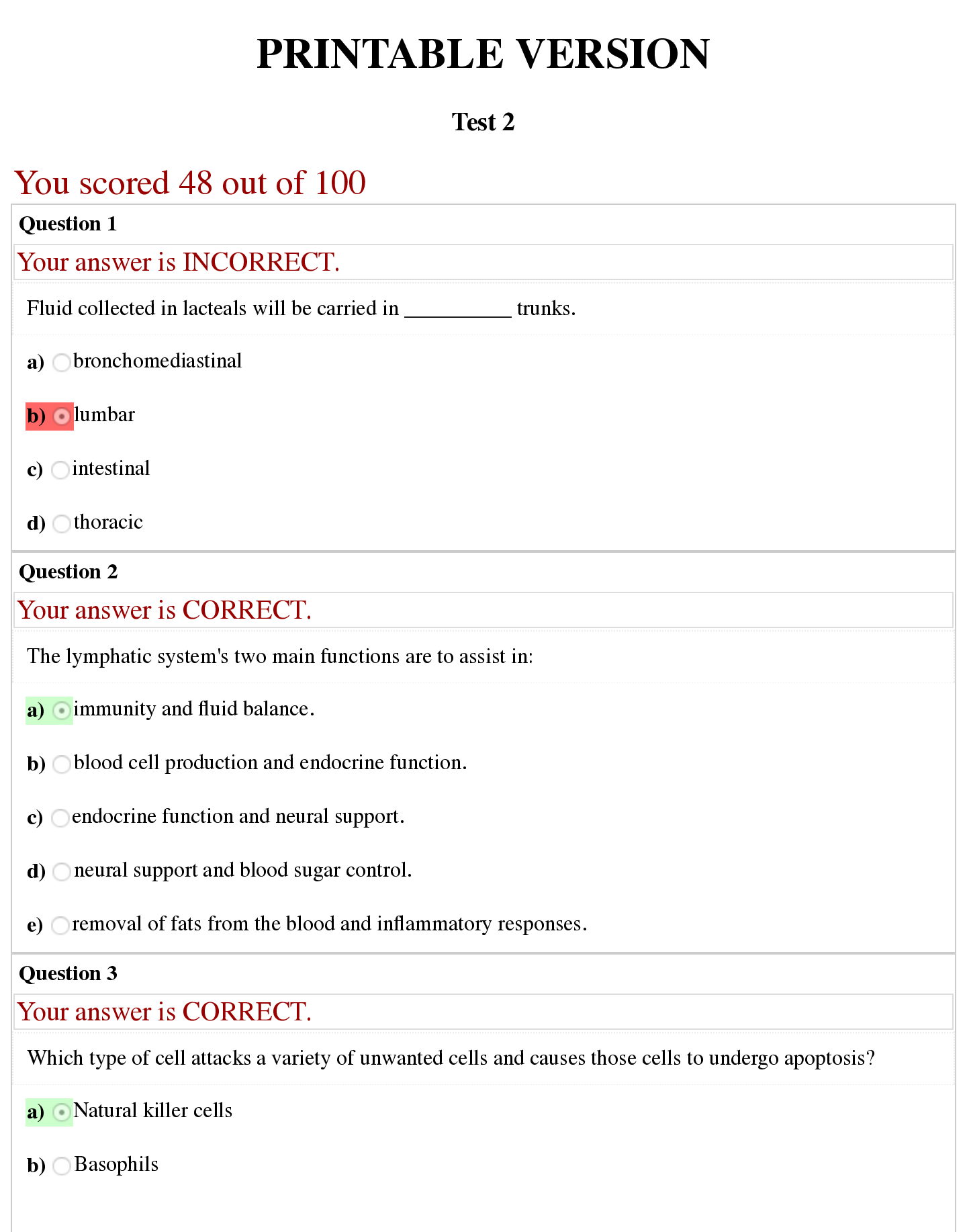
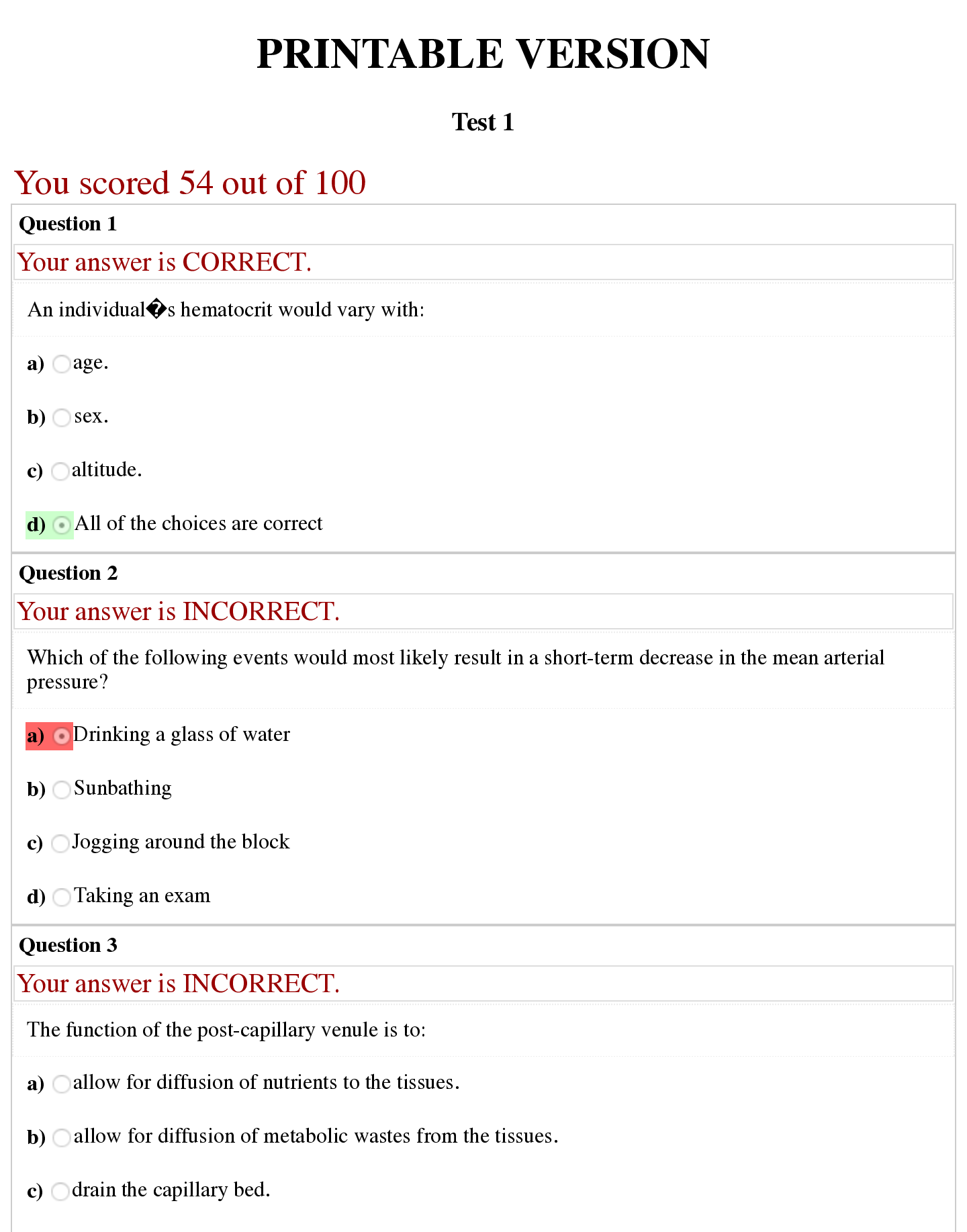
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 530 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 21, 2021
Number of pages
530
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 21, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
82